Updated May 29, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL TO_DATE()
PostgreSQL TO_DATE() function is used to convert a literal string into a date value; the to_date function will convert the string into a date. We have given two input parameter arguments with the to_date function in PostgreSQL, i.e., text and format; the to_date function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL to convert the string into a date value. To_date function returns the date from the function as we have provided input parameters from the to_date function in PostgreSQL. We use the to_date function to handle input formats that simple casting cannot convert. This function interprets input with minimal error checking.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of the to_date function in PostgreSQL.
- to_date (text, format)OR
- to_date (text, text)OR
- to_date (string, format)
Below is the parameter description syntax of the to_date function in PostgreSQL.
- to_date – We use the to_date function to convert a date represented as a character string to a date data type.
- Text –Text is the first parameter accepted by the to_date function in PostgreSQL. Text is a string argument, which we have converted into the date.
- Format –The second argument is the input format of the to_date function, which returns the date value. It will define the input string format in the form of date parts.
- String – We define the string argument as the string we converted into the date. We have also defined a string as text in the to_date function.
Working of PostgreSQL TO_DATE() function
- Below is the working of the to_date function in PostgreSQL.
- The main use of the to_date function in PostgreSQL is to convert the string lateral into the date; the to_date function is used to convert the string into date format.
- We have pass two arguments with the to_date function in PostgreSQL, i.e., string and format.
- We can format the date value using the to_date function in PostgreSQL as follows.
Patterns for formatting date values using the to_date function in PostgreSQL.
- Y,YYY – We define this as a four-digit year separated by a comma after the first two digits.
- YYYY – This format will define as the year in four digits. We have not used any string to divide the year.
- YYY – This format will define the last three digits of the year.
- YY – This format will define the last two digits of the year.
- Y – This format will define the last one digits of the year.
- IYYY – This is defined as the ISO numbering of the year. It will display the last four or more digits as output.
- IYY –This format of ISO numbering will define the last three digits of the week numbering year.
- IY – This format of ISO numbering will define the last two digits of the week numbering year.
- I – It will define the last digit of the ISO 8601 week numbering year.
- MONTH – Used to specify the uppercase version of the English month name.
- Month – We define this as a fully capitalized English month name.
- month – Define this as a fully lowercase English month name.
- MON –This is an abbreviated uppercase English month name, i.e., JAN, FEB.
- Mon – An abbreviated capitalized English month name, i.e., Jan, Feb.
- mon – This is an abbreviated lowercase English month name, i.e., Jan, feb.
- MM – We define this as the month number, ranging from 0 to 12.
- DAY – Define this as a day name in full uppercase.
- Day – We define this as a day name in fully capitalized form.
- day – We define this as the day name in fully lowercase form.
- DY – It is an abbreviated uppercase day name.
- Dy – We define this as a capitalized abbreviated day name.
- dy – An abbreviated lowercase day name.
- DDD – We define this as the day of the year, ranging from 000 to 366.
- DD – We define this as the day of the month, ranging from 01 to 31.
- D – We define the day of the week with Sunday represented as 1 and Saturday represented as 7.
- We can convert the date using the to_date function as we specified a format; we can use any format as above in the to_date function.
- If suppose we have to convert the string as 2020 May 20 into a date value, we can use the pattern as “DD Mon YYY” or “YYYY Mon dd”.
Examples
Below is an example of the to_date function in PostgreSQL.
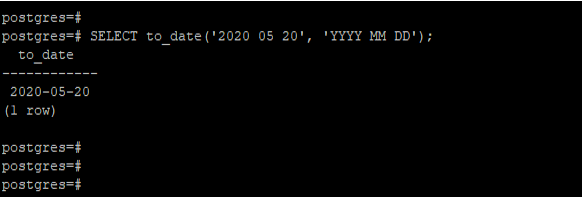
Example #1 – Convert the string using the ‘YYYY MM DD’ format
We have converted the ‘2020 05 20’ date using the ‘YYYY MM DD’ format in the below example.
SELECT to_date('2020 05 20', 'YYYY MM DD');Output:
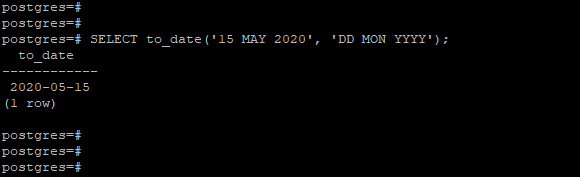
Example #2 – Convert string using the ‘DD MON YYYY’ format
We have converted the ’15 MAY 2020′ date using the ‘DD MON YYYY’ format in the below example.
SELECT to_date('15 MAY 2020', 'DD MON YYYY');Output:
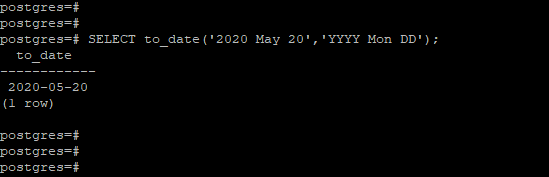
Example #3 – Convert the string using the ‘YYYY Mon DD’ format
In the below example, we have converted the ‘2020 May 20′ date using’YYYY Mon DD’ format.
SELECT to_date('2020 May 20','YYYY Mon DD');Output:
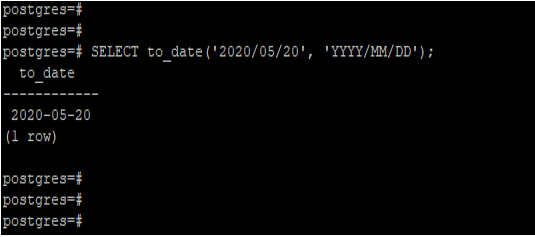
Example #4 – PostgreSQL to_date gotchas
In the below example, we have passed an invalid date string to the to_date function. After passing an invalid date sting, we converted the string into the date format.
SELECT to_date('2020/05/20', 'YYYY/MM/DD');Output:
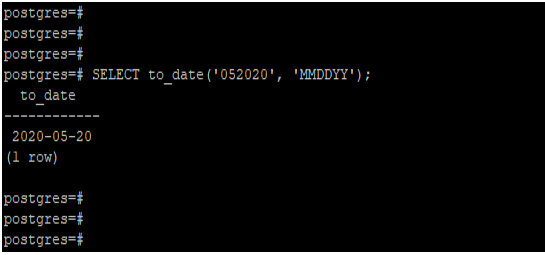
Example #5 – Convert the string using’MMDDYY’ format
We have converted the ‘052020’ date using the ‘MMDDYY’ format in the below example.
SELECT to_date('052020', 'MMDDYY');Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL TO_DATE()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.