Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell File Extension
Generally, when someone thinks of PowerShell and the file extension, only .ps1 comes to their mind. It is not possible for 95% of the users that there are other file extensions associated with PowerShell. This article will throw the limelight on those file extensions.
3 Different PowerShell File Extension
Following are some of the other extensions that are associated with PowerShell:
- .psm1
- .psd1
- .ps1xml
1. .psm1 Files
This represents a PowerShell module file. A module is a collection of cmdlets, variables, functions, and workflows put together as a package. Modules were first introduced in PowerShell version 2. Modules are generally stored in the following two primary locations.
- %windir%\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\Modules this is the location for system-wide modules available to any user in the system.
- %USERPROFILE%\Documents\WindowsPowerShell\Modules.
Each module has a dedicated folder in which it is saved. It also contains a psd1 file called Module Manifest. The manifest file contains the setting of the module like the version of PowerShell, author, and other settings. The list of available modules can be got by running the Get-Module -ListAvailable cmdlet.
A module is generally comprised of four basic blocks.
- A piece of code
- Assemblies
- Manifest file
- A directory to contain the above three.
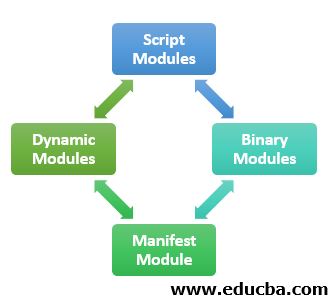
Types of Modules
There are four different types of modules:
- Script Modules: It contains PowerShell variables, functions, and workflows.
- Binary Modules: It is a compiled .net framework code written in a language like c#.
- Manifest Module: It doesn’t have any direct code, instead it uses a manifest file to use features of other modules.
- Dynamic Modules: These modules are not stored anywhere, instead they are generated dynamically by the New-Module cmdlet.
2. .psd1 Files
These files are manifest files. It describes the content of the module and dictates the processing of the module. It is a text file with a hashtable that has a key-value pair. A manifest file is linked to a module by naming the manifest the same as a module and storing the manifest in the module’s root directory. The following are some of the elements that will be present in a manifest file. The New-ModuleManifest cmdlet is used to create a new module manifest file.
- RootModule: Its type is a string and it represents the script module or binary module that is associated with the manifest.
- ModuleVersion: Its type is version. It denotes the version of the module to which the manifest file is associated.
- GUID: Its type is GUID, it denotes the unique identifier of the module.
- Author: Its type is a string and it represents the author of the module. If the value is not specified, the New- ModuleManifest uses the current user name as the author’s name.
- Description: Its type is a string and it provides a description of the module’s functionality.
- CLRversion: Its type is version and it denotes the minimum CLR version that is used to run or use the module.
- RequiredModules: Its type is an object and it denotes the other modules that need to be loaded before importing this module.
- RequiredAssemblies: Its type is a string and it denotes the other assemblies that need to be loaded before importing this module.
3. .ps1xml Files
It is the extension for PowerShell XML files. These are configuration files that contain the details about how the output is displayed and other formatting related styles that are being used. .ps1xml files are automatically installed with PowerShell. They are digitally signed to prevent it for editing as editing these files requires immense knowledge and any changes made to them can have a huge impact. Generally, the XML files are used to extend the functionality of PowerShell objects.
There are three ways in which extended data type can be loaded into a PowerShell session as follows:
- They are either loaded automatically by PowerShell.
- When types.psxm1 file modules are imported to the current session.
- Using Update-TypeData Cmdlet.
There are many in-built XML files in PowerShell. They are present in the home directory and are loaded automatically to every session. To add new properties or methods to an existing PowerShell object, it must be done via the types.ps1xml file.
To add a new .ps1xml file below are the steps:
- Copy an existing .ps1xml file.
- Make the changes and save the file with the extension .ps1xml.
- It is advisable to save the file in the home directory though it is not mandatory.
- Use the Update-TypeDate cmdlet to include the file in the current session.
Examples of PowerShell File Extension
Given below are the examples of PowerShell File Extension:
Example #1: Creation of new .psm1 file
Code:
Write-Host "Demo of module creation"
param(
[string[]] $name,
[string[]] $age,
[string[]] $phonenumber,
[string[]] $address
)
function function1 ()
{
Write-Host "Sample function1"
}
function function2 ()
{
Write-Host "Sample function2"
}
function function3 ()
{
Write-Host "Sample function3"
}
Export-ModuleMember -Function function1
Export-ModuleMember -Function function2
Export-ModuleMember -Function function3
Save the above code as .psm1 file in any location but it is advisable to store in the location the same as PowerShell.
To import the above file into a PowerShell session using the below cmdlet.
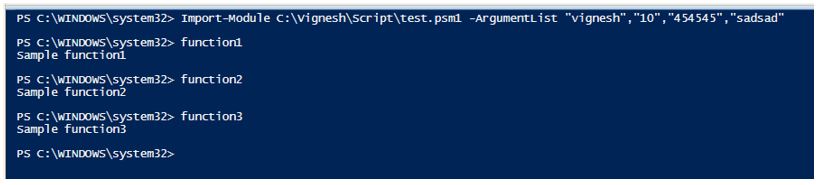
Import-Module C:\Vignesh\Script\test.psm1 -ArgumentList "vignesh","10","454545","sadsad"
Once the module is imported the functions inside the module can be accessed.
Output:
Example #2: Creation of .psd1 File
Code:
@{
Author ='Vignesh Krishnakumar'
CompanyName='test company'
Copyright ='All rights are subject to test company'
GUID = 'b000090c-dzzz-4340-9df4-3b8326000000'
ModuleVersion = '6.6.6'
Description='Test Manifest file'
}
Save the above as a .psd1 file.
To import the manifest file, use the below cmdlet:
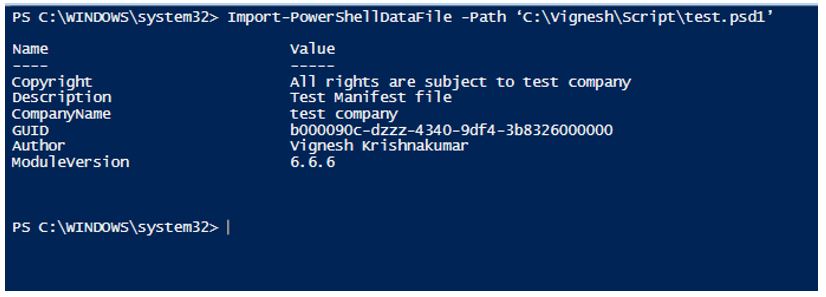
Import-PowerShellDataFile -Path ‘C:\Vignesh\Script\test.psd1’
Output:
Conclusion
Thus, the article covered a few of the commonly used file extension types available in PowerShell other than .ps1. It covered in detail about .psd1, .psm1 and .ps1xml file extension in detail along with their usage and functionalities. The article also showed examples of creating a module file, accessing a module, creating a manifest file, and importing them.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to PowerShell File Extension. Here we discuss the introduction, 3 different PowerShell file extensions, and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –