Updated May 15, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL MOD()
The PostgreSQL MOD() function is a mathematical function. The keyword MOD stands for the ‘modulo’, which is used to perform a modulo operation(divide the two number and return the remainder). The remainder of an integer is computed and returned using it. It takes two numbers as an input parameter. It divides the first and second numbers using a formula, then returns the remaining. If the second parameter value is zero, then the MOD() function throws an error or exception, which is the divide by zero error message.
Syntax:
Given below is the syntax:
MOD(p,q)Explanation:
- p: This defines the number whose remainder is to be calculated.
- q: This defines the number which is used to divide into value n.
How does MOD() Function work in PostgreSQL?
- The PostgreSQL MOD() function takes two numbers as input and divides them, and returns the remainder.
- It divides the first parameter by the second parameter and then returns the remainder.
- If we consider the p as the first parameter and q as the second parameter, then the value of the second parameter q should be non-zero (0). If the value of the second parameter q is zero, it throws an error or exception divided by a zero error message.
- The return type is the same as the type of the arguments passed to the function.
- We can use this function with PostgreSQL 8.4, PostgreSQL 9.0, PostgreSQL 9.1, PostgreSQL 9.2, PostgreSQL 9.3, and PostgreSQL 9.4, etc. versions.
- It does not accept non-numeric data type values as input. This will throw an error or exception related to typecasting if we try do use non-numeric values.
Examples
Given below are the examples:
Example #1
First argument value as a positive number
Code:
SELECT MOD(13,2) AS MOD_13_BY_2;Output:
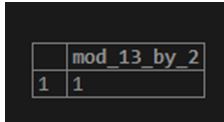
Code:
SELECT MOD(13,-2) AS MOD_13_BY_MIN_2;Output:
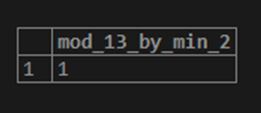
Here we firstly kept the second parameter as a positive value. Secondly, we have kept the second parameter as a negative value, but the result of both examples is the same: the positive remainder.
Example #2
First argument value as a negative number
Code:
SELECT MOD(-13,2) AS MOD_MIN_13_BY_2;Output:
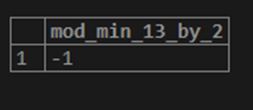
Code:
SELECT MOD(-13,-2) AS MOD_MIN_13_BY_MIN_2;Output:
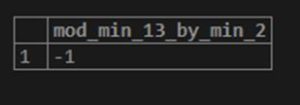
Here we firstly kept the second parameter as a positive value. Secondly, we have kept the second parameter as a negative value, but the result of both examples is the same: the negative remainder.
Example #3
General examples to perform modulo operation.
Code:
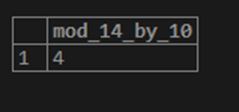
SELECT MOD(14,10) AS MOD_14_BY_10;Output:
Code:
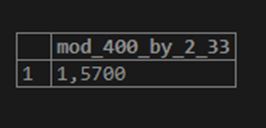
SELECT MOD(400,2.33) AS MOD_400_BY_2_33;Output:
Example #4
Example to illustrate the divide by zero error in modulo operation.
Code:
SELECT MOD(10,0) AS MOD_10_BY_0;Output:
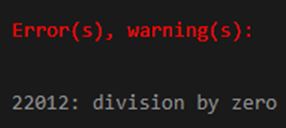
In the above example, we have used the second parameter as zero value, which will throw an error or exception divided by zero error.
Example #5
Example with a non-numeric value as an input. Consider the following example in which we will pass the first and second parameter as in text format.
Code:
SELECT MOD('10','0') AS MOD_10_BY_0;Output:
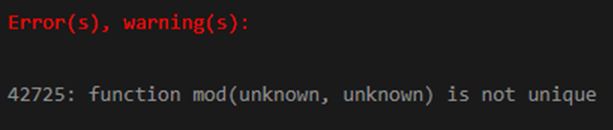
In the above snapshot, we can see that it shows an error message in which the data type of the arguments is unknown and not able to cast them to the numeric value implicitly.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL MOD()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

