Updated March 6, 2023
Definition of PowerShell Tail
PowerShell tail command which is a Unix equivalent Tail command and considered as a parameter in the PowerShell’s Get-Content cmdlet and it is to retrieve the specified number of lines from the bottom of the content of the file and it can wait for the next continuous logs and with -Wait parameter it can wait until the new logs are retrieved and display it on the console or can be saved to another log file using the pipeline.
Syntax:
Get-Content Syntax:
Get-Content
[-ReadCount <Int64>]
[-TotalCount <Int64>]
[-Tail <Int32>]
[-Path] <String[]>
[-Filter <String>]
[-Include <String[]>]
[-Exclude <String[]>]
[-Force]
[-Credential <PSCredential>]
[-UseTransaction]
[-Delimiter <String>]
[-Wait]
[-Raw]
[-Encoding <FileSystemCmdletProviderEncoding>]
[-Stream <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Get-Content
[-ReadCount <Int64>]
[-TotalCount <Int64>]
[-Tail <Int32>]
-LiteralPath <String[]>
[-Filter <String>]
[-Include <String[]>]
[-Exclude <String[]>]
[-Force]
[-Credential <PSCredential>]
[-UseTransaction]
[-Delimiter <String>]
[-Wait]
[-Raw]
[-Encoding <FileSystemCmdletProviderEncoding>]
[-Stream <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Although for the PowerShell tail command, we aren’t going to use the whole set we need the specific parameters like -Wait, -Tail, etc. We can also minimize this command as shown below.
Get-Content -Path Filepath -Tail <int>
Or,
Get-Content -Path Filepath -Tail <int> -Wait
PowerShell Tail equivalent command – Select-Object -Last <int>
Syntax:
Get-Content -Path Filepath | Select-Object -Last <int>
Description:
The Tail command is popular in the Unix language and it is used to retrieve the specific number of lines from the end of the document or the log files. PowerShell doesn’t have the command with the same name but from the PowerShell v3.0 onwards, PowerShell has added -Tail parameter in the Get-Content cmdlet.
The get-Content command is useful in retrieving the content of a file whether it is a script, log file, text file, and with the -Tail parameter we can retrieve the number of lines from the end of the file. For example,
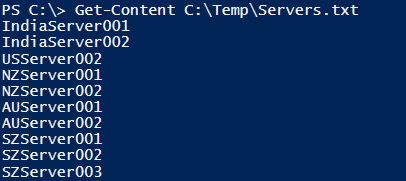
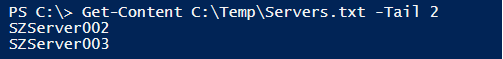
We want to retrieve the last 2 lines of the Servers.txt file. First, we will check the content of the Servers.txt for our better understanding.
Get-Content C:\temp\Servers.txt
Output:
Get-Content C:\temp\Servers.txt -Tail 2
Output:
If your file is the log file that continuously gets updated like the monitoring logs, database logs, mailbox logs, etc in that case we can use the -Wait parameter which waits for the new input to the specified file and displays on the screen. We will see this in the Examples section.
Examples
Let us discuss examples of PowerShell Tail.
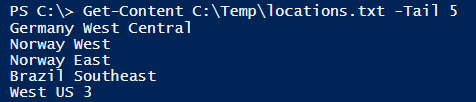
Example #1: Retrieving the last 5 lines from the text file.
In this example, we have the list of azure locations stored in the text file Locations.txt and we need the last 5 locations from the file. So we will use the below command.
Get-Content C:\Temp\locations.txt -Tail 5
Output:
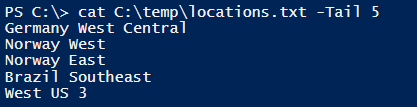
Example #2: Using the Get-Content aliases to read the file and retrieve the last 5 lines.
We know that PowerShell can run the few Unix and DOS commands in the PS console because these commands are used as PowerShell aliases. For example,
Get-Alias cat
So we can run the Unix cat command instead of the Get-Content and it will support all the parameters that the Get-Content command supports.
cat C:\temp\locations.txt -Tail 5
Output:
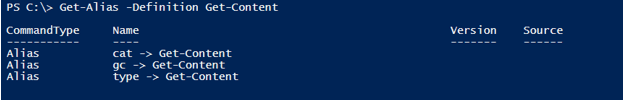
In fact, we can use any aliases that are supported by the Get-Content command and can select few lines with the -Tail parameter. Below are the supported aliases.
