Updated May 19, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL Median
PostgreSQL median is defined as find the median value from the column on which we have used median, there is no such built-in function available like median we can implement the same by creating a user-defined function. Also, we can find the median of the column using the percentile_disc (0.5), while using percentile 0.5 will return the median from the PostgreSQL column table. We are using the order by the operator with a column name to find the median value from the table column.
Syntax and Parameter
Below is the syntax of the median in PostgreSQL:
1. Find the median using percentile_disc (0.5)
Select percentile_disc(0.5) (Percentile disc with 0.5 used to find median from the table column.)within group (order by name_of_table.name_of_table);2. Find the median by creating a function and aggregate
SELECT median (We have calling aggregate function with specifying column name) (name_of_column) AS (alias of column name) FROM name_of_table;Parameter:
- Select: We use the “select” operation to retrieve a specified column from the table from which we are calculating the median value.
- Name of the column: This is defined as a column name from which we are retrieving the median value.
- Name of the table: The name of the table refers to the specific table from which we are calculating the median value based on the column name.
- Percentile disc (0.5): We are using percentile_disc (0.5) to find the median from the column. There is no function available like the median, so we are using percentile_disc (0.5) instead of the median.
- Median: This is defined as finding the median from the table column. We have to find the median value on the basis of the column which we have used in the median.
- Alias of column name: This is defined as using another name of a column displayed in the output.
- Within group: The “within group” clause is used to determine the median value from a table column in PostgreSQL.This clause is used to calculate the percentile value from the specified group.
How does Median Work in PostgreSQL?
- The median is the calculated value representing the middle point of a series used in the query. We can also use column name instead of series in PostgreSQL.
- If suppose we have used a series value as an even number, then the median will return the mean of two values as the median in PostgreSQL.
- The median value in PostgreSQL is more representative as compared to the mean value in PostgreSQL.
- If suppose we have used the series value as an odd number, then the median will return the middle value as the median in PostgreSQL.
- The below example shows that if we have used a series value as an odd number, then the median will return the middle value as the median.
- In the below example, the stud1 table contains 11 records, i.e., odd number so the median will return as the 6th number of value from the table.
- We have used the id table to find the median from the column.
select * from stud1;
select percentile_disc(0.5) within group (order by stud1.id) from stud1;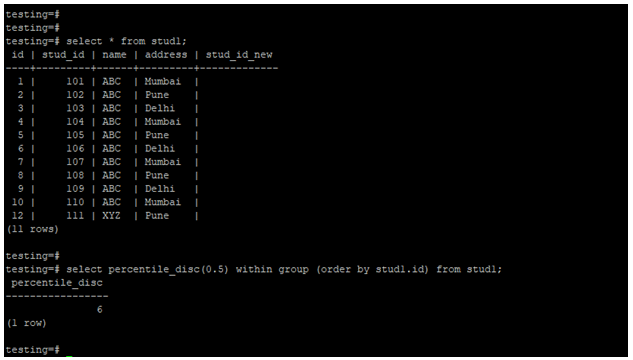
- We create a user-defined median function in PostgreSQL and subsequently use it later.
- While creating a function, it will show the median value in PostgreSQL of an even number of series.
- We can also calculate the median in PostgreSQL by using the 50th percentile value because there is no built-in function available in PostgreSQL to calculate the median.
- We use a within-group clause and order by clause with percentile (0.5). The main use of order by clause in percentile is to sort the value as per order before calculating the median in PostgreSQL.
Examples
Below is an example of the median in PostgreSQL.
We are using the function as median_function1 and aggregate as median_function2 to describe an example of the median in PostgreSQL.
- Below is the structure of aggregate and function.
\sf median_function1
\da+ median_function2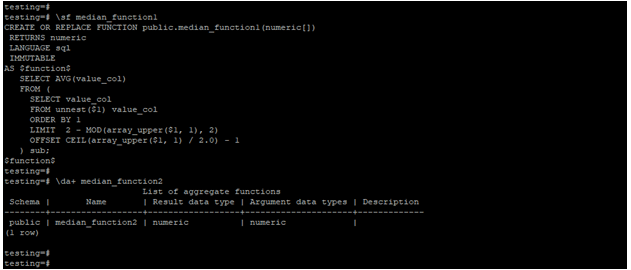
- Also, we are using the median_function table to describe an example of the median. Below is the median_function table and data.
