Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Show Databases
The PostgreSQL provides a show database command. The PostgreSQL Show Databases command is used to see how many databases are present on the server, and this command works on the command line tool psql as well as the query tool in pgadmin4, this is the most common task of the administrator. PostgreSQL, in which single progres(by default database) can store multiple databases, and each database stores a set of files. The PostgreSQL provides different kinds of features to users, like creating a database, drop database and show database, etc.
Psql provides the facility to connect the server and execute a different query against the server. MySQL uses the show databases command to show database, but the show database statement does not work directly in PostgreSQL, it provides some different meta-commands to show database and different query statement.
Syntax of PostgreSQL Show Databases
Given below is the syntax:
\l or \listExplanation:
- In the above syntax, where \l is used to list all database lists from the server and the same database list, we can get by using another syntax \list.
- The function of both syntaxes is the same. It is a Meta command we directly perform on the terminal.
select datname from pg_database;Explanation:
- The catalog stores all databases in the above syntax, where datname is used to show available databases from pg_database by default.
How does Show Databases Statement work in PostgreSQL?
Before going to see how to show database statement works, we need some prerequisites as follows:
- First, you must install PostgreSQL on your system.
- Use the below command to check whether PostgreSQL is working correctly or not. If the status is active, that means PostgreSQL is installed successfully.
Code:
service postgresql status- Also, install the psql command-line PostgreSQL interface.
- Multiple databases are available to users but can be accessed when a connection is established between client and server.
- Users perform different operations on databases with the help of show database commands by using like operators.
Show Database Statement as follows:
Code:
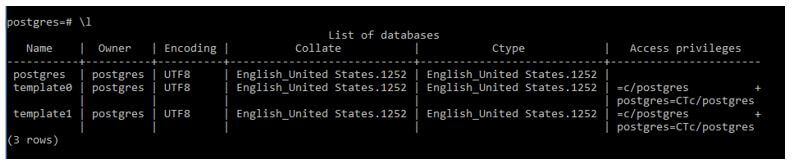
\lThis is Meta Command. It is used for the listing of the database for the PostgreSQL database.
Output:
The above screen snapshot, it lists all databases that are present on the server.
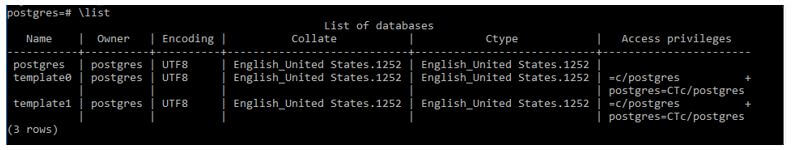
Code:
\listThis is also Meta Command, the function of \List is the same as \l.
Output:
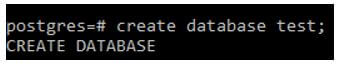
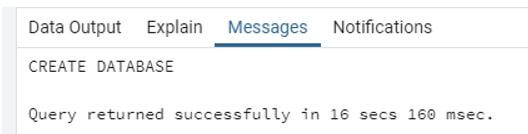
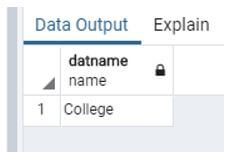
We create a database by using the following statement.
Code:
create database test;Output:
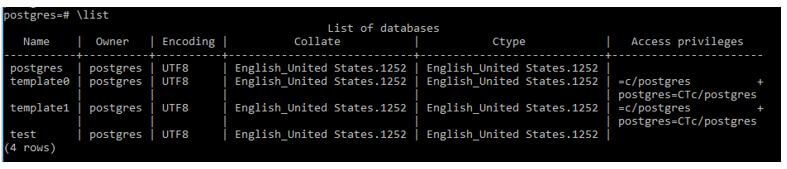
Then use \list Meta Command to see the database.
Code:
\listOutput:
We can also show database by using the PostgreSQL query:
Example #1
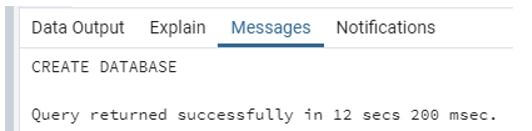
First, we create a database with a name demo.
Code:
create database demo;Output:
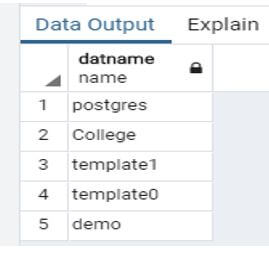
After we perform the show database query as follows:
Code:
select datname from pg_database;Output:
The created database demo shows the fifth number in the above snapshot.
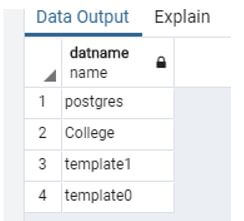
Another example of a database is before creating a new database, we need to see how many databases may be available on the server then, so we use the following query.
Code:
select datname from pg_database;Output:
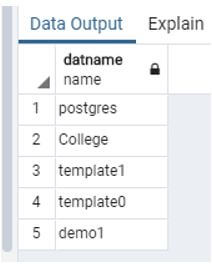
The above snapshot shows 3 by default databases like, Postgres, template1, template, and college is, a user-created database.
Example #2
PostgreSQl provides the facility to create a database with the owner.
Code:
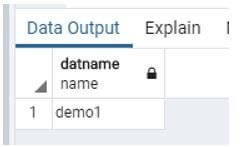
create database demo1 with owner =pg_monitor;In the above statement, we use a create a statement to create a database, and we created a demo1 database with owner pg_monitor.
Output:
Now see the database column demo1 is created.
Code:
select datname from pg_database;Output:
Example #3
In PostgreSQL, by default database is Postgres, but different users created several databases, and we need only to see those names start with d characters. PostgreSQL provides such a facility.
Code:
Select datname from pg_database
where datname like 'd%';Explanation:
- In the above statement, we find all databases whose names start with d using the like operator.
Output:
Let’s see another situation: suppose we need a database whose name ends with e.
Code:
select datname from pg_database
where datname like '%e';In the above statement where datname is the database name, pg_database by default database of PostgreSQL, here we use the like operator to show the database.
Output:
Example #4
Suppose in our server number of databases is present, and we don’t want to see those database names start with t.
Code:
select datname from pg_database
where datname not like 't%';Explanation:
- In the above statement, we use not like operators to get the desired result.
Output:
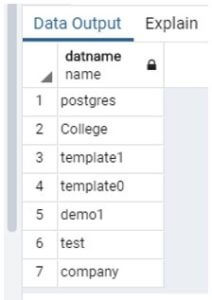
Before the Execution of the above statement, the result is shown in the snapshot.
After the Execution of the above statement, the result is shown in the snapshot.
The above snapshot discards the database name that starts with a t character.
Conclusion
From the above article, we also saw the show database Meta command as we implemented the show database using query statements. In a query statement, we use a like operator to perform a smooth search on the database means that as per our requirement, we perform the show database. Finally, it is a time-saving process in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Show Databases” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.