Updated May 18, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL MIN() Function
PostgreSQL supports various aggregate functions. The PostgreSQL MIN function is one of them, which is used to return the minimum value from the set of record values. We can use the PostgreSQL MIN function to find the minimum value for the column within the table. We need to pass the name of the column to the PostgreSQL MIN function specified in the SELECT SQL statement. The column we can pass to the PostgreSQL MIN function can have the data types such as string, number, or any other data type which can be compared. We can use the PostgreSQL MIN function with various clauses as well as with other aggregate functions as well.
Syntax:
MIN (* | [DISTINCT] ALL | column_name)Explanation:
- *: This shows all of the rows.
- column_name: This specifies the name of the column.
- DISTINCT: It is used to show uniqueness and is an optional clause.
- ALL: It specifies the default clause, and it is optional.
How does PostgreSQL MIN() Function Work?
- The PostgreSQL MIN function is used for finding the minimum value for the specific column within the table, and it takes the name of the column as a parameter.
- The column we can pass to the PostgreSQL MIN function can have the data types such as string, number, or any other data type which can be compared.
- We can use the PostgreSQL MIN function with various clauses as well as other aggregate functions as well.
Examples
Let’s create a table named ‘furniture’ in order to understand the examples:
CREATE table furniture
(
furniture_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
furniture_name VARCHAR (256) NOT null,
furniture_type VARCHAR (256) NOT null,
furniture_price int NULL
);Now, insert some data in the furniture table in order to execute SQL statements.
INSERT INTO furniture (furniture_name,furniture_type,furniture_price)
VALUES
('Chair','Wood',2500),
('Chair','Plastic',2000),
('Chair','Rexine',3000),
('Table','Wood',5000),
('Table','Plastic',4000),
('Table','Rexine',5500),
('Sofa','Wood',10000),
('Sofa','Plastic',8000),
('Sofa','Rexine',8500),
('Bed','Wood',15000),
('Bed','Plastic',13000),
('Bed','Rexine',14000);Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot and the SELECT statement.
SELECT * FROM furniture;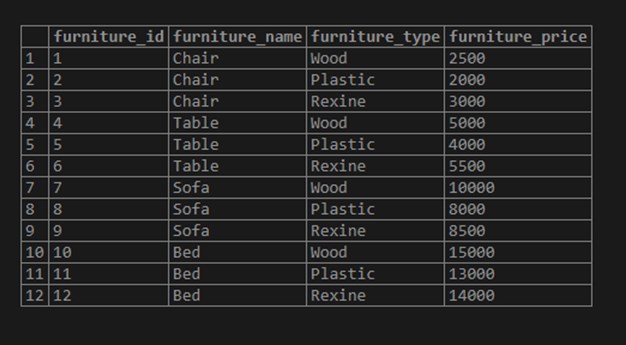
Example #1 – The PostgreSQL MIN() Function as a Level
Consider the following examples, which will show how to get the furniture with the minimum price from a table named ‘furniture’.
We can achieve this by writing a SQL statement in different ways as follows:
SELECT MIN(furniture_price) "Minimum price furniture"
FROM furniture;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot:
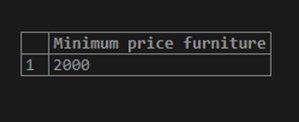
SELECT MIN(DISTINCT furniture_price) "Minimum price furniture"
FROM furniture;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot:

SELECT MIN(ALL furniture_price) "Minimum price furniture"
FROM furniture;Use the image below to demonstrate the outcome of the above statement:

Example #2 – WHERE Clause with the MIN() Function
Consider the following example, which will show how to get the furniture with the minimum price from the table named ‘furniture’ where the name of the furniture is Chair.
SELECT MIN(furniture_price) "Minimum price furniture"
FROM furniture6
WHERE furniture_name='Chair';Use the image below to demonstrate the outcome of the above statement:

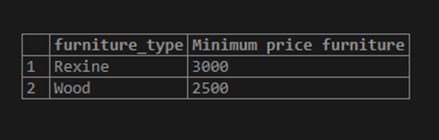
Example #3 – GROUP BY with the MIN() Function
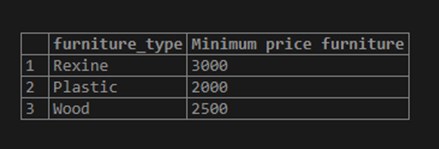
Consider the following example for getting the minimum furniture price for each furniture type from the furniture table.
SELECT furniture_type, MIN(furniture_price) "Minimum price furniture"
FROM furniture
GROUP BY furniture_type;Use the image below to demonstrate the outcome of the above statement:
Example #4 – HAVING CLAUSE with the MIN() Function
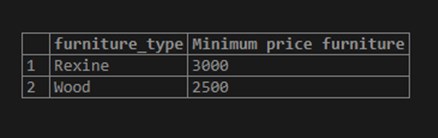
Consider the following example for getting the minimum furniture price for each furniture type whose minimum price is 2500 and below 13000 in the furniture table.
SELECT furniture_type, MIN(furniture_price) "Minimum price furniture"
FROM furniture
WHERE furniture_price < 13000
GROUP BY furniture_type
HAVING MIN(furniture_price) >= 2500;Use the image below to demonstrate the outcome of the above statement:
Example #5 – GROUP BY and ORDER BY with the MIN() Function
Consider the following example for getting the furniture with a minimum furniture price is 2500 and below 13000 and the minimum furniture price for each furniture type as in descending order.
SELECT furniture_type, MIN(furniture_price) "Minimum price furniture"
FROM furniture
WHERE furniture_price < 13000
GROUP BY furniture_type
HAVING MIN(furniture_price) >= 2500
ORDER BY MIN(furniture_price) DESC;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL MIN()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

