Updated May 10, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL Tablespace
The PostgreSQL Tablespaces is a physical location on a drive or disk where the PostgreSQL stores data files containing database objects like indexes and tables etc. PostgreSQL uses it to map logical names to a physical location on a disk or drive.
It has the following two default tablespaces:
- pg_default: Stores all users data.
- pg_global: Stores all global data.
How does Tablespaces work in PostgreSQL?
- The user who executes the CREATE TABLESPACE is the owner of the PostgreSQL tablespace.
- The SQL statement also allows us to assign the ownership of it to a different user by specifying the name in the OWNER clause.
- The path defined under the LOCATION clause is used to create the PostgreSQL tablespace; this path is an absolute path to an empty. In order to read and write data from/to the directory, the system user must own this directory.
How to create Tablespaces in PostgreSQL?
Let’s illustrate the following syntax for creating a new tablespace:
Syntax:
CREATE TABLESPACE tablespace_name
OWNER user_name
LOCATION directory_path;Explanation:
1. tablespace_name
The name of the PostgreSQL tablespace to create a new PostgreSQL tablespace. We can not define the name which begins with pg_; the names starting with pg_ are reserved for PostgreSQL system tablespaces.
2. user_name
The name defined is the user who will own the newly created PostgreSQL tablespace. If the user_name is not specified when creating a new PostgreSQL tablespace, then the user who executes the statement will become the owner of the new Tablespace. Only superusers can create this Tablespace, but they can assign ownership of the Tablespace to non-superusers.
3. directory_path
It will use the directory defined under the LOCATION clause. The directory path should be defined as an absolute path. Also, the defined directory should be owned by the user and must be empty.
Let’s have a look at the following snapshot showing default tablespaces:
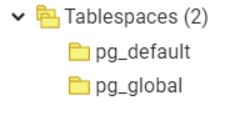
The following example will create a tablespace named ‘edutablespace’ at a specified location.
CREATE TABLESPACE edutablespace
OWNER postgres
LOCATION 'C:\MyFolder\Articles\Tablespaces';Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
<img class=”alignnone size-medium wp-image-321346″ src=”https://www.educba.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/PostgreSQL-Tablespaces-2-300×133.jpg” alt=”PostgreSQL Tablespaces 2″ width=”300″ height=”133″ /
How to Alter Tablespaces in PostgreSQL?
To perform some alter operations on Tablespace using the ALTER TABLESPACE statement, you should be a superuser or the owner of it. We can not change the location used by Tablespace as it’s not supported by PostgreSQL yet.
Consider we have a tablespace that is created, and we want to change the tablespace definition with the help of the ALTER TABLESPACE as follows:
ALTER TABLESPACE action;Explanation:
Action:
It allows us to perform some actions like renaming the tablespace name, changing the tablespacehe own, and settinget some tablespace parameters.
1. To modify the tablespace name, we use the following statement:
ALTER TABLESPACE tablespace_name RENAME TO new_name;The following statement renames edutablespace Tablespace to edutablespace_new:
ALTER TABLESPACE edutablespace RENAME TO edutablespace_new;Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
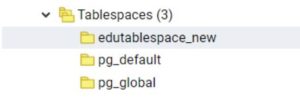
2. To modify the tablespace owner, we use the following statement:
ALTER TABLESPACE tablespace_name OWNER TO new_owner;Currently, the owner of the edutablespace_new is Postgres have a look at the following snapshot
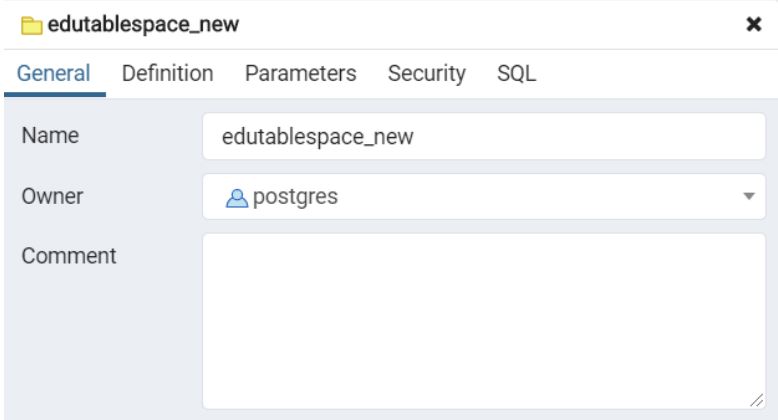
The following statement changes the owner of the edutablespace_new Tablespace to ‘educba.’
ALTER TABLESPACE edutablespace_new OWNER to educba;Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
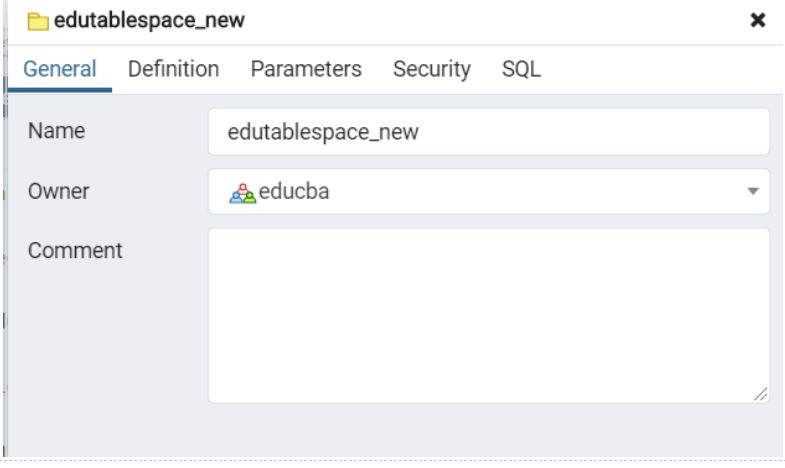
3. Modify the parameters of the Tablespace.
ALTER TABLESPACE tablespace_name SET parameter = value;How to delete Tablespaces in PostgreSQL?
In order to remove it, you should be the owner or the superuser.
Consider the following syntax:
DROP TABLESPACE IF EXISTS tablespace_name;Explanation:
Define the name of it after the DROP TABLESPACE clause.
The IF EXISTS helps us to prevent the error of deleting a non-existent tablespace.
We need to ensure the Tablespace is empty before removing it, which means verifying no database objects are inside the Tablespace.
DROP TABLESPACE edutablespace_new;The above statement will drop the edutablespace_new Tablespace.
Conclusion
We hope from the above article, you have learned how to create a tablespace using CREATE TABLESPACE statement and change the Tablespace’s definition with the PostgreSQL ALTER help TABLESPACE statement.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Tablespaces” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

