Updated March 6, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Function Parameters
PowerShell function parameters make function-rich by using attributes and arguments to restrict users to enter certain values. It adds a few checks and validations to avoid writing long codes for them, and they are easy to use. Once the function parameters are declared, arguments can be passed with the command line as well. Function parameters include named parameters, positional parameters, switch parameters, and dynamic parameters. Function parameters also help to convert simple function to advanced function.
Syntax of PowerShell Function Parameters
Parameters inside the functions are generally described inside the Param() block.
1. Named Parameter syntax with Single parameter.
function TestFunction{
param (
[Parameter()]
[TypeName]
$ParameterName
)
<Statement list>
}
In the above example, we can add multiple parameter values. There are different named parameter attributes like Mandatory, ValueFromPipeline, Position, ParameterSetName, etc. Typename is the datatype for the ParameterName like String, Integer, Character.
2. Named parameter syntax with Advanced function.
When we add the Cmdletbinding attribute, it converts a function into an advanced function. When the advanced function is created, the function uses other common parameters.
function TestFunction{
[CmdletBinding()]
param (
[Parameter()]
[TypeName]
$ParameterName
)
<Statement list>
}
3. Parameters with attributes.
a. The parameter with a single argument.
function testparam{
param(
[Parameter(Argument=Value)]
[ParameterType]
$ParameterName)
}
b. The parameter with multiple arguments.
function testparam{
param(
[Parameter(Argument1=Value1,
Argument2=Value2)]
[ParameterType]
$ParameterName)
}
4. Parameter sets syntax.
function testparam{
Param(
[Parameter(AttributeValue1)]
[ParameterType]
[$ParameterName],
[Parameter(AttributeValue2)]
[ParameterType]
[$ParameterName]
)
}
How Does Function Parameter work in PowerShell?
When we use the function parameters, and when PowerShell calls the function, it first checks the parameters declared in the function, like if the parameter is declared mandatory or specified the value from the pipeline or any other parameter specified.
You can also pass those parameters using the command line.
Example:
Code:
function Testfunct{
param(
[Parameter (Mandatory = $false)]
[String]$Name
)
Write-Output "Name : $name"
}
You can pass the parameter as shown below.
Code:
Testfunct -Name "PowerShell"
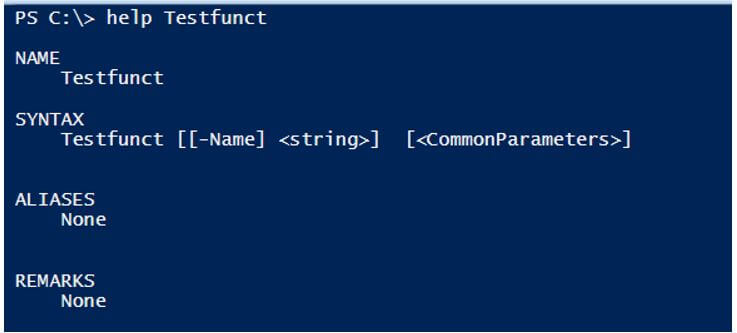
You can also use the help for the function to the available parameters.
Output:
Examples of PowerShell Function Parameters
Given below are the examples of PowerShell Function Parameters:
Example #1
Simple function without parameter block.
In the below example, only the Param block is defined but not the Parameter block. We have simply declared the Name variable with String datatype.
Code:
Function PrintName{
param(
[String]$Name
)
Write-Output "Hello : $name !!! "
}
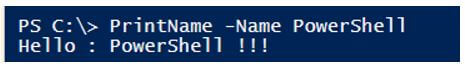
PrintName -Name PowerShell
Output:
Example #2
Function with mandatory parameter.
When you specify a mandatory parameter with $true value, you must pass the variable value while calling the function; otherwise, an error is generated.
The first example is equivalent to the mandatory parameter as false.
Code:
Function PrintName{
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[String]$Name
)
Write-Output "Hello : $name !!! "
}
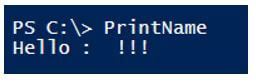
PrintName
If you call a function directly without specifying any values, then it will not give any error.