Get-Alias -Definition Get-Content
Output:
Here, we can use cat, gc, or type instead of the Get-Content command. We can write the above example as,
type C:\temp\locations.txt -Tail 5
or,
gc C:\temp\locations.txt -Tail 5
Example #3: Using the -Wait and -Tail combined parameters with the Get-Content command.
-Wait parameter keeps the file opens in the PowerShell console until the console is interrupted by the Ctrl+C command. It checks if the file has any new updates every one second and if the file has the new input, it displays it on the console.
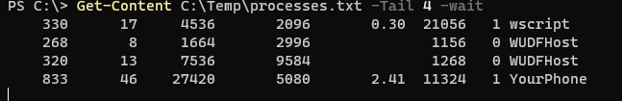
In this example, we have a text file called processes.txt which has a list of processes and it updates whenever any new process starts with the last 4 processes displayed on the screen.
Get-Content C:\Temp\processes.txt -Tail 4 -wait
Output:
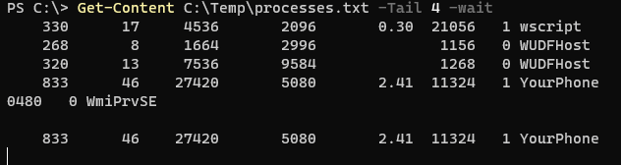
Now we when the file is updated by the new processes then they should display the output on the console.
Press Control+C when you want to terminate the above command output.
Example #4: Using Select-Object command with the -Last parameter.
There is another alternative option of the -Tail parameter in the Get-Content command is to use the Select-Object in the Pipeline with the -Last parameter which works similar to the Tail command.
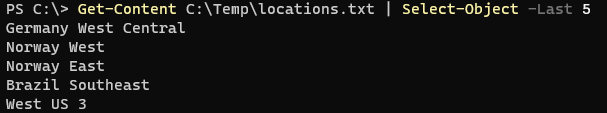
Get-Content C:\Temp\locations.txt | Select-Object -Last 5
Output:
Please note: You can use the Select alias instead of the Select-Object.
The Select-Object has also the -First parameter which retrieves the first specified lines but this won’t serve the purpose of the Tail command.
The Select-Object command is helpful with the -Last parameter more than the -Tail parameter in the Get-Content command because the Get-Content command is only used with the files but if we want to retrieve the last few lines directly from the command then the Tail command will not be helpful but Select-Object will be used there.
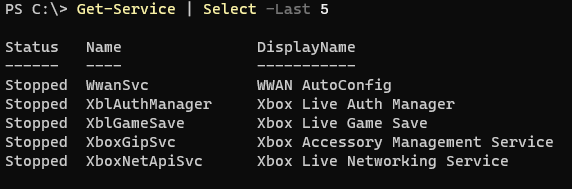
For example, we need to retrieve the list of the last 5 services then we can use the Select-Object command as shown below.
Get-Service | Select -Last 5
Output:
Example #5: Using Filter in Get-Content command.
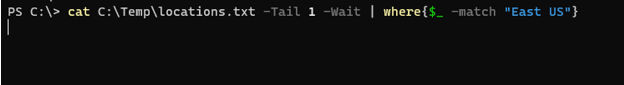
We can use the Where-Object command to filter the specific content. For example, we need in the locations.txt file that if the “East Us” region is entered then it should display the output. The code is shown below.
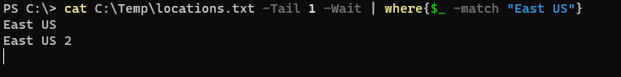
cat C:\Temp\locations.txt -Tail 1 -Wait | where{$_ -match "East US"}
Output:
Once the East US is entered into the locations.txt file,
Conclusion
PowerShell tail command is very helpful when we are dealing with the new content of the file because many times we need to see updated logs on the screen and redirect the new logs to another storage location or we need to take action based on the recently updated file. Logs can be monitoring logs, security logs, database logs, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Tail. Here we discuss definition, syntax, and parameters, examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –