Updated March 8, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell comment
PowerShell comment is one kind of help to give the basic short details of the code. You can add a comment to any section of the PowerShell script, like a comment you can provide for the function or comment you can provide for the conditions, loops, etc. The scripter who is reading the code will easily understand what the code is about. We can also use the comments to provide the help sections. The comment won’t be displayed when the script is executed; it is only for the user information.
Types of PowerShell comment
There are two types of PowerShell comments we can use:
- Single Line Comment: This is also called the Inline comment, and it can comment out only one line.
- Multi-Line comment: This is also called the block comment, and it is applied to the few line of codes or the whole code.
Syntax:
Single line comment or Inline comment can be described with Hash (#) syntax while the multi-line comments or block comments can be described with the tags and Hash like <#..#>
Examples
Given below are the examples of PowerShell comment:
Example #1
Single line Comment to describe the code.
Code:
Rename-Item C:\Temp\azgroup.json -NewName azuregroup.json # This command will rename the item
Example #2
Single Comment to describe the function.
Code:
function GetData{
#Function will get the data from azure blob
}
Example #3
Comment to disable the specific code.
Code:
# Copy-Item C:\Temp\NewUsers.csv -Destination \\test1-win2k12\c$\temp
When you comment on any code, you may notice that the color of the line changes. It depends on the editor and the theme you applied for that editor. If you have the block that describes the multiple lines together like ” loop, ” ” function, ” ” for loop, ” etc., and if you apply comment for a single line, that might generate an error.
Code:
while($i -gt 10){
Write-Output $i
$i++
}
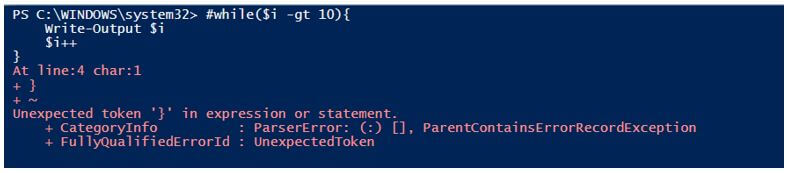
If you disable the first line using a comment in the above example, it will generate an error.
Code:
# while($i -gt 10){
Write-Output $i
$i++
}
Output:
The error says the additional ‘}’ is not expected because we have already disabled the ‘{‘. You can use the single-line comment to disable the multiple lines of code.
Code:
# while($i -gt 10){
# Write-Output $i
# $i++
#}
But this method is not recommended; instead, we can use the multi-line comment to disable them, and it is shown in the subsequent examples.
Example #4
Multi-Line comment to describe script.
Code:
<#
This program is to test the server connectivity.
Once connectivity establishes it checks the WINRM connection on the server.
The third step is to push the Application agent on the servers
In the final step, server will be rebooted
#>
In the above example, we have created a multi-line comment block using PowerShell, and it won’t be executed. It is used when you want to put the specific details about parameters, for example, date format, or the user should note before executing the script like the output path of the logs.
Example #5
Multi-line comment to disable the function or part of the code.
As shown in example ‘c’, we can disable the entire while loop using single-line comments, but it would be much easier to use the multiline comments.
Code:
<#while($i -gt 10){
Write-Output $i
$i++
}#>
It is much easier than the single-line comment.
PowerShell comments Based Help
This is also a type of multi-line comment. PowerShell comments based help work on Keywords. Each Keyword describes the specific topics for their intended use, and they can be used inside the multi-line comment section.
These keywords can appear in any order, and they are not case-sensitive, and they start with a dot (.). Mentioning all keywords are not necessary. You can add a few of them as per your requirement.
- .SYNOPSIS: A brief description of the function or the script. This keyword is used only once.
- .DESCRIPTION: A detailed description of the script. This keyword is used only once.
- .EXAMPLE: A sample example for the script along with input and output. We can add multiple examples.
- .PARAMETER <Parameter-Name>: Description of the parameter. This keyword can be used for each parameter in the script. It can be in any order, but the order in which they are mentioned in the Param() block will appear in the help section.
- .INPUTS: Description of the input objects or the types of objects that can be piped to the script or function.
- .OUTPUTS: Description of the returned object or the types of the objects that the cmdlet returns.
The above are the basic keywords that we generally need to describe the comment-based help section of the function. Apart from that, there are other keywords that you can also specify, Like NOTES, LINK, COMPONENT, ROLE, FUNCTIONALITY, etc.
