Updated March 14, 2023

Introduction to PowerShell ComputerName
It is always useful and handy to know the computer name or the local host of the system you are logged into. It is also needed to run certain cmdlets as they require computer name as a mandatory parameter. It is also very important while working with remote computers or when some script needs to be run on remote computers. This article will cover various ways in which the computer name can find out using PowerShell.
Ways of Finding the Computer Name
There are many ways and commands in which the Computer Name can be identified. The following are some of the ways.
- From the Environment variable
- Using hostname process way
- Using WMI/CIM
- Using .Net machine value
- From Kernel function
- Using Gethostname() function of .Net
We will see each of the above in detail.
1. Finding Computer Name from the Environment Variable
The easiest way of finding out the computer name is by reading the environment variable. This is the simplest, most effective, and fastest way. It also suffers from a major drawback, since the environment variable can be easily overwritten it comes with a bit of risk factor. The result may be skewed.
Input:
$env:computername
Output:
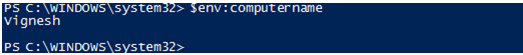
To get all the environment variables the following cmdlet can be used.
Get-Childitem env:
To get the computer name the following cmdlet can be used.
Input:
get-childitem env:computername
Output:
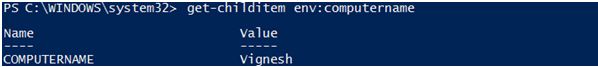
2. Using Host Name Process Way
Like linux, windows also have some binaries which can be used to fetch information. Executing the hostname.exe will return the computer name. Running the below command will display the computer name
Input:
hostname.exe
Output:
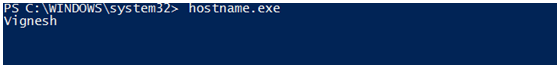
3. Using the WMI
Wmi is available on windows machines since the windows 2000 version. In the versions prior to it, it was an external package. The same can be achieved using the CIM Instance.
Input:
Get-WMIObject Win32_ComputerSystem | Select-Object -ExpandProperty name
(Get-CIMInstance CIM_ComputerSystem).Name
Output:
4. Using .Net Class
The computer name can be found using the .Net class.
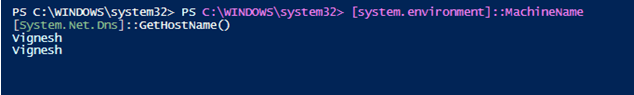
Input:
[system.environment]::MachineName
Similarly using the gethostname function the computer name can be found out.
[System.Net.Dns]::GetHostName()
Output:
5. Renaming a Computer Name
It is possible that sometimes an administrator needs to rename the computer name. In that case, the Rename-Computer cmdlet can be used.
Syntax:
NAME
Rename-Computer
SYNTAX
Rename-Computer [-NewName] <string> [-ComputerName <string>] [-PassThru] [-DomainCredential <pscredential>] [-LocalCredential <pscredential>] [-Force] [-Restart]
[-WsmanAuthentication {Default | Basic | Negotiate | CredSSP | Digest | Kerberos}] [-Protocol {DCOM | WSMan}] [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
ALIASES
None
Parameters
- -ComputerName: This denotes the computer to be renamed. It can be either the local system or a remote computer. By default, it refers to the local system. To rename the local computer, mention as localhost or. To rename the remote computer, specify the ip address or netbios name or the fqdn name of the remote system. Its type is a string. It accepts pipeline input, but wild card characters are not supported.
- -Confirm: This denotes that a confirmation message must be shown before the cmdlet is executed. The data type is a switch and can also be accessed using cf. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are not allowed.
- -DomainCredential: This denotes the account with which to connect to the domain. If a system is joined to a domain, then credentials are mandatory. Its type is PSCredential and the default value is none. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are not allowed.
- -Force: This denotes the cmdlet to be run without user confirmation.
- -Local Credential: This denotes the account which has permission to the computer. By default, current user credentials are taken. If the prompt for credentials shouldn’t appear domain credential parameter should be used. Its type is PSCredential. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are not allowed.
- -NewName: This is the new name of the computer. Spaces and periods are not allowed. The maximum number of characters allowed is 63 and it can’t contain only numbers. It is of data type string. Pipeline input is accepted.
- -PassThru: This is used to show the preview of the command if run. It will not generate any output. The data type of this parameter is a switch. By default, the value is false.
- -Restart: This denotes for the system to be restarted after the name change. Mostly a restart is required for the name change to be effective. Its type is a switch. Its default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are also not allowed.
- -Whatif: This will not result in any output. It is like a preview. The data type of the parameter is a switch and can be accessed as wi. If the value is not supplied, it is considered false.
- -WsmanAuthentication: It denotes the mechanism of the WSman protocol that will be used to authenticate the credentials. The possible values are basic, Credssp, Default, Digest, Kerberos, and negotiate. Its type is a string. The default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wild card characters are also not allowed.
Example of PowerShell ComputerName
Example of PowerShell computername is given below:
Input:
Write-Host "Welcome to renaming of computer name demo"
Write-Host "Renaming of local computer"
Rename-Computer -NewName "vigneshnew" -DomainCredential home\vignesh
Write-Host "Computer renamed successfully"
Write-Host "Renaming of remote computer"
Rename-Computer -ComputerName "testserver1" -NewName "testservernew" -DomainCredential test\vignesh -Force
Write-Host "Computer renamed successfully"
Output:

Conclusion
Thus, the article covered in detail identifying the name of a local computer or a remote computer name in PowerShell. It also explained the various ways in which it can be obtained using examples. The article also covered in detail the ways in which a computer name can be changed. To learn more in detail it is advisable to write sample scripts and practice them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell ComputerName. Here we also discuss the introduction and ways of finding the computer name along with an example and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