Output:
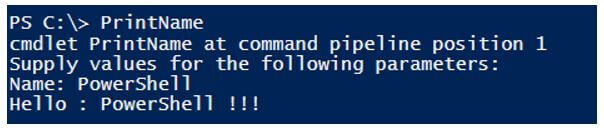
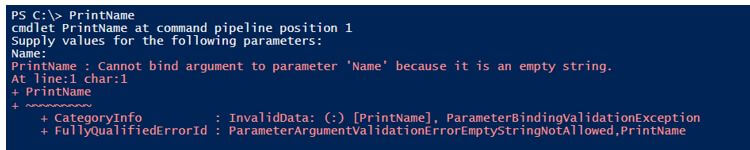
If you specify the mandatory parameter as true and call the function without passing any values, then it will ask for the value, and if you don’t specify that time, then It will generate a function error.
Providing value.
Without providing a mandatory value.
The above output generates the parameter binding exception.
Example #3
Function with positional parameter.
When we specify a function with a positional parameter, the keyword (Position), you don’t need to specify the parameter’s name. It is not necessary and mandatory with positional parameters.
Code:
Function Get-ServersInfo{
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,Position=0)]
[String[]]$ComputerName
)
Write-Output "Computers :"
$ComputerName
}
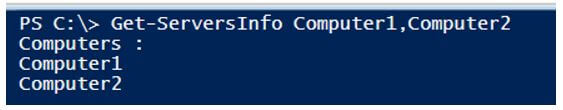
Get-ServersInfo Computer1,Computer2
Output:
In the above example, function Get-ServersInfo uses the default positional parameter Position=0, so we have directly passed computer names. If we have multiple positional parameters, then we will increment position with each parameter name.
Code:
Function Get-ServersInfo{
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,Position=1)]
[Int]$port,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,Position=0)]
[String[]]$ComputerName
)
Write-Output "Computers :"
$ComputerName
}
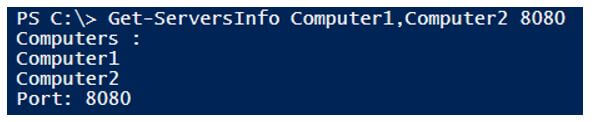
Get-ServersInfo Computer1,Computer2 8080
Output:
In the above example, even if we declared port variable first but its positional value is 1, and the ComputerName variable position value is 0, so it is taking first the computer names.
Example #4
Function parameter with ValueFromPipeline Attribute.
When the ValueFromPipeline value is set to true, we can pass the variables using the Pipeline.
Code:
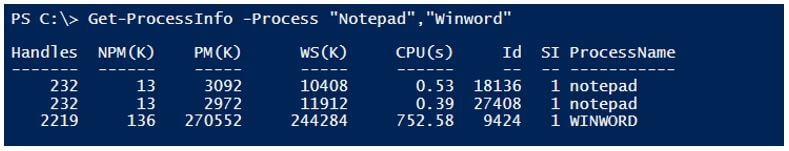
Function Get-ProcessInfo{
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,
ValueFromPipeline=$true)]
[String[]]$Process
)
Get-Process -Process $Process
}
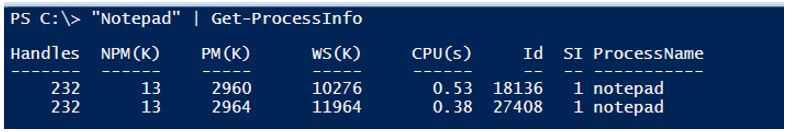
“Notepad” | Get-ProcessInfo
Output:
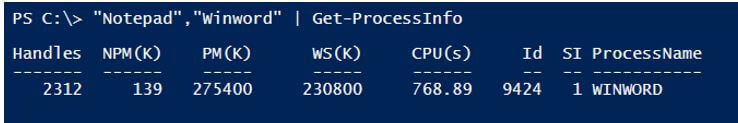
When we pass the multiple processes using Pipeline, it might not work, but the same will work by directly passing value.
Passing values using the pipeline.
In that case, we can use the Begin, Process, and End blocks.
Code:
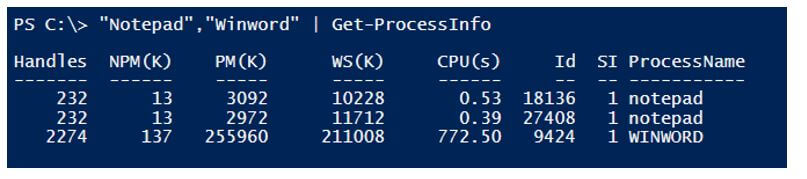
Function Get-ProcessInfo{
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,
ValueFromPipeline=$true)]
[String[]]$Process
)
Begin{}
Process{Get-Process $Process}
end{}
}
“Notepad”,”Winword” | Get-ProcessInfo
Output:
Example #5
Function parameter with switch attribute.
Like the Switch function, we can use the switch parameter inside the function. In the below example, if we set the reboot switch value to true the true block will be executed; otherwise, the false block will be executed.
Code:
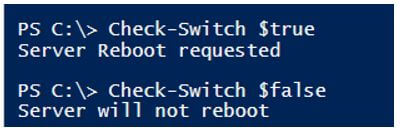
Function Check-Switch{
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false,Position=0)]
[Switch]$Reboot
)
if($Reboot){"Server Reboot requested"}
else{"Server will not reboot"}
}
Check-Switch $true
Check-Switch $false
Output:
Example #6
Function parameter with a help message.
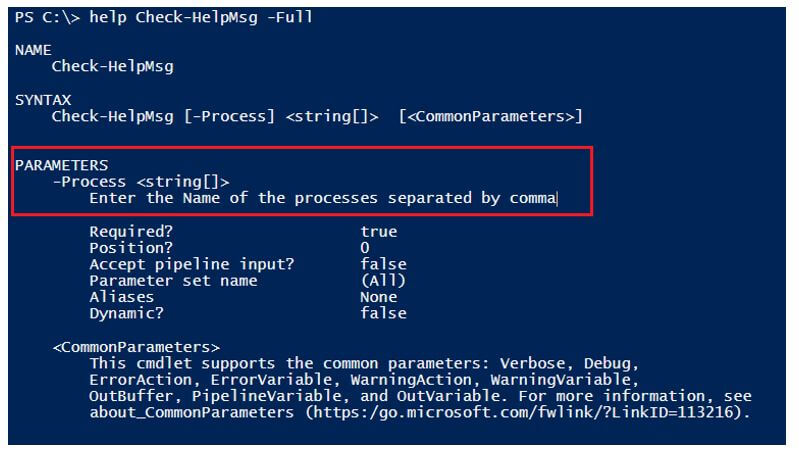
When you need to show a description of the parameter or need to put any help command related to that parameter, you can use the HelpMessage functionality. To show the message, you need to use, Get-Help command.
Code:
Function Check-HelpMsg{
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,HelpMessage="Enter the Name of the processes separated by comma")]
[String[]]$Process
)
Begin{}
Process{Get-Process $Process}
End{}
}
help Check-HelpMsg -Full
Output:
Example #7
Function parameter with validation set attributes.
Instead of writing the long validation inside the script, we can provide validation directly inside the Parameter block with validation sets.
Code:
Function Validate{
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[ValidateSet("Cat","Dog","Cow","Tiger")]
[String[]]$Animals,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[ValidateRange(10,20)]
[Int]$Age
)
Write-Output "Animals:"
$Animals
Write-Output "Age: $Age"
}
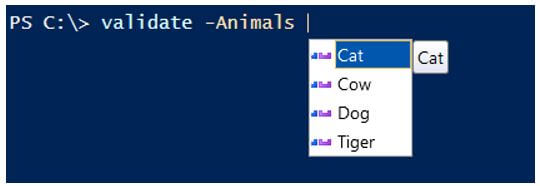
validate -Animals
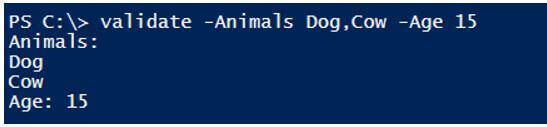
validate -Animals Dog,Cow -Age 15
Output:
When you type the name of the parameter defined in the validation set, it pops up values. This is applicable in ISE but may not appear in the different consoles. In that case, we can use.
Values within the validation range.
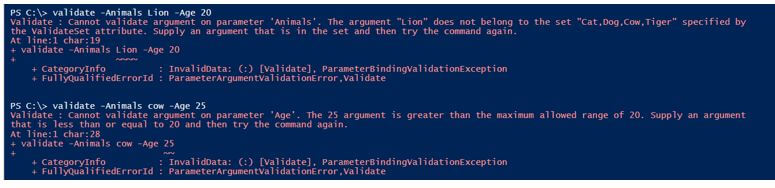
Values outside the validation range throw exception.
Conclusion
PowerShell function parameters are very useful, as we have seen in the above example. It reduces the code complexity by specifying them at the beginning of the function, and we don’t need to write the extra code to validate the data. We can use the exception handling mechanism to handle the exceptions.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Function Parameters. Here we discuss the introduction, how does function parameter work in PowerShell? and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –