Updated May 9, 2023

Definition of PostgreSQL NOT NULL
PostgreSQL provides us with the NOT NULL constraint; by using NOT NULL, we can ensure that the columns in which we have mentioned the NOT NULL constraint do not accept any NULL value. The NULL keyword defines the information is missing or unknown as per the database theory. The meaning of a NULL value differs from a value zero or an empty string. Consider a scenario where we have a student information details, and if we don’t know the student’s mobile number, then we use the value as NULL while inserting the mobile number information in student information details, which shows that while inserting mobile number information in student details the information is unknown. If the student is not using a mobile phone and not having a mobile number, then we can use the empty string instead.
Syntax:
column_name data-type NOT NULLExplanation: The column_name on which the NOT NULL constraint is defined will not allow NULL values to get inserted
How NOT NULL Works in PostgreSQL?
- The PostgreSQL NOT NULL constraint is syntactically used after the column’s data-type, which causes to rejection of a NULL value to get inserted if the column does not have the NOT NULL constraint defined on it the NULL values to get inserted.
- To check whether the given value is NULL or not, we have to use the boolean operator IS NOT NULL or IS NULL. We will get the result as NULL if we compare the NULL = NULL expression.
- The meaning of the NOT NULL constraint is while performing INSERT or UPDATE operation on the table; we should have a value that is not equal to the NULL value.
- The NOT NULL constraint is used with the column so-termed as a column constraint, not a table constraint.
- In PostgreSQL, the column can have multiple constraints defined on it, which means that a column may have different constraints along with NOT NULL constraints.
Examples to Implement NOT NULL in PostgreSQL
We will go through the following examples one by one to understand the PostgreSQL NOT NULL constraint in detail.
1. Add NOT-NULL Constraint on Columns during Table Creation
We will create a table of name products that will have a NOT-NULL constraint added on some columns. Consider the following CREATE TABLE statement to create a new table name products with a not-null constraint.
CREATE TABLE products(
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
price numeric NOT NULL
);We have used the NOT NULL keyword after the data-type of the column to define the NOT NULL constraint. In PostgreSQL, we can have multiple constraints on a single like NOT NULL, FOREIGN KEY, UNIQUE, and CHECK defined one after the other. The order of the constraint definition is not important.
We will insert some acceptable values in the products table using the INSERT INTO statement.
INSERT INTO products(name, price)
VALUES ('Chair', 2000);Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
SELECT * FROM products;Output:
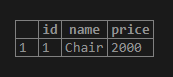
Now, we will try to insert some NULL values in the products table using the following INSERT INTO statement.
INSERT INTO products(name, price)
VALUES ('Chair', NULL);As you can see, we are trying to insert a NULL value in price, which violates the constraint added on the price column, so we will get the following exception as an output.
Output:
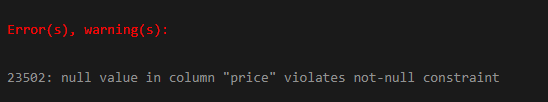
2. Add NOT-NULL Constraint on Columns which are Already Exist
We can use the ALTER TABLE statement to add the NOT NULL constraints on the columns of the existing tables as follows:
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ALTER COLUMN col_name SET NOT NULL;We can update the multiple columns at the same time to have multiple columns with NOT NULL constraints on an existing table; consider the following syntax for the same:
ALTER TABLE tbl_name
ALTER COLUMN col_name1 SET NOT NULL,
ALTER COLUMN col_name2 SET NOT NULL;Consider the following example where we will create a table product_orders with the following CREATE table statement.
CREATE TABLE product_orders (
product_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
product_desc VARCHAR (40) NOT NULL,
prod_mat_id VARCHAR (16),
prod_quantity NUMERIC,
prod_price NUMERIC
);Now, we will insert some records in the product_orders table by using the following INSERT INTO statement:
INSERT INTO product_orders (product_desc)
VALUES
('Made in India');Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
SELECT * FROM product_orders ;Output:
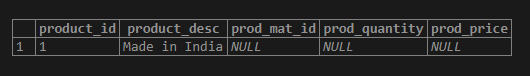
If we want to have the prod_quantity column be NOT NULL, then we can add the not-null constraint to the prod_quantity column by using an ALTER TABLE statement. But the product_orders table is not empty, which throws cause an error if we try to update the table for having a NOT-NULL constraint on the prod_quantity column.
If we execute the following statement on the product_orders table, which is not empty right now, we will get an error as follows:
ALTER TABLE product_orders ALTER COLUMN prod_quantity SET NOT NULL;Output:
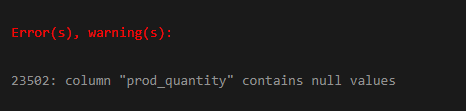
So we have to update the product_orders table first as follows.
UPDATE product_orders SET prod_quantity = 10;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
SELECT * FROM product_orders;Output:
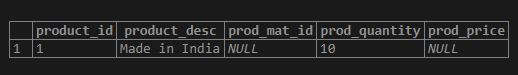
ALTER TABLE product_orders ALTER COLUMN prod_quantity SET NOT NULL;Similarly, we can update the not-null constraints for the prod_mat_id and prod_price columns of the product_orders table. To do the same, we again need to insert some value in both the prod_mat_id and prod_price columns.
UPDATE product_orders
SET prod_mat_id = 'QQQ',
prod_quantity = 10;
prod_price = 3000;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
SELECT * FROM product_orders;Output:
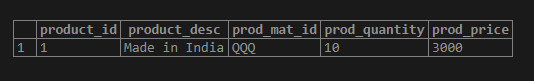
Now we will add NOT NULL constraints to prod_mat_id and prod_price columns using a single statement as follows.
ALTER TABLE product_orders
ALTER COLUMN prod_mat_id SET NOT NULL,
ALTER COLUMN prod_price SET NOT NULL;Now we can make sure that the prod_price column of the product_orders table.
UPDATE product_orders
SET prod_quantity = NULL;Advantages of Using NOT NULL in PostgreSQL
- We can avoid NULL values to get inserted or updated in/to the table by using the PostgreSQL NOT-NULL constraint.
- The PostgreSQL NOT-NULL constraint will cause the table to have data in the column.
- It will always help us insert valid data in the table containing a column with a NOT-NULL constraint.
Conclusion
We hope from the above article, you have understood how to use the PostgreSQL NOT NULL and how the PostgreSQL NOT NULL works. Also, we have added some examples of PostgreSQL NOT NULL to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Not Null” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

