Updated March 4, 2023
Definition of PowerShell Boolean
PowerShell Boolean operators are $true and $false which mentions if any condition, action or expression output is true or false and that time $true and $false output returns as respectively, and sometimes Boolean operators are also treated as the 1 means True and 0 means false.
Syntax:
Boolean type is the form of the output and its output is True or False but for the syntax, it uses the comparison and conditional operators to compare the two or multiple values.
<Value1> -eq <Value2>
<Value1> -ne <Value2>
And there are other syntaxes based on the commands and conditions as well. Which are shown in the examples.
How Boolean type works in PowerShell?
When evaluating the Boolean expression it compares the left side of the value to the right side of the value. If the value of the left side is equal to the value of the right side then it is evaluated true otherwise false as shown below.
"Hello" -eq "hello"
Output:
It depends on the condition we apply. For example, the above operator is not case sensitive. If we use the case-sensitive operator then the output will be false. For example,
"Hello" -ceq "hello"
Output:
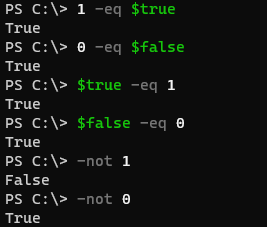
In the Boolean type, 1 is treated as $true, and 0 is treated as $false. For example,
1 -eq $true
0 -eq $false
$true -eq 1
$false -eq 0
-not 1
-not 0
Output:
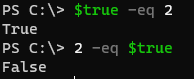
In the above examples we have seen that the left side of the object is compared to the right side of the object in the -EQ operator but let evaluate the below expressions.
$true -eq 2
2 -eq $true
Output:
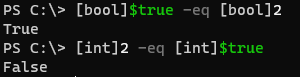
In the above example, the first is true but the second is false. So when the first example is true, its reverse should be also true but the Boolean operator doesn’t work that way. It works on the typecasting and the left side of the object type plays the main role here. In the first example, 2 is automatically type-casted to Boolean while in the second example, $true is type-casted to the integer as shown below.
[bool]$true -eq [bool]2
[int]2 -eq [int]$true
Output:
Condition like IF/Else also uses the Boolean output. If the condition is true then it uses the ‘IF’ block, otherwise else block is executed. For example,
if(5 -gt 6){"5 is greater than 6"}
else{"5 is less than 6"}
In the above example, if the condition checks whether the expression is true or false and that is a Boolean value and based on it, the script executes the block.
Few commands also directly return the Boolean values like Test-Path, Test-Connection, etc.
Test-Path C:\Temp\10vms.csv
Output:
While Test-Connection, by default doesn’t produce the Boolean output but when we add -Quiet parameter, it produces the Boolean output.
Test-Connection google123.com -Count 2 -Quiet
Output:
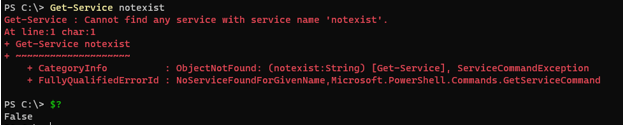
Dollar + QuestionMark syntax ($?) also produces the Boolean output. It checks whether the last command run was successful or failed and it gives the output accordingly.
Get-Service notexist
$?
Output:
Examples
Let us discuss examples of PowerShell Boolean.
Example #1: Using Comparison Operators to check Boolean values.
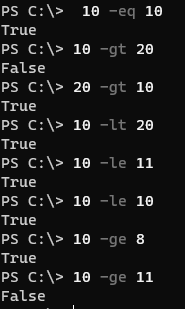
10 -eq 10
10 -gt 20
20 -gt 10
10 -lt 20
10 -le 11
10 -le 10
10 -ge 8
10 -ge 11
Output:
With String objects,
"abc" -eq "def"
"abc" -eq "abc"
"abc" -eq "abc","def"
"abc" -ne "abc"
Output:
Example #2: Using the cmdlets
Using those cmdlets which returns the output Boolean type. For example,
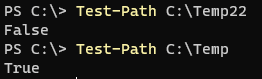
- Test-Path command.
This command directly returns the Boolean value based on the path existence. For example,
Test-Path C:\Temp22
Test-Path C:\Temp
Output:
- Test-Connection command.
Some command returns the value but not the Boolean value but they support parameter which returns the Boolean value. For example, the Test-Connection command uses -Quiet parameter to return a Boolean value.
Test-Connection www.google.com -Count 2 -Quiet
Output:
Using the above command with If condition,
If(Test-Connection google.com -count 2 -Quiet -EA Ignore){
Write-Output "Connection reachable"
}
else{
Write-Output "Connection is not reachable"
}
Output:
Example #3: Commands without supported Boolean output parameter
Some commands don’t support the output which has true or the false value as the output and in that case, we can use those commands inside the IF/else condition to handle the Boolean output.
if(Get-Service WinRm -EA Ignore){
Write-Output "WINRM service is exist"
}
else{
Write-Output "WinRM service doesn't exist"
}
Output:
You can also use the Where block after a pipeline to evaluate if the output is true or false. For example,
If(Get-Process | where{$_.Name -eq "Wrong Process"} -EA Ignore){
Write-Output "Process exist"
}
else{
Write-Output "Process Doesn't Exist"
}
Output:
In the above example, if the process doesn’t exist, it produces the output false and executes the else condition. Otherwise, the true output and will execute the IF condition.
Example #4: Boolean type output for multiple conditions
When there are multiple conditions used, the output will be as below.
-And will check if both the conditions are true then the output is True, otherwise False.
-OR will check if any of the condition is true then the output is True, otherwise False.
(5 -lt 6) -and (4 -lt 5)
(5 -lt 6) -and (5 -lt 4)
(5 -lt 6) -or (5 -gt 4)
(5 -lt 6) -or (4 -gt 5)
(6 -lt 5) -or (4 -gt 5)
Output:
Conclusion
Boolean types (True and False) are very useful while working with the scripts. While writing scripts, programmers need to evaluate the previous output and moves to the next commands if they are true or false. It also helps to create a flow chart properly for scripts.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Boolean. Here we discuss the definition, How Boolean type works in PowerShell? examples with code implementation respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –