Updated May 9, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL JSON
JSON is an abbreviation of JavaScript Object Notation. JSON stores value in key-value pair; it is an open standard format. We generally prefer JSON for sending/receiving or exchanging data between servers and in web applications. The data within JSON is in text format, which is easily human-readable. PostgreSQL version 9.2 introduced support for the native JSON data type. PostgreSQL provides various methods and operators to work with JSON data.
Syntax:
column_name json Explanation: The name of the column whose data type will be JSON.
How JSON Works in PostgreSQL?
- We need to make sure the given data is in a valid JSON format before adding it to the table.
- If JSON data is incorrect, then it will throw an error.
- PostgreSQL provides the two native operators to work with JSON data.
- The -> operator Returns JSON data in the form of a key.
- The ->> operator: Returns JSON data in the form of text.
How to Insert JSON Data?
To understand the insertion of JSON data, let us create a ‘student’ table with the following structure.
The student table consists of two columns:
- stud_id: The column is the primary key column that uniquely identifies the student.
- stud_data: The column which stores the student’s information in the form of JSON.
Let’s create the table by using the CREATE TABLE statement:
CREATE TABLE student (
stud_id serial NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
stud_data json NOT NULL
);Now we will insert the data into the stud_data column, which is of type JSON. Before adding JSON data to the table, we need to ensure the given data is invalid in JSON format. Now insert the JSON data with the help of the following INSERT statement, which will add a new row into the ‘student’ table.
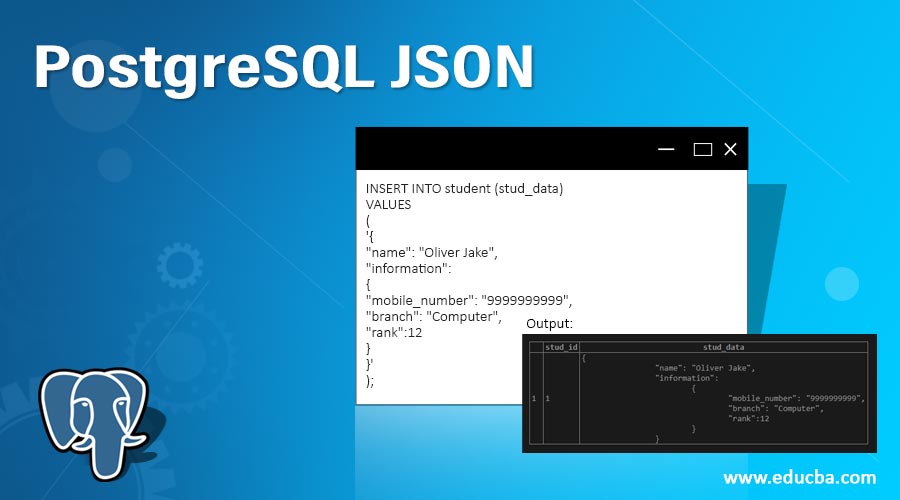
INSERT INTO student (stud_data)
VALUES
(
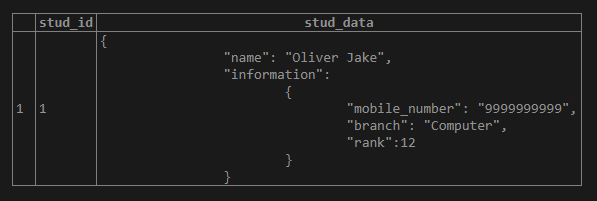
'{
"name": "Oliver Jake",
"information":
{
"mobile_number": "9999999999",
"branch": "Computer",
"rank":12
}
}'
);After executing the above statement, illustrate the student table’s content using the following snapshot and SQL statement.
select * from student;Output:
We can insert multiple rows in the table using the following INSERT statement:
INSERT INTO student (stud_data)
VALUES
(
'{
"name": "Jack Connor",
"information":
{
"mobile_number": "9999999910",
"branch": "Computer",
"rank":1
}
}'
),
(
'{
"name": "Harry Callum",
"information":
{
"mobile_number": "9999999911",
"branch": "Civil",
"rank":2
}
}'
),
(
'{
"name": "Jacob John",
"information":
{
"mobile_number": "9999999912",
"branch": "Electrical",
"rank":6
}
}'
);
select * from student;We can fetch the data from the student table by using the following snapshot and SQL statements.
Output:
Examples of PostgreSQL JSON
We have created a student table in the above section; let’s use the same for understanding the following examples.
Example #1 – Get all students in the form of JSON key
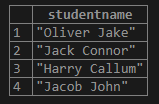
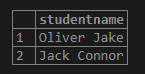
SELECT
stud_data -> 'name' AS StudentName
FROM
student;Output:
Example #2 – Get all students in the form of JSON text
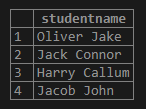
SELECT
stud_data ->> 'name' AS StudentName
FROM
student;Output:
Example #3 – Get specific JSON node using operators
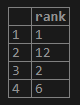
SELECT
stud_data -> 'information' ->> 'rank' as rank
FROM
student
ORDER BY
rank;Output:
Example #4 – Use JSON operator in WHERE clause
In order to filter rows from the result set, we can use the JSON operators in the WHERE clause. Consider the following example, which gives us the record whose branch is Computer by using the following statement.
SELECT
stud_data ->> 'name' AS StudentName
FROM
student
WHERE
stud_data -> 'information' ->> 'branch' = 'Computer'Output:
Example #5 – PostgreSQL JSON functions
PostgreSQL provides us with some functions to handle JSON data.
json_each function
By using the json_each() function, we can expand the outermost JSON object into a set of key-value pairs as follows:
SELECT
json_each (stud_data)
FROM
student;We can use the json_each_text() function to get a set of key-value pairs as text.
json_object_keys function
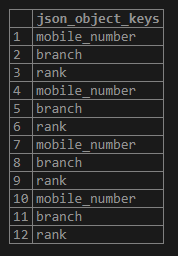
We can use the json_object_keys() function to get a set of keys in the outermost JSON object as follows:
SELECT
json_object_keys (stud_data->'information')
FROM
student;Output:
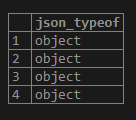
json_typeof function
With the help of the function json_typeof(), we can get the type of the outermost JSON value as a string. The type of JSON value can be a boolean, number null, string, object, and array.
We can get the data type of the information using the following statement:
SELECT
json_typeof (stud_data->'information')
FROM
student;Output:
