Updated March 4, 2023

Introduction to PowerShell Administrator
PowerShell administrator is a person who is responsible for maintaining the overall windows-based servers of an organization. They are also responsible for maintaining the integrity of the data of the organization. They also play a pivotal role in maintaining the on-boarding and off-boarding of employees as they are the ones responsible for maintaining the active directory of the organization. PowerShell administrators are also known as windows administrators.
Different ways of Running as PowerShell Administrator
There is a major difference between running a cmdlet or a script in PowerShell in a normal mode from that of an administrator mode. It is because most of the operations require admin access and only a PowerShell administrator has the privilege to perform those operations.
The following are the different ways in which PowerShell can be run in admin mode:
- Search for PowerShell and right-click and select run as administrator.
- Open PowerShell using the run command. Once the PowerShell window is opened, type as Start-Process PowerShell -verb run as and press the enter key.
- By using task manager, create a new task. In the name, type PowerShell and check the “Create this task with administrative privileges” and press enter.
Roles and Responsibilities of PowerShell Administrator
Given below are the roles and responsibilities :
1. Check for patches
One of the main responsibilities of a PowerShell administrator is to check for the latest patches that are available and install them. This is a crucial part for any organization to prevent the resources from vulnerabilities attacks and other security related issues. Most of the organization’s patches are installed on a monthly basis to avoid any threats. Get-Hotfix cmdlet is used to find the patches. If we know the id of the patch, then that KB article value should be passed.
Example:
Code:
Get-Hotfix
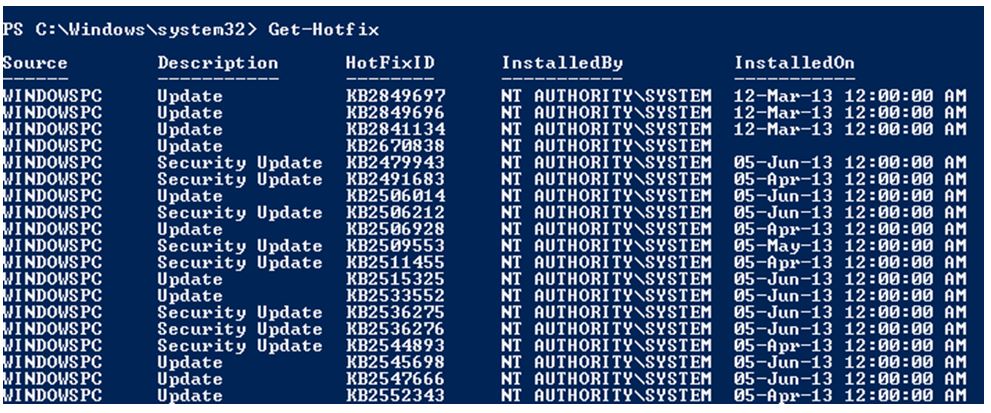
Output:
It will display the list of all patches that are installed in the local computer.
2. Monitoring the disk space availability
The other important task of the PowerShell administrator is to monitor the available disk space in the system. This process will be tedious in case if there are multiple servers in the system and can’t be done manually. This job is automated by most of the admins with the help of a script which regularly checks for the disk space and sends a trigger based on the condition. These scripts are run using a task scheduler, which will run during non-business hours.
Example:
Code:
$ServerList= Import-csv -path "C:\serverlist.csv"
ForEach ($s in $ServerList)
{$reportlist=Get-WmiObject win32_logicaldisk -ComputerName $s -Filter "Drivetype=3" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Where-Object {($_.freespace/$_.size) -le '0.2'}
$vi=($reportlist.DeviceID -join ",").Replace(":",""
If ($reportlist)
{
$Eto = "[email protected]"
$Efro = "[email protected]"
$username = '[email protected]'
$pwd = '#$5555'
$sub = "Disk space less than 20%"
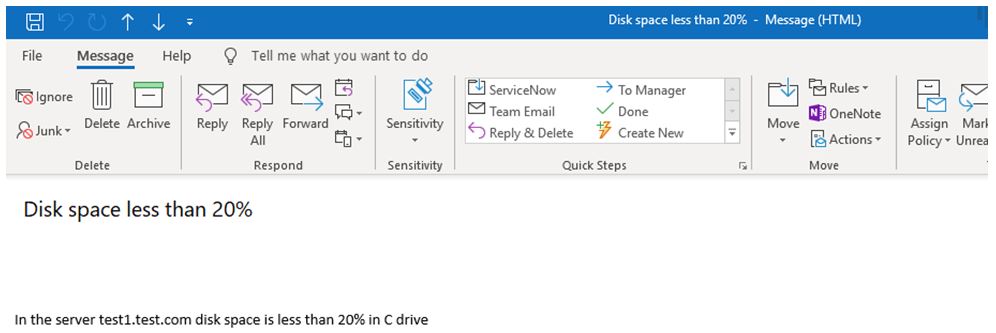
$bdy = "In the server $s disk space is less than 20% in $vi"
$smser = "[email protected]"
$smmsg = New-Object System.Net.Mail.MailMessage($Efro,$Eto,$sub,$bdy)
$smtcli = New-Object Net.Mail.SmtpClient($smser, 587)
$smtcli.EnableSsl = $true
$smtcli.Credentials = New-Object System.Net.NetworkCredential($username, $pwd)
$smtcli.Send($smmsg)
}
}
Output:
3. Adding users from csv to an AD Group
Example:
Code:
write-host "Adding users from csv to a AD group"
Import-Csv “C:\vignesh\userlist.csv” | ForEach-Object {
$USPN = $_.SAN + “@test.com”
New-ADUser `
-DisplayName $_.DN `
-Name $_.”Na” `
-GivenName $_.”GN” `
-Surname $_.”SN” `
-SAN $_.”samname” `
-UserPrincipalName $USPN `
-Office $_.”Of” `
-EmailAddress $_.”emadd” `
-Description $_.”des” `
-AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString “Tes$@123!” -AsPlainText -force) `
-ChangePasswordAtLogon $true `
-Enabled $true `
Add-ADGroupMember “testgroup” $_.”samname”;
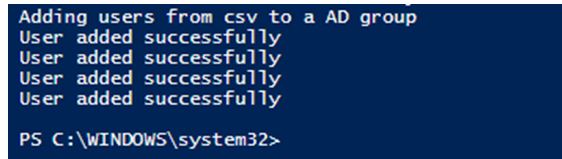
write-host "User added successfully"
}
Output:
4. Check if patch is installed in a server or not
Example:
Code:
#list of servers to be checked
$servers = get-content -path C:\servers.txt
#list of patch id's
$patdet = get-content -path C:\padetails.txt
foreach ($ser in $servers)
{
foreach ($pa in $patdet)
{
Get-HotFix -id $pa -ComputerName $ser -OutVariable re -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
if ($re -ne $null) {
write-host "Patch $pa is present in the $($ser)"
}
else {
write-host "patch $pa is not present in the $($ser)"
}
}
}
Output:
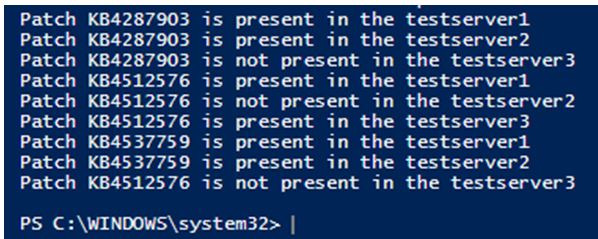
In the above example, a list of servers is maintained in one csv and the list of patch ids to be checked for installation in maintained in another csv. For each of the servers mentioned in the csv, all the patch ids are checked if it is installed or not. The server details and patch id’s can be mentioned in the same csv but it would be convenient to have them in different csv’s.
5. Deleting IIS logs older than 10 days
Code:
Write-Host "Welcome to the iis logs archive example"
$iislogpath = Import-Csv "C:\Vignesh\logpath.csv"
foreach($path in $iislogpath)
{
write-host "The iis log location is" $path
$deleteddays = "-10"
$CurrentDate = Get-Date
$noofdays = $CurrentDate.AddDays($deleteddays)
Get-ChildItem $Path -Recurse | Where-Object { $_.CreationTime -lt $noofdays } | Remove-Item
Write-Host "log files older than 7 days are deleted "
}
Output:
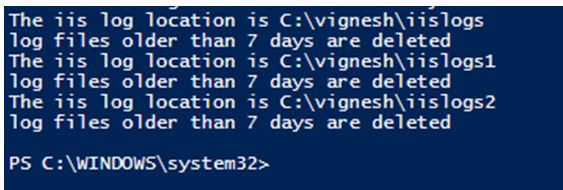
In the above script, a list of log locations is mentioned in the text file. Then in each of the paths, the files that are greater than 7 days are deleted. This can also be scheduled in a task scheduler and can be run daily during non-business hours.
Conclusion
Thus, the article covered in detail who is a PowerShell administrator and what are his roles and responsibilities. The mentioned roles are only a few but there are more tasks than a PowerShell administrator does on his day-to-day activities. The roles are explained with appropriate examples. In some cases, the PowerShell administrator is also responsible for the overall infrastructure of an organization.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Administrator. Here we discuss the introduction to PowerShell Administrator, 5 different ways of running administrator with roles and responsibilities. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