select * from median_function;
\d+ median_function;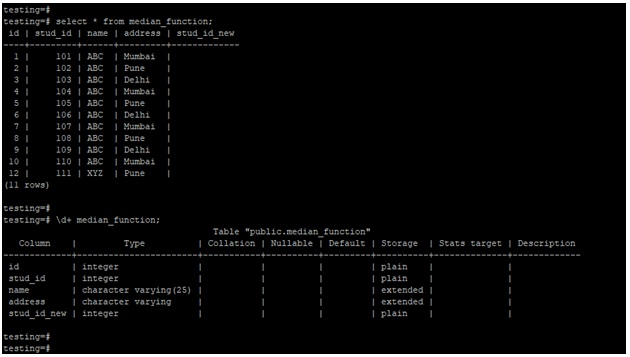
Find the median by creating a function and aggregate.
- The below example shows that find the median by creating a function and aggregate. We have already created a function name as median_function1 and an aggregate name as median_function2.
- We are using the id column with aggregate as median_function2 to find the median from the median_function table.
SELECT median_function2(id) AS median_value_id FROM median_function;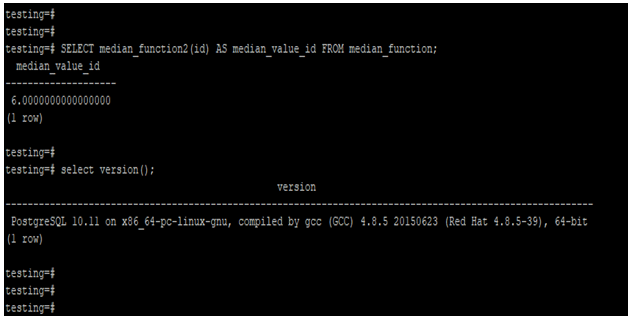
Find the median of even number column values by creating a function and aggregate.
- The below example shows that find the median of even number column values by creating a function and aggregate.
- We are using the function name as median_function1 and the aggregate name as median_function2.
delete from median_function where id = 12;
SELECT median_function2(id) AS median_value_id FROM median_function;
select * from median_function;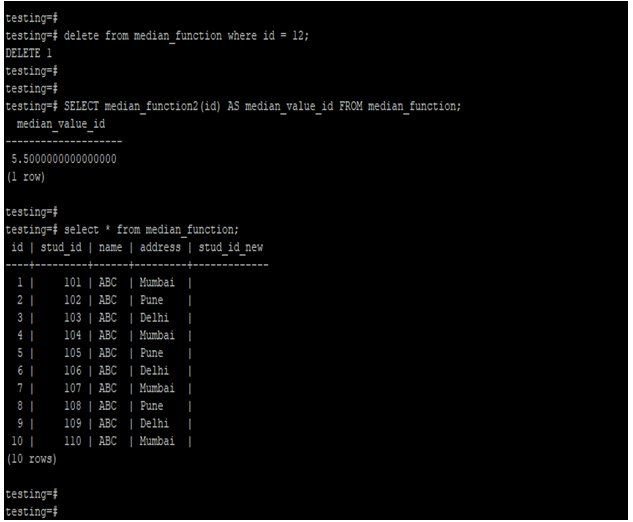
Find the median by using percentile_disc (0.5).
- The example below shows that find the median using percentile_disc (0.5).
- We use the id column to find the median from the median_function table.
insert into median_function values (11, 111, 'ABC', 'Delhi');
select percentile_disc(0.5) within group (order by median_function.id) from median_function;
select * from median_function;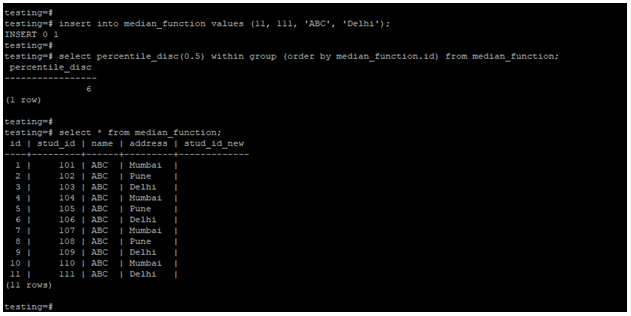
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Median” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

