Updated May 16, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Logical Replication
PostgreSQL logical replication is used to replicate the table from master to slave, we are replicating the specified table using logical replication in PostgreSQL. Feature of PostgreSQL logical replication is started from the version of PostgreSQL 10, before PostgreSQL 10 version, logical replication is not available in PostgreSQL, in the old version, we are using slony replication to replicate specified table in PostgreSQL. We have to replicate specified table data without replicating the whole data of the server.
How PostgreSQL Logical Replication works?
For configuring logical replication, we need to add listen address as the database master private IP address and need to configure the wal level as logical. After configuring this parameter, we need to take restart of PostgreSQL service to effect this parameter. For configuring logical replication, we need to configure publication on master server and subscription on slave server.
Below is the working of publication and subscription.
1. Publication
- In PostgreSQL, we define publication as the publisher node. We can add a specified table to the publication to replicate it on the slave server.
- Publication is also defined as changes made on the master server being reflected on the slave server.
- PostgreSQL logical replication will be different from the other object which was used in PostgreSQL, like schema or database.
- We can create a publication by using create publication command in PostgreSQL.
Below is the syntax of create a publication in PostgreSQL.
Syntax:
create publication publication_name;- In the above syntax, create publication is defined as a command to create a new publication in PostgreSQL.
- Publication name is defined as the name of the publication which we are creating to set up logical replication.
- To create a publication in PostgreSQL, we need to have super user privileges to create it.
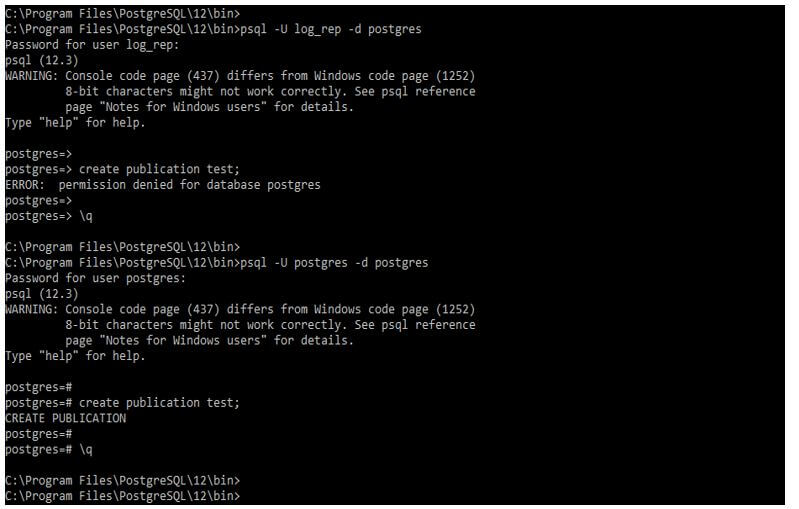
Below example shows that we need to have super user privileges to create a publication.
Code:
psql -U log_rep -d postgres
create publication test;
psql -U postgres -d postgres
create publication test;Output:
- PostgreSQL logical replication publication contains only table which we were replicating from the master to the slave server.
- Insert, update, and delete statement will be replicate from the master server to the slave server.
- When adding a table to a publication, a replica identity will be created for each table.
- After creating one publication on the master server, we can create multiple subscription for one publication.
- We can create multiple PostgreSQL publications to replicate the data on different servers.
2. Subscription
- We have created a subscription on the slave server. Subscription is defined as a subscriber in PostgreSQL.
- Using publication, we can setup a subscription in logical replication. Subscription database or slave server is working the same as other instance of PostgreSQL.
- We can create multiple subscription if required. In logical replication, we can create multiple subscription of a single publication.
- To receive changes from the publication server and apply them to the slave server, use a replication slot.
- In streaming replication, the subscription server is also known as the standby server.
- To create a subscription in PostgreSQL, we need to have super user privileges to create it.
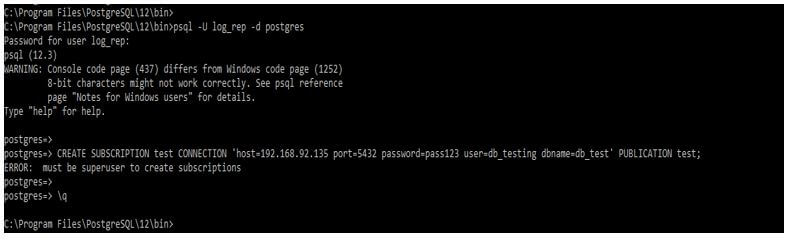
Below example shows that we need super user privileges to create a subscription.
Code:
psql -U log_rep -d postgres
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION test CONNECTION 'host=192.168.92.135 port=5432 password=pass123 user=db_testing dbname=db_test' PUBLICATION test;Output:
Example of PostgreSQL Logical Replication
Given below is the example mentioned:
Below are the steps to create logical replication
Step#1
We are defining the below IP of enslaver and slave.
192.168.92.135 – Master
192.168.92.134 – Slave
Step #2
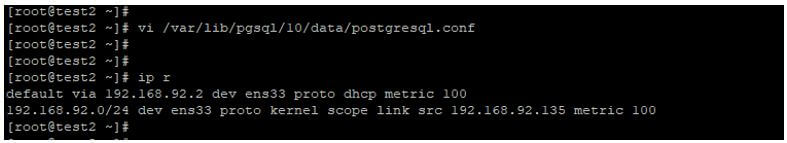
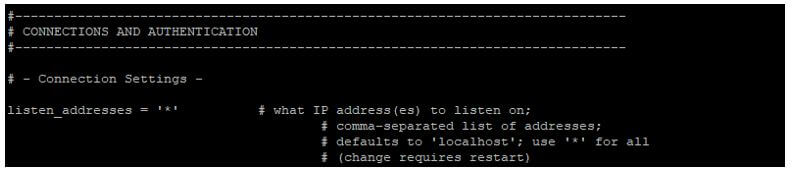
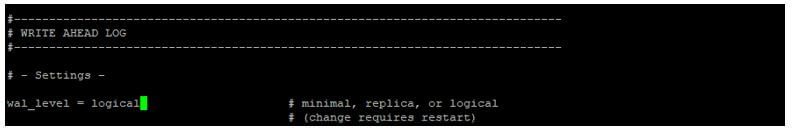
Configuring PostgreSQL configuration file on master server. We need to add below parameter on master server in postgresql.conf file.
Code:
Listen_address = "*"
Wal_level = logical
vi /var/lib/pgsql/10/data/postgresql.confOutput:
Step #3
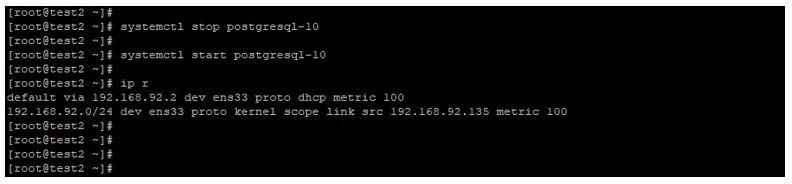
Take a restart of PostgreSQL service on master server to effect the configuration parameter changes.
Code:
systemctl stop postgresql-10
systemctl start postgresql-10Output:
Step #4
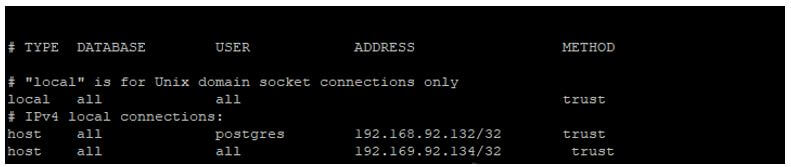
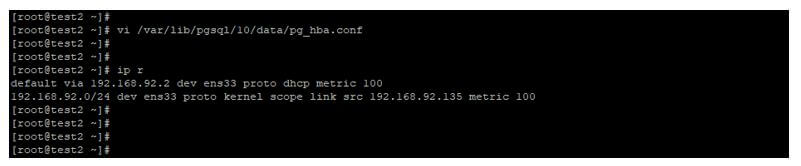
Add entry of slave server in hba. conf file on master server.
Code:
vi /var/lib/pgsql/10/data/pg_hba.conf
host all all 192.169.92.134/32 trustOutput:
Step #5
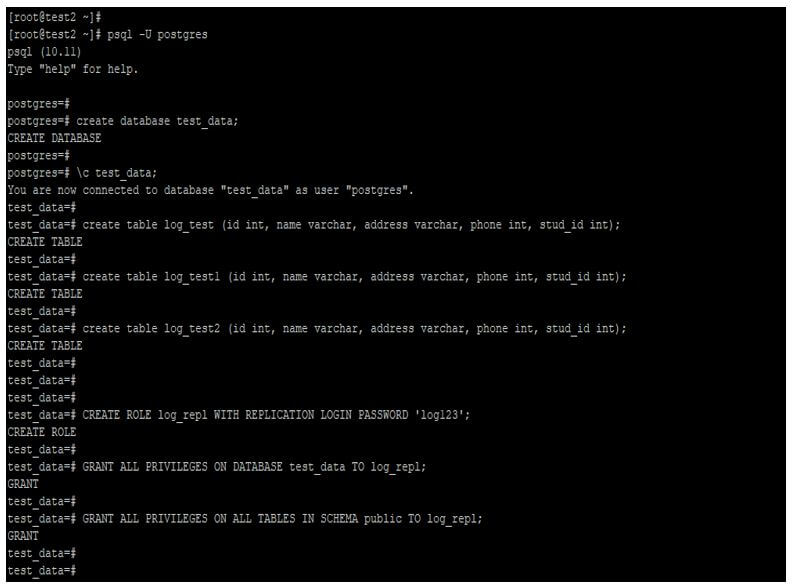
Create a database, user, and table on the master server.
Code:
psql -U postgres
create database test_data;
\c test_data;
create table log_test (id int, name varchar, address varchar, phone int, stud_id int);
create table log_test1 (id int, name varchar, address varchar, phone int, stud_id int);
create table log_test2 (id int, name varchar, address varchar, phone int, stud_id int);
CREATE ROLE log_repl WITH REPLICATION LOGIN PASSWORD 'log123';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE test_data TO log_repl;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO log_repl;Output:
Step #6
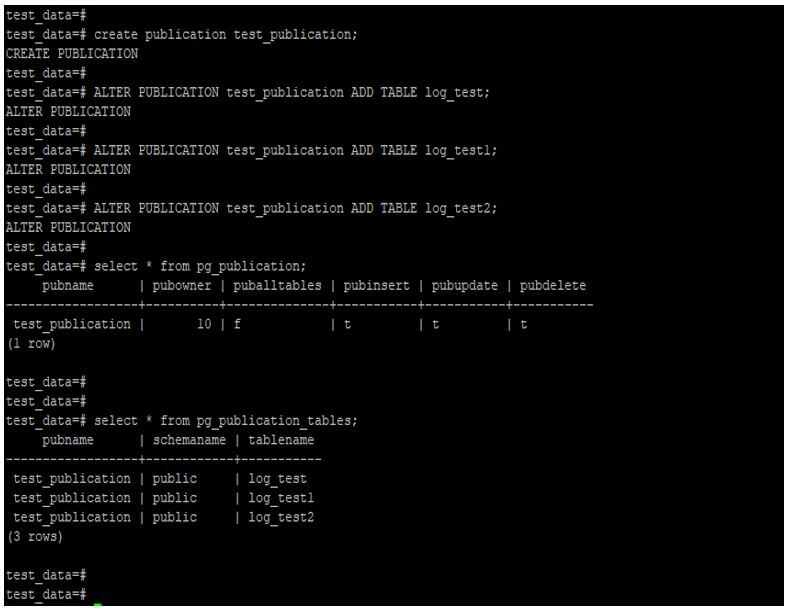
Create publication on master server and add a table into the publication.
Code:
create publication test_publication;
ALTER PUBLICATION test_publication ADD TABLE log_test;
ALTER PUBLICATION test_publication ADD TABLE log_test1;
ALTER PUBLICATION test_publication ADD TABLE log_test2;
select * from pg_publication;
select * from pg_publication_tables;Output:
Step #7
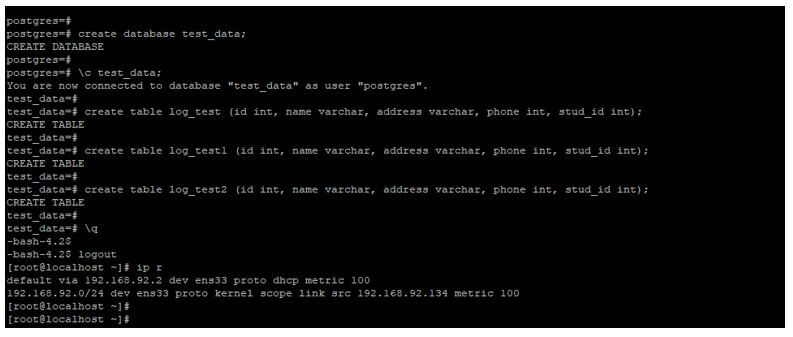
Create the same database and table on replica server.
Code:
create database test_data;
\c test_data;
create table log_test (id int, name varchar, address varchar, phone int, stud_id int);
create table log_test1 (id int, name varchar, address varchar, phone int, stud_id int);
create table log_test2 (id int, name varchar, address varchar, phone int, stud_id int);Output:
Step #8
Create a subscription on slave server.
Code:
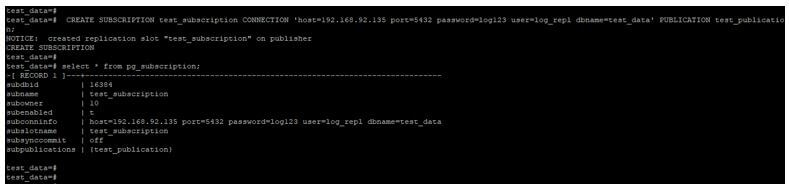
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION test_subscription CONNECTION 'host=192.168.92.135 port=5432 password=log123 user=log_repl dbname=test_data' PUBLICATION test_publication;
select * from pg_subscription;Output:
Step #9
Test the replication.
a. On master server.
Code:
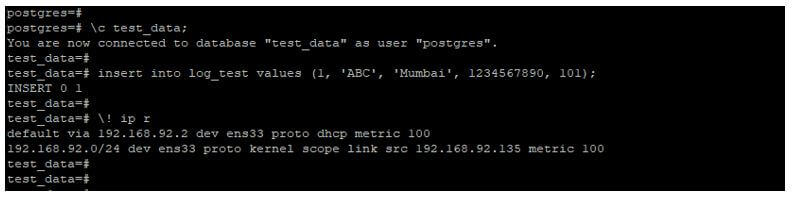
\c test_data;
insert into log_test values (1, 'ABC', 'Mumbai', 1234567890, 101);Output:
b. On slave server.
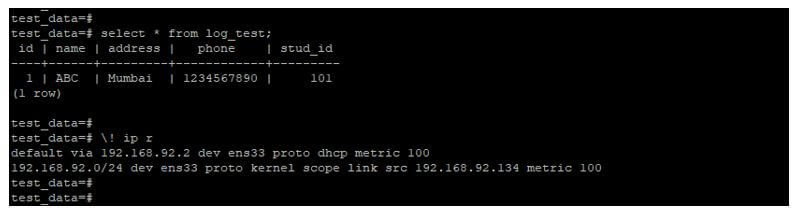
Code:
select * from log_test;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Logical Replication” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

