Updated March 4, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Execution Policy
The PowerShell execution policy is the security feature for the PowerShell environment, which determines whether users can load the configuration files such as PowerShell profile, basic configuration files or users can run the script. It also determines whether scripts should be digitally signed before they run instead of allowing any user to run the script like VBScript. The PowerShell execution policy is not the hardcore security feature that prevents the user action, rather it prevents the malicious code or script from being run in the environment. Users can change the execution policy with the command line to run the script.
PowerShell Execution Policy Scopes
When an execution policy is applied, it is applied to the particular scopes. Scopes are mentioned below in their precedence level.
- Machine Policy
- User Policy
- Process (Current Session)
- Current User
- Local Machine
1. Machine Policy
This policy is set by the group policy for all the users of the computer. It can be set through GPO : Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows PowerShell.
2. User Policy
This policy can be set by the group policy for the current user of the computer. It can be set through GPO : User Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows PowerShell.
3.Process (Current Session)
This policy is valid till the PowerShell session when the session is closed this policy is removed. This policy is set in the windows environment variable $Env: PSExecutionPolicyPreference. By default, this variable doesn’t exist and created only when this policy is set.
$env:PSExecutionPolicyPreference
4. Current User
This policy is for the current user only. When this policy is set, it is stored in the registry
5. Local Machine
This policy is set for the local computer. When this policy is set, it is stored in the registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
PowerShell Execution Policy Modes
Below are PowerShell Execution Policy Modes:
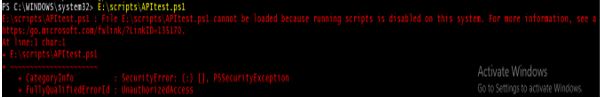
1. Restricted
This is the default execution policy for the Windows Systems for PowerShell. Meaning that you can’t run any scripts (.ps1), configuration files (.ps1xml), and module script (.psm1) but you can run the cmdlets. When this mode is set and you try to run the script, you will get the error as shown in the below example.
2. All Signed
Users can run scripts that are only digitally signed by trusted publishers. Scripts which are not digitally signed, users will get prompt for it.
3. Remote Signed
Scripts that are running from the local computer, they do not require digitally signed but they should not be downloaded from the internet and run. Scripts which are downloaded from the internet including email applications and instant messaging app, they require digitally signed. PowerShell can run the script from which are downloaded from the internet and not digitally signed if the file is unblocked. The file can be unblocked using the file property or through the Unblock-File
4. Unrestricted
Users can run the script which is not signed but this can run malicious scripts as well. PowerShell warns the users when they run the script which is downloaded from the internet.
5. Bypass
No script requires digitally signed when this execution policy is set. Users will not get any prompt for running unsigned scripts. This is useful when there is a large application that need the PowerShell as the base model and needs to run several configuration files. This generally not recommended policy because it is easy to target windows machines to run malicious code when this policy is set.
6. Undefined
When the undefined policy is set then it would be the default policy. The default policy would be Restricted To remove the current execution policy generally, this policy is set.
Examples to Implement PowerShell Execution Policy
Below are some examples mentioned:
Example #1
To get the current execution policy on the machine
Code:
Get-ExecutionPolicy
Output:
Example #2
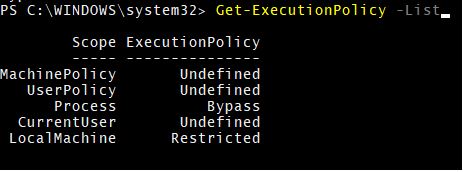
To get all the execution policies and to check which policy is applied for the scope you need to use the below command.
Code:
Get-ExecutionPolicy -List
Output:
Explanation: Here, as per the output of the above example, the Bypass policy is applied for the current session (process) scope.
Example #3
To get the execution policy for the particular scope, you need to use –Scope For example, to get the execution policy for the Process scope, use the below command.
Code:
Get-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process
Output:
Similarly, you can set the policy for different scopes. For example,
Get-ExecutionPolicy -Scope MachinePolicy
Get-ExecutionPolicy -Scope UserPolicy
Get-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentPolicy
Example #4
To set the execution policy, you need to use the Set-Execution policy
Code:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
When you set the execution policy without any scope, it will be set for the local machine by default.
Example #5
Set the execution policy with the -Scope
Code:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope LocalMachine -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope LocalMachine -ExecutionPolicy Restricted
Example #6
Set the Execution Policy with the –Force
When you set the execution policy, PowerShell prompts for the user confirmation. To avoid this step, you need to use the Force parameters. This parameter directly applies the policy to the particular scope or the default scope.
Code:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope LocalMachine -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Force
Example #7
Remove execution Policy
To remove the execution policy for any scope, you need to use an undefined policy. It will set the policy to the default. i.e. Restricted.
Code:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope LocalMachine -ExecutionPolicy Undefined –Force
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope LocalMachine -ExecutionPolicy Undefined -Force
Conclusion
The PowerShell Execution policy is the critical component of windows systems security for restricting users from recklessly running any scripts from the console. System admins can use the group policy to deploy the execution policy in a large windows environment system so running script from the internet and other applications can be prevented from running accidentally.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Execution Policy. Here we discuss introduction to PowerShell Execution Policy, scopes, modes and programming examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –