Updated April 3, 2023
Introduction to Power Function in C
Power Function is a normal function in C which help in calculating the power raised to the base value. It is declared under the “ math.h ” header file in C library. If we have two number in which one is the base number while the other one is an exponent. POW() function is used to calculate the value a raised to the power b this means ab. For instance, to calculate the value of ab,Pow() function is used. It is used to compute the power of the numbers as it takes two arguments power value and base value.
Syntax
double pow ( double base, double exponent);Parameters used in Power Functions in C
Below are the parameters mentioned:
- BASE: In the above syntax, base is the floating point base value where as,
- EXPONENT: In the above syntax, exponent is the floating point value.
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main() {
double a = 7.5 ;// assigning values to the declared variables a,b.
double b = 3.0 ;
double power ; // this variable will store the value of power
power = pow (a, b) ; // calling power function for calculation
printf ( " The value of a raised to the power b is : %lf " , power );
return 0 ;
}Output:
![]()
Explanation: In the above code, you can see we have declared 3 variables a, b and power. After that we are calling the power function to calculate the value of a raised to the power b.
Examples to Implement Power Function in C
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Here is the C code to demonstrate the working of Power Functions:
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
double base, value_exponent, value_power ;
printf ( " Please enter the base value to calculate the power: " ) ;
scanf ( " %lf " , &base ) ;
printf ( " \n Please enter the exponent value to calculate the power: " ) ;
scanf ( " %lf " , &value_exponent ) ;
value_power = pow ( base , value_exponent ) ;
printf ( " %.1lf ^ %.1lf = %.2lf " , base , value_exponent , value_power ) ;
return 0 ;
}Output:
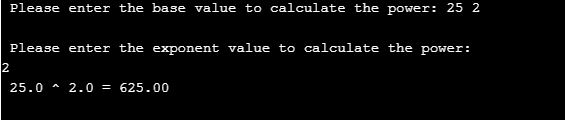
Explanation: As you can see in the above code, we have included math.h file so that we can use the functions of the math library. After that, in the main class, we have declared three double data type parameters. In those parameters, one is the base value, other is exponent value, and the last one is value_power to store the calculated value. Similarly, by using input and output classes we are taking input values from the users and then calculating the Power of the numbers using a Power function.
Example #2
Here is another C code to demonstrate the working of Power Functions:
Code:
#include <stdio.h> // Header files
#include <math.h>
int main ( int argument , const char * argv[] )
{
double temp1 , temp2 ; // temporary variables for taking input from the user
double output ; //temporary variables for output
temp1 = 6 ; // assigning values to the temporary variables
temp2 = 4 ;
output = pow ( temp1 , temp2 ) ;
// temp1 raised to the power of temp2 calculation
// printf to display the final result of calculated power
printf ( " The Output of %f raised to the power of %f is %f \n " , temp1 , temp2 , output ) ;
return 0 ;
}Output:

Explanation: As you can see in the above code, we have declared two temporary variables named as temp1, and temp2 and one more output variable are declared to store the output value. After that, we have assigned value 6 to temp1 whereas 4 to temp 2. Now using the power function we are calculating the value of 6 raised to the power 4 and the displaying the final result through printf method.
Example #3
Here is the C code to demonstrate the working of Power function :
Code:
#include <stdio.h> // Header files
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
int output ;
double output_1 , output_2 , output_3 , output_4 ;
output = pow ( 1 , 2 ) ;
printf ( " \n The output of %d to the power %d = %d " , 1 , 2 , output ) ;
output_1 = pow ( 2 , 3 ) ;
printf ( " \n The output_1 of %d to the power %d = %f " , 2 , 3 , output_1 ) ;
output_2 = pow ( 3 , 4 ) ;
printf ( " \n The output_2 of %d to the power %d = %f " , 3 , 4 , output_2 ) ;
output_3 = pow ( -4 , 5 ) ;
printf ( " \n The output_3 of %d to the power %d = %f " , -4 , 5 , output_3 ) ;
output_4 = pow ( 5 , -6 ) ;
printf ( " \n The output_4 of %d to the power %d = %f " , 5 , -6 , output_4 ) ;
return 0 ;
}Output:
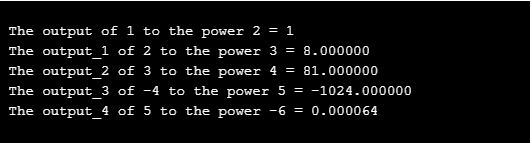
Explanation: In the above code, you can see we have declared five temporary variables to calculate the power named as “output, output_1, output_2, output_3, output_4”. After declaration, we are calling the power function for each and every temporary variable we have declared bypassing the argument value to the power function. We are also displaying the result of power values side by side using a print method of c. As in the output you can see all the results with raise power to the specified base value.
Conclusion
power function in C plays a crucial role in the complex as well as large mathematic calculations in quick time duration. Write the syntax and pass the value as arguments and rest will be done by power function irrespective of values as it can calculate positive and negative numbers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Power Function in C. Here we discuss an introduction to Power Function in C, syntax, examples for better understanding. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


