Updated May 25, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL String Contains
PostgreSQL provides a pattern-matching function to the user, which we also call String Contains (LIKE operator). Pattern matching means retrieving specific data or records from the database table using different methods. String Contains play a very important role in database management systems because we store huge amounts of data and need to retrieve specific data in minimum time. At that time, we could not read all the data line by line because it was time-consuming. So the best solution for this problem is String Contains means pattern-matching functions such as like operator.
Syntax:
select column name1 column name2
from specified table name where
specified column name like 'matching pattern';Explanation: In the above syntax, we implement a pattern-like matching function by using the select, and where clause where column name is specified column name in the table, table name means specified table name.
Working of PostgreSQL String Contains Function with Examples
- We must install PostgreSQL in your system.
- We required basic knowledge about PostgreSql.
- Must require tables to perform the String Contain operation.
- The like operator serves as a logical operator in order to match specified matching patterns.
Pattern matching we can implement by using different methods as follows. In a matching pattern function, we use the like operator to find the desired matching pattern from the database table.
So first, we create a table by using the following statement.
CREATE TABLE emp_info (
emp_id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
emp_name TEXT NOT NULL,
emp_age INT NOT NULL,
address CHAR(50),
salary REAL);Now we will be inserting values into the table.
insert into emp_info (emp_id, emp_name, emp_age, address, salary) values
(1,'Poll',28,'london',30000),
(2,'Alex',30,'Hongkong',40000),
(3,'John',35,'Newyork',50000),
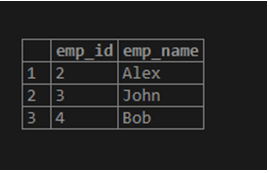
(4,'Bob',32,'Sydney',20000);For selecting the table emp_info, we will use the following:
select * from emp_info;Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Now see how we can use a like operator to find the matching pattern using the below methods.
1. LIKE
Suppose we need to find out the employee’s name; you do not remember her exact name. But you remember the first two characters like bo. So how can we find the exact name of an employee? You may find names in emp_info tables, but it is time-consuming. So you can use the like an operator that PostgreSQL provides.
Like operator uses two signs below
- %(Percentage sign): This sign matches any sequence of characters; the character size may be zero or more.
- _(Underscore sign): This sign is used to match any single character.
Example
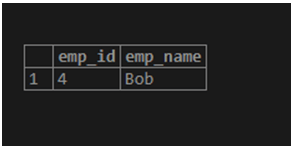
Consider the above example. We need to find out the employee’s name, and you do not remember the exact name of the employee, but you remember the first two characters, for example, bo. Let’s see how it works. We use the following statement to find out employee names like bo.
select emp_id, emp_name from
emp_info where emp_name like 'bo%';Explanation: With the help of the above statement, we find those names start with ‘bo’ characters which we use to select and where clause to implement the above statement, and we return two-column emp_id and emp_name. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
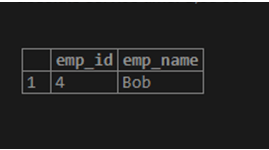
Consider another example, suppose we need to find those employee names that end with an ex. By using the following syntax, we return the ex character.
Syntax:
Like '%ex'Let’s see the example, consider the following statement.
Select emp_id, emp_name from
emp_info where emp_name like '%ex';Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
We can combine percentage and underscore signs to get the desired pattern
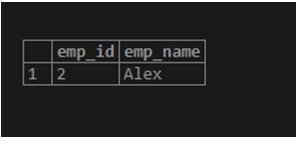
Considering the above example, we need to find Alex’s employee name, and we know the last three characters, like lex. So you can use % sign to find out Alex’s employee but also use % and _ sign to find out ales user.
Select emp_id, emp_name from
emp_info where emp_name like '_oll%';Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
2. NOT LIKE
This operator is totally opposite from like. Let’s see how it works.
Example
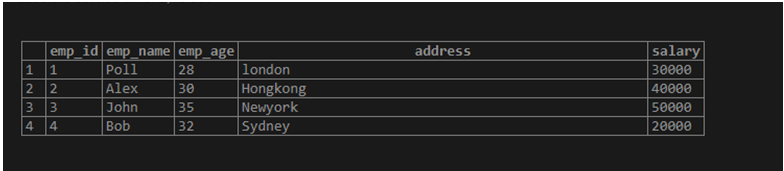
Suppose we need to find all employees whose names do not start with po. Use the following statement to implement not like operator.
Select emp_id, emp_name from
emp_info where emp_name not like 'po%' ;Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the following snapshot.
3. ILIKE
The ilike operator in PostgreSQL is used for case-insensitive conditions.
Example
Suppose we need to find out bob employee name, and we do not know bob character is a capital letter or a small letter. That time we used the ILIKE operator. See the following statement to implement the ILIKE operator.
select emp_id, emp_name from
emp_info where emp_name ilike 'BOB%';The BOB% pattern matches any string beginning with BOB, Bob, and bob. But if you use only like operators, it does not return any row. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Let’s see what happens when we use only the like operator in the same statement.
select emp_id, emp_name from
emp_info where emp_name like 'BOB%';Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot. In the output, it will display nothing, as mentioned above.
PostgreSQL also provides similar operators with like, ilike, not like, and not like, as shown in the table below.
| Operator Name | Substitute with Description |
| ~~ | It is used instead of like |
| ~~* | It is used instead of ilike |
| !~~ | It is used instead of not like |
| !~~* | It is used instead of not ilike |
Advantages
Some of the advantages are given below:
- The like operator finds or retrieves data based on specified matching patterns.
- % (wildcard) is used to get all characters.
- % It is used to retrieve one or more characters from the database
- _ (Underscore) is used to match any number of single characters.
- It is a time-saving process instead of searching the whole table manually.
Conclusion
We hope you understand the PostgreSQL String Contain statement from this article. From the above article, we learn the basic syntax of LIKE operator statements and how we can implement LIKE operators using different methods with multiple examples. From this article, we know how we can handle different LIKE operators.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL String Contains” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.