Example:
Code:
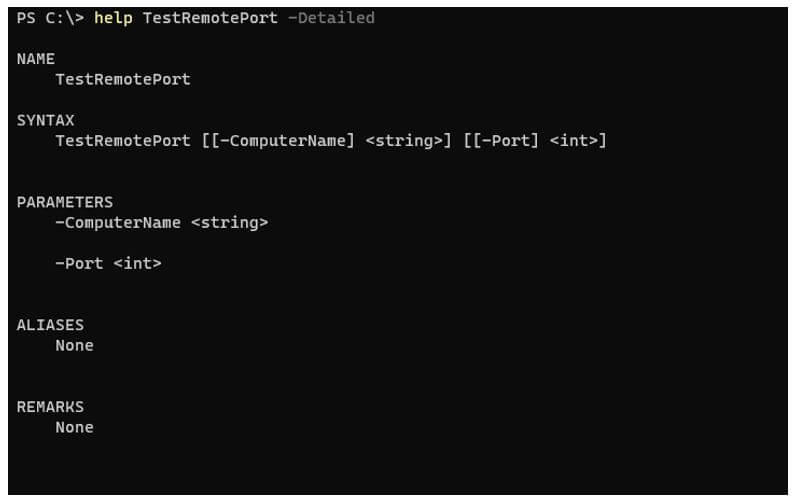
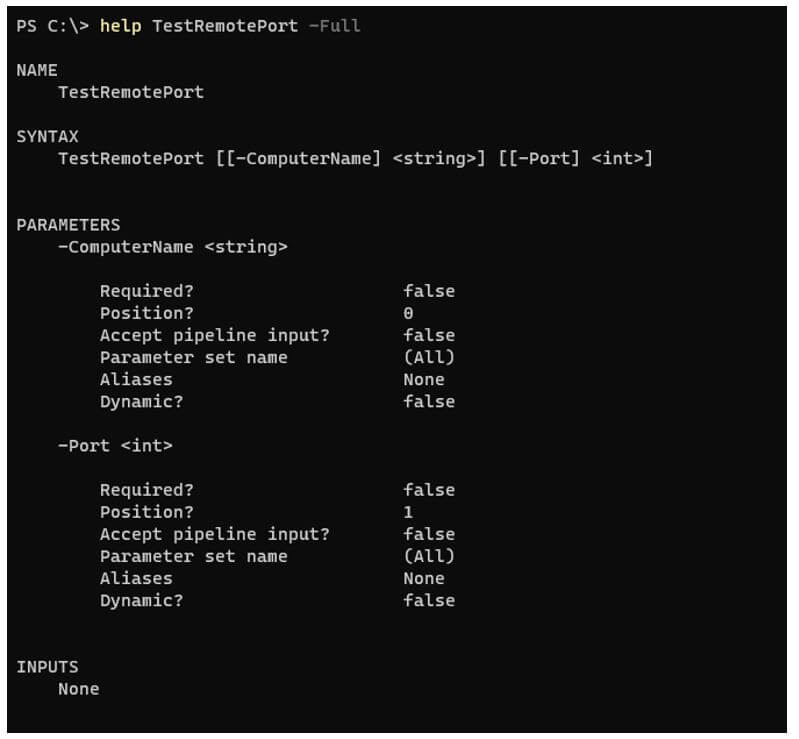
function TestRemotePort{
param(
[String]$ComputerName,
[Int]$Port
)
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Function to test remote ports.
.DESCRIPTION
This script checks port on the remote computers
.EXAMPLE
TestRemotePort -ComputerName ServerName -Port 8080
.PARAMETER ComputerName
Remote Server Name
.PARAMETER Port
Remote port number
.INPUTS
ComputerNames can be passed and a port can be passed
.OUTPUTS
True or False
#>
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName $ComputerName -Port $Port
}
Output:
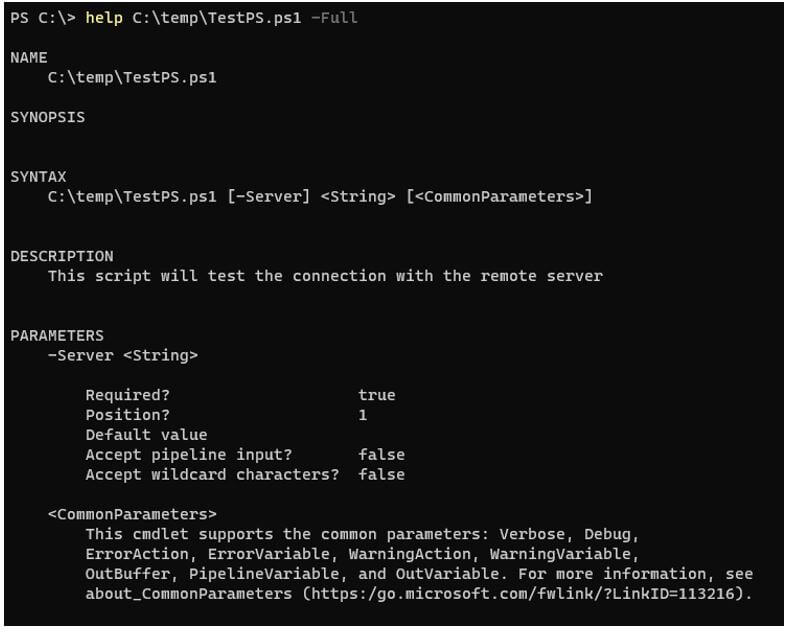
You can also place the comment-based help at the beginning of the script.
Code:
<#
.DESCRIPTION
This script will test the connection with the remote server
#>
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[String]$Server
)
Test-Connection -ComputerName $Server -Count 2 -quiet
Output:
And the comment-based help can be placed at the end of the script.
Code:
function TestNetConnection{
Test-Netconnection -ComputerName $computername -Port $port
}
<#
.DESCRIPTION
The above function checks the port on the remote computer.
#>
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the PowerShell comment. Here we discuss the introduction, types, examples and PowerShell comments based help. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –