Updated May 12, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Select
According to our requirements, one of the most important purposes of any database is to store the data so that it can be retrieved and fetched whenever we want. Users mostly use the retrieved records for reporting and analysis or sometimes to modify existing results. You use the SELECT clause in the PostgreSQL database to fetch the data. We can retrieve the results from zero, one, or more tables using the select clause. This article will learn how to use the select clause to build the query statements, their Syntax, and examples to understand query building in PostgreSQL better.
Syntax of PostgreSQL Select
Below is the Syntax of postgresql select:
Syntax:
SELECT [ ALL | DISTINCT | DISTINCT ON (column_or_expression) ]
columns_or_expressions
FROM tables
[WHERE conditional_restrictions]
[GROUP BY column_or_expression]
[HAVING conditional_restrictions]
[ORDER BY column_or_expression [ ASC | DESC | USING operator ] [ NULLS FIRST | NULLS LAST ]]
[LIMIT [ row_count | ALL]
[OFFSET value_of_offset [ ROW | ROWS ]]
[FETCH { FIRST | NEXT } [ rows_to_be_fetched ] { ROW | ROWS } ONLY]
[FOR { UPDATE | SHARE } OF table [ NOWAIT ]];The select clause’s Syntax is very complex and involves many possible combinations to provide flexibility to the user. We will learn the Syntax by learning all the above-used clauses with the select clause.
- ALL: To retrieve all the records that the query will fetch after applying all the conditions, restrictions, and expressions.
- DISTINCT: To retrieve only unique values of the column and expression from the retrieved results and further filter out the unique entries with respect to the column or expression mentioned in the distinct parameter.
- columns_or_expressions: This is the list of the column names or expressions that you wish to retrieve using the select query.
- FROM: This keyword helps specify the name of the table from which you wish to retrieve the records. Further, we can use joins of the type left join, right join, natural join, etc., to combine the results of two or more tables while retrieving the records.
- WHERE: This clause helps specify the conditions, restrictions, and expressions to filter out the results while retrieving the records in the select query.
- GROUP BY: You can group the result set based on a specific column or expression using the group by statement. People most frequently use this when retrieving manipulated columns with aggregate functions, such as the sum or product of certain columns.
- HAVING: You can further filter the result by applying conditions and restrictions to the retrieved columns and expressions, including any aggregated values used in the retrieval process.
- ORDER BY: You can arrange the result set in an orderly format based on specific columns and expressions by specifying them after the ORDER BY keyword. We can arrange the data in ascending or descending order by using ASC or DESC keyword.
- LIMIT: You can limit the number of rows retrieved by using the limit keyword. For example, if the query result would have resulted in 55 records and after applying the limit of 10 statements in the select query, only the first 10 records will be retrieved.
- OFFSET: This is the number of the row from which you want to begin retrieving the records. For example, if you specify the offset as 5, the result’s rows will be retrieved starting from the 5th record.
- FETCH: Like the limit keyword, this function restricts the number of records that can be retrieved to a specific number.
- FOR: The records can be restricted for access and are write-locked if FOR UPDATE is specifies and is allowed for reading operation but not update and insert operations by other transactions when FOR SHARE is specified.
Except for FROM, all other clauses/keywords used in the above select clause syntax are optional in nature.
Examples of PostgreSQL Select
Following are the examples of postgresql select:
Let us create one example and insert a few records in the table to learn how to use a select clause to retrieve the records. Open your PostgreSQL command-line prompt and enter the following command to create a table named educba –
CREATE TABLE educba
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
technologies VARCHAR,
workforce INTEGER,
address VARCHAR);
Let us insert some values in the educba table using the following statement –
INSERT INTO educba VALUES (1,'java',20,'satara'),(2,'javascript',30,'mumbai'),(3,'java',20,'satara'),(4,'psql',30,'mumbai'),(5,'mysql',20,'satara'),(6,'maven',30,'mumbai'),(7,'hibernate',20,'satara'),(8,'spring',30,'mumbai'),(9,'angular',20,'satara'),(10,'html',30,'mumbai'),(11,'css',20,'satara'),(12,'reddis',30,'mumbai');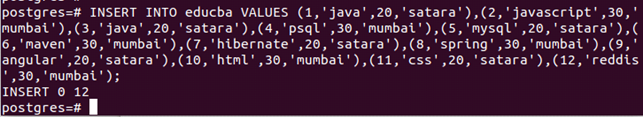
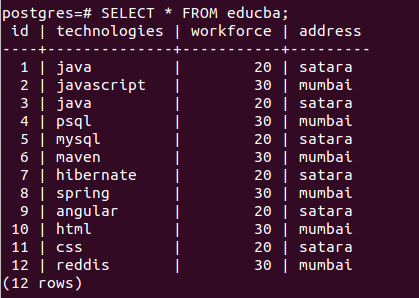
Let us create a simple select query statement to retrieve all the records from the educba table. Our query statement will be as follows:
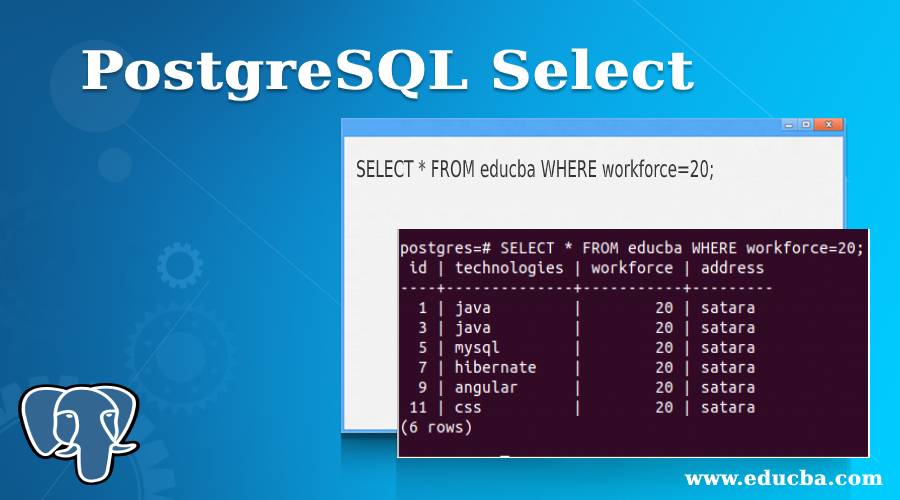
SELECT * FROM educba;Here, * represents all the columns to be retrieved, and firing the above query results in the following output –
Now we will apply the conditions using the where clause and retrieve only records with a workforce of 20 persons. For this, we will have to mention the condition as workforce = 20 in the where clause, and our query statement will be as follows –
SELECT * FROM educba WHERE workforce=20;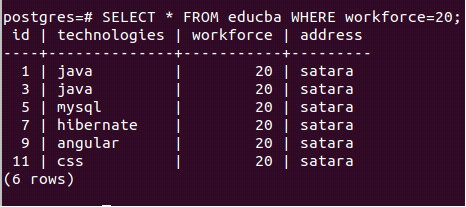
Now, suppose we only want to retrieve the list of name of technologies with the workforce as 20, then the query statement will be as follows –
SELECT technologies FROM educba WHERE workforce=20;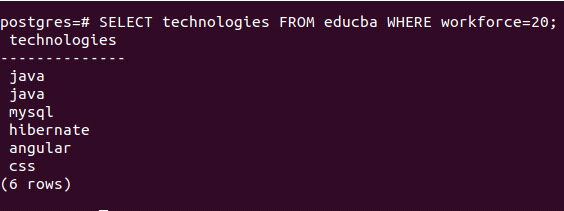
Let us see how we can group the result based on workforce count and retrieve the technologies’ comma-separated string. For this, the query statement will be as follows:
SELECT string_agg(technologies,','), workforce FROM educba GROUP BY workforce;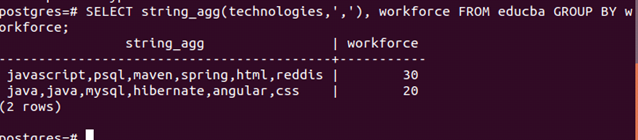
Suppose that instead of retrieving the column head as string_agg, we can give the alias for the same using the “as” keyword as follows:
SELECT string_agg(technologies,',') as "List Of Technologies", workforce FROM educba GROUP BY workforce;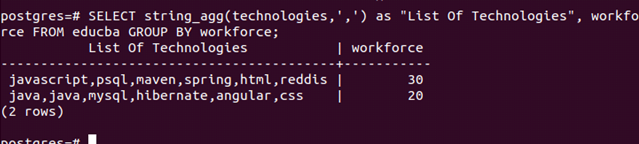
Let us order the results alphabetically based on the technology’s name and limit the records to only 7 by using the limit clause. Our query statement will be as follows –
SELECT * FROM educba ORDER BY technologies ASC LIMIT 7;
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Select” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

