Updated May 25, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Superuser
PostgreSQL provides the facility to create different types of user roles like user and superuser. The superuser is a system account with high-level privileges beyond other users. Superuser has direct access to any data or user. There is no need to take permission to access data. A superuser is useful for controlling management-related functions, but it is necessary to control them; otherwise, it can make some changes in data. The superuser is not a good option when considering security issues because it controls all access controls. When we create a user at that time, we assign a different role to the user.
Syntax
alter user user name with super;Explanation
In the above syntax, we use alter user statements to alter the user’s role. For example, where the username is a specified user name, the keyword super is the role we want to assign.
How does superuser work in PostgreSql?
- We must install PostgreSql in your system.
- Required basic knowledge about PostgreSql.
- We need basic knowledge about user management, which means how it is used.
PostgreSql provides a facility to manage database access permission using the different privileges of the user. It bypasses all permission as follows.
- create db: In creating a db, the user can create a database.
- create a role: In creating roles, the user assigns roles to other users using this privilege.
- Login: In login, PostgreSQL provides a facility to do user login.
- Password: With the help of a password, we secure user data and the user environment.
PostgreSQL provides some Meta commands for users to perform different activities on the psql terminal.
How to check the current user through PSQL?
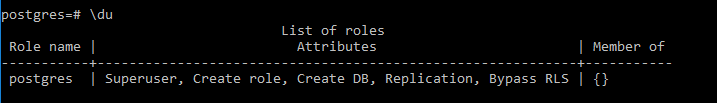
\duSuppose we need to check the existing user role when we use the above command. Then, illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Explanation
Postgres is a user role or name in the above snapshot and is, by default, a superuser.
Let’s see how we can create a superuser using the above syntax in pgAdmin.
Command:
Create user john with superuser;Explanation
In the above example, we create a user statement to create a user, where John is the specified user name, with the keyword, and superuser is the user’s role, which we want to assign. Next, illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Let’s see how we can create a superuser with different privilege
Syntax
create role role name with superuser option;Explanation
In the above syntax, we use the create role statement to create a user. The create a role statement is equivalent to creating a user. Role name is a specified user name, superuser is the role of the user we want to assign, and the option is used to assign different privileges to the user.
Example
CREATE ROLE john WITH LOGIN SUPERUSER
CREATEDB CREATEROLE INHERIT NOREPLICATION
CONNECTION LIMIT -10 VALID UNTIL '2020-08-08T22:28:08-07:00'
PASSWORD '123';Explanation
In the above example, we use a create role statement to create a user. In this example, we created a John user with it who has a different privilege. First, we assign a superuser role to John users; we also permit creating a database, logging in, creating a role, etc. We also provide a connection limit and password with a valid password date. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Suppose we have an existing user and want to change the user’s role, which means we assign the superuser roles to specific users; at that time, we use the following syntax. Using the following syntax, let’s see how to assign superuser roles to existing users.
Syntax
alter user user name with superuser;Explanation
In the above syntax, we use alter user statements to alter the role of existing users, where username is used to a specific user name, with is a keyword, and superuser is the role of the user we want to assign.
Example
alter user Sam with superuser;In the above example, Sam is an existing user, and suppose we need to change the role of Sam user at that time, we use the above statement where we use alter user statements, which is a keyword, and superuser is the user’s role. Next, illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Revoke the superuser role in PostgreSQL.
In this method, we revoke the user role. For example, suppose we need to revoke the superuser role, then; we use the following syntax.
Syntax
alter user user name nosuperuser;Explanation
In the above syntax, we alter the user statement to revoke the superuser role where the user name is specified, and nosuperuser is used to revoke the role.
Command:
alter user sam with nosuperuser;Explanation
In the above example, we revoke the superuser role of the same user. Next, illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Drop superuser
Due to security purposes, suppose we need to drop the superuser at that time, we use the following syntax.
Syntax
drop user user name;Explanation
In the above syntax, we use drop user statements to delete the superuser, where the user name means the specified user name we want to delete.
Command:
drop user Sam;Explanation
In the above example, Sam is a superuser. Where we use drop user statements to delete Sam users. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Conclusion
We hope from this article; you understand the PostgreSQL superuser role of users. Superuser has all access permissions. Therefore, considering a security point of view superuser is not a good option. We have learned the basic syntax of altering a superuser, creating a superuser, and deleting a superuser from the above article. We have also learned how to implement them in PostgreSQL with different examples of each type. Finally, this article taught us how to handle superusers in PostgreSQL on the server.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Superuser” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.