Updated March 6, 2023
Definition of PowerShell Dictionary
PowerShell Dictionary is also known as Hashtable or associate array is a compact data structure and composed of the key and the value pair. Hashtable is a .Net namespace System.Collections.Hashtable while the dictionary is from a .Net namespace called Systems.Collection.Specialized.OrderedDictionary and it’s the order of the output that differentiate them, ordered dictionary has the ordered output while the Hashtable doesn’t have the ordered output.
Syntax:
Syntax for Hashtable:
@{ <name> = <value>; [<name> = <value> ] ...}
The syntax for Ordered Dictionary:
[ordered]@{ <name> = <value>; [<name> = <value> ] ...}
This [Ordered] attribute was introduced in PowerShell v3.0.
When we create a Hashtable or Dictionary, it starts with the at-sign (@) and is surrounded by the curly braces {}.
Inside the braces, we define the key and values. Value is assigned to the key using the equal (=) symbol and multiple key values are separated using a semicolon (‘;’).
If the hashtable is in the ordered format (dictionary) then [Ordered] should be written ahead of it.
How does the dictionary work in PowerShell?
PowerShell dictionary or the hashtables are the same in manner but the only difference is Dictionary produces the ordered output while the Hashtable output is not in the order.
You can create an empty hashtable using the below command,
$htable = @{}
When you check the type of the hashtable, its base type is a System. Object and it is the hashtable.
$htable.GetType()
Output:
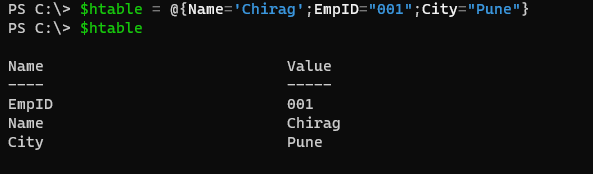
We can simply insert values to the hash table by adding the keys and their values.
$htable = @{Name='Chirag';EmpID="001";City="Pune"}
$htable
Output:
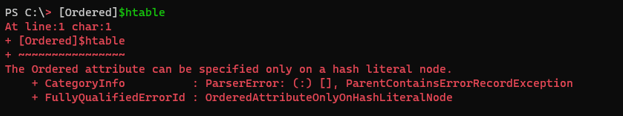
Once the hashtable is created and if you want to create an ordered dictionary from it you can’t directly cast a hash table, it will throw an alert.
[Ordered]$htable
Output:
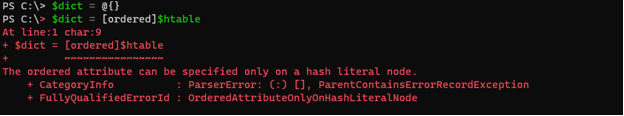
Even if we create a new empty hash table and assign and cast the hash table to it, it won’t work.
$dict = @{}
$dict = [ordered]$htable
Output:
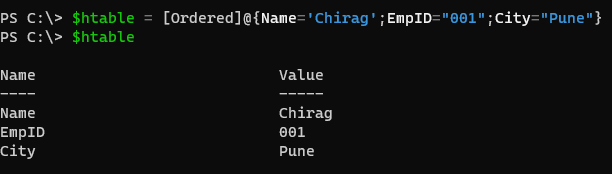
To create a dictionary, we initially need to cast the [Ordered] hashtable when we assign values as shown below.
$htable = [Ordered]@{Name='Chirag';EmpID="001";City="Pune"}
Output:
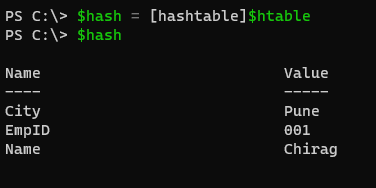
The Output will appear in the order we assign values to them. We can reverse typecast here. It is possible.
$hash = [hashtable]$htable
Output:
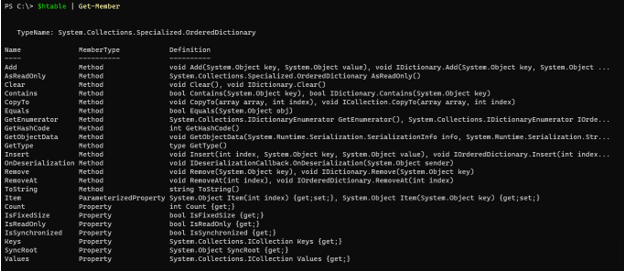
There are also a few methods and properties supported by Hashtable or the dictionary to perform the operation or to retrieve the data from the hashtable.
$htable | Get-Member
Output:
Examples
Lets us discuss examples of PowerShell Dictionary
Example #1: Create a Hashtable and adding values.
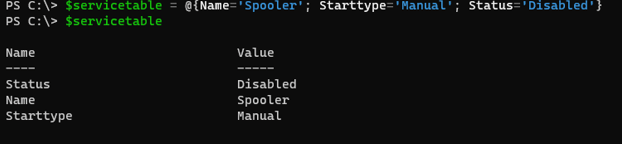
This example creates a service table that stores information about a particular service.
$servicetable = @{Name='Spooler'; Starttype='Manual'; Status='Disabled'}
$servicetable
Output:
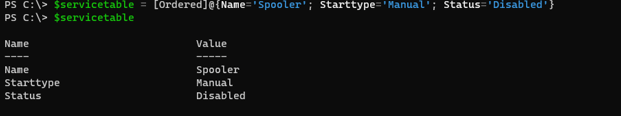
The output is not in the ordered format as input so we create a dictionary (ordered hashtable).
$servicetable = [Ordered]@{Name='Spooler'; Starttype='Manual'; Status='Disabled'}
$servicetable
Output:
Throughout other examples, we will use this created hashtable.
Example #2: Retrieving Hashtable values and keys.
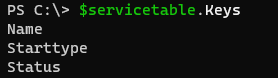
To get the hashtable keys, we need to select its property Key as shown below.
$servicetable.Keys
Output:
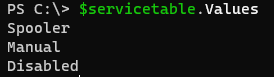
To retrieve hashtable values,
servicetable.Values
Output:
To retrieve the particular value from the Key, we can provide the key name.
$servicetable.Name
Output:
Example #3: Adding new Keys and Value to the Hashtable
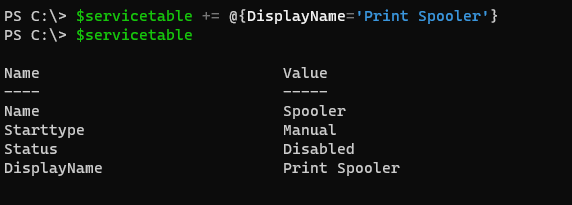
To add a new key and associated values to the hashtable, we can use the following method.
$servicetable += @{DisplayName='Print Spooler'}
$servicetable
Output:
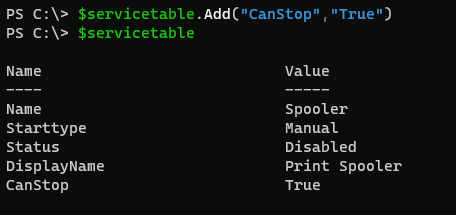
The above one is an explicit method, we can also use Add() method as well.
$servicetable.Add("CanStop","True")
$servicetable
Output:
Example #4: Deleting Hashtable Key
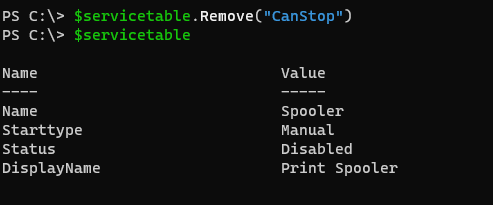
To Remove the hashtable key, we need to use the Remove() method. We just need to provide Key inside the Remove() function.
$servicetable.Remove("CanStop")
$servicetable
Output:
Example #5: Modify the Hashtable key value.
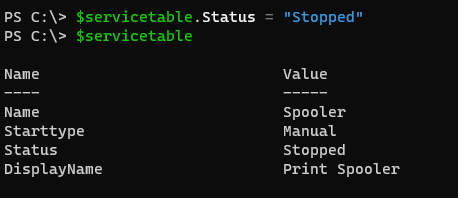
To modify the specific hashtable’s key value, we just need to access the key and assign the value to it.
$servicetable.Status = "Stopped"
$servicetable
Output:
Example #6: Assign multiple values to the hashtable key.
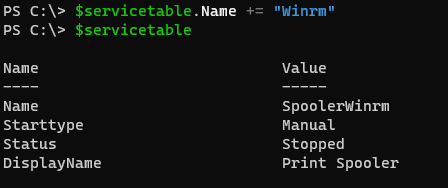
We can’t directly assign multiple values to the hashtable key because the individual key is considered a string as shown below.
$servicetable.Name += "Winrm"
$servicetable
Output:
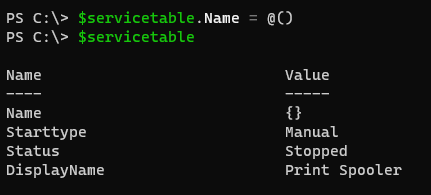
To solve this we initialize the particular key as an array and then create multiple values but the problem is if we initialize the key as an array after creating a hashtable its existing value will be wiped out and we need to create it again.
$servicetable.Name = @()
$servicetable
Output:
We need to add values now.
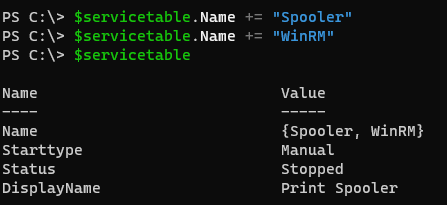
$servicetable.Name += "Spooler"
$servicetable.Name += "WinRM"
$servicetable
Output:
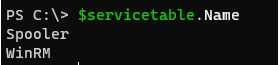
Name property will give multiple values now.
$servicetable.Name
Example #7: Converting string data to the hashtable.
To convert the string output to the hashtable, we can use the ConvertFrom-StringData command.
$stringdata = @"
Book = The Owl
Genre = Fiction
Author = Greg Truth
"@
Output:
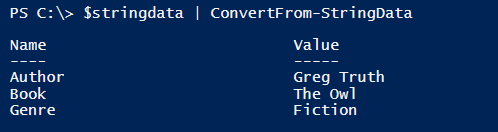
To convert to the hashtable,
$stringdata | ConvertFrom-StringData
Output:
Example #8: Hashtable with Object Types.
In this method, we are storing Objects (which have multiple keys and values) in the Value field.
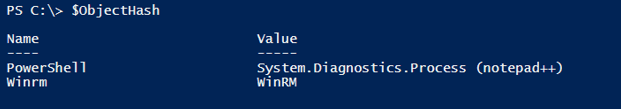
$ObjectHash = @{
'PowerShell'= (Get-Process notepad++)
'Winrm' = (Get-Service WinRM)
}
Output:
When we check the individual key’s value, we can use the value as a separate hashtable as shown below.
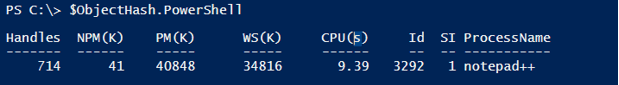
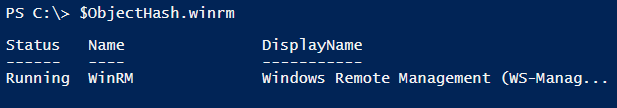
$ObjectHash.PowerShell
$ObjectHash.winrm
Further expanding,
$ObjectHash.PowerShell.Id
$ObjectHash.Winrm.DisplayName
Example #9: Convert Hashtable output to the JSON / XML format.
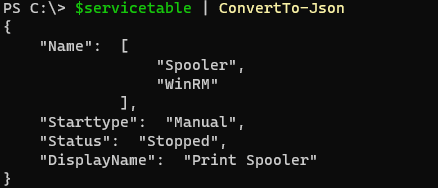
We can convert the output of the hashtable to JSON or XML format using ConvertTo-JSON or ConvertTo-XML command.
$servicetable | ConvertTo-Json
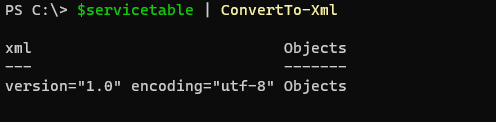
For XML,
$servicetable | ConvertTo-Xml
Conclusion
Hashtables are heavily used in the PowerShell language because of their flexibility. We can easily store values, search values, and retrieves the values and the most useful thing is the output is in the table format so it can be converted to the JSON format as well. ConvertFrom-StringDate converts the output to the hashtable format.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Dictionary. Here we discuss the definition, syntax, How does the dictionary work in PowerShell? and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –