Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell add user to group
Adding users to a local group or an active directory group is an integral part of windows administrator. It will be a tedious process to add them manually. Also, in case if bulk adding of users is required, it can’t be achieved manually. To overcome this, there are cmdlets in PowerShell that will add users to the local group as well as an AD group. This article will cover in detail those cmdlets along with appropriate examples. In this topic, we are going to learn about PowerShell add user to group.
Add-LocalGroupMember
This cmdlet is used to add users to users to a local security group in the system. It can be used to add groups also. The group’s permission is inherited by its members. People part of the admin group of a system ha full permissions, and therefore care must be taken to ensure that only a selected few are added to that group. If a system is joined with domain accounts from that particular domain as well as trusted domains can be added to a group on the local system.
Syntax:
Input:
Get-Help -Name Add-LocalGroupMember
NAME
Add-LocalGroupMember
SYNTAX
Add-LocalGroupMember [-Group] <LocalGroup> [-Member] <LocalPrincipal[]> [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
Add-LocalGroupMember [-Name] <string> [-Member] <LocalPrincipal[]> [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
Add-LocalGroupMember [-SID] <SecurityIdentifier> [-Member] <LocalPrincipal[]> [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
ALIASES
algm
Parameters:
Below are the parameters:
-Confirm:
This asks for user confirmation before proceeding to execute. The data type of the parameter is the switch. Its alias is cf. False is the default value. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wildcard characters are also not permitted.
-Group:
This denotes the group name in which the users or group needs to be added. The data type of this parameter is Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.LocalGroup. This is a mandatory parameter. The default value is none. . It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wildcard characters are also not permitted.
-Member:
This denotes the users or groups that need to be added to the group. The SID of the members can also be specified. This is a mandatory parameter. The data type of this parameter is Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.LocalPrincipal[]. Its positional value is 1. The default value is none. . It accepts pipeline input, but wildcard characters are also not permitted.
-Name:
This refers to the group to which the members need to be added. The data type of this parameter is a string. None is the default value. Pipeline input is not accepted also; wild card characters are not permitted.
-SID:_
This denotes the security id of the group to which the members need to be added. The data type of this parameter is SecurityIdentifier. None is the default value. Pipeline input is not accepted also; wild card characters are not permitted.
-Whatif:
This denotes what will happen if the cmdlet is run. Its alias is wi, and the data type is the switch. False is the default value. Pipeline input is not accepted also; wild card characters are not permitted.
On a 64-bit system and on a 32 bit PowerShell The Microsoft.PowerShell.LocalAccounts module is not available. Local, Active Directory, Azure Active Directory, and Microsoft account are the possible principal source properties.
The principal source is supported and available only on Windows 10, server 2016, and above.
Add-ADGroupMember
This cmdlet is used to add members to an AD group. The members can be users, computers, or service accounts.
Syntax:
Add-ADGroupMember [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [-AuthType <ADAuthType>] [-Credential <PSCredential>] [-Identity] <ADGroup> [-Members] <ADPrincipal[]> [-MemberTimeToLive <TimeSpan>] [-Partition <String>] [-PassThru] [-Server <String>] [-DisablePermissiveModify] [<CommonParameters>]
Parameters:
-AuthType:
This refers to the authentication to be used to add users to the AD group. It can either negotiate (0) or basic(1). By default, negotiate is used. The basic method requires an established SSL connection. The data type of this parameter is ADAuthType. The default value is none. Pipeline input is not accepted, and wild card characters are also not permitted.
-Confirm:
Whenever a user confirmation is needed before running the cmdlet, this parameter is used. The alias is cf. The data type of this parameter is cf. False is the default value. Pipeline input is not accepted also; wild card characters are not permitted.
-Credential:
This denotes the credential under which the cmdlet will be run. By default, the current user’s profile is considered. If the cmdlet is being run from a drive, the drive’s account is used. The data type of this object is PSCredential. None is the default value. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wildcard characters are also not allowed.
-DisablePermissiveModify:
This prevents the system from throwing an error when trying to add an existing user to a group. The data type of this parameter is a switch. The default value is false. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wildcard characters are also not permitted.
-MemberTimeToLive:
This denotes the lifeline of the members being added to the group. The data type of this parameter is a timespan. None is the default value. It doesn’t accept pipeline input, and wildcard characters are also not permitted.
Examples of PowerShell add user to group
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
Input:
Add users to an Active Group
try
{
Import-Csv “D:\test123\test.csv” | ForEach-Object {
$Name = $_.Name + “test.com”
New-ADUser `
-DisplayName $_.”Dname” `
-Name $_.”Name” `
-GivenName $_.”GName” `
-Surname $_.”Sname” `
-SamAccountName $_.”Name” `
-UserPrincipalName $UPName `
-Office $_.”off” `
-EmailAddress $_.”EAddress” `
-Description $_.”Desc” `
-AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString “vig@123” -AsPlainText -force) `
-ChangePasswordAtLogon $true `
-Enabled $true `
Add-ADGroupMember “OrgUsers” $_.”Name”;
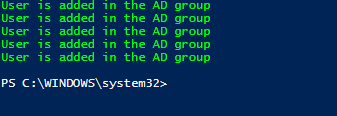
Write-Host "User is added in the AD group" -ForegroundColor Green
}
}
catch
{
$msge=$_.Exception.Message
Write-Host "Exception is" $msge
}
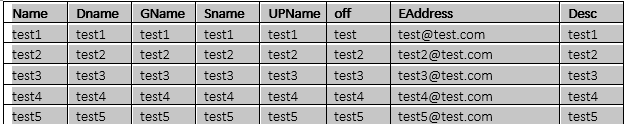
Sample Input:
Output:
Example #2
Input:
Write-Host "Example of adding users to admin group" -ForegroundColor Green
Import-Csv “C:\test\test.csv” | ForEach-Object {
$groupname= $_.Group
$member=$_.Member
Add-LocalGroupMember -Group $groupname -Member $member
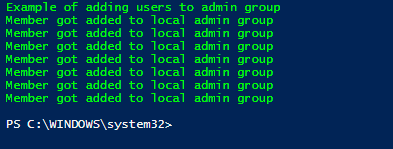
Write-Host "Member got added to local admin group" -ForegroundColor Green
}
Output:
Conclusion
Thus, the article explained in detail about adding users to a local group and an AD group in detail. It explained the cmdlets and their associated parameters in detail, along with appropriate examples. To learn more in detail, it is advisable to write sample scripts and practice them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell add user to group. Here we discuss adding users to a local group and an AD group in detail. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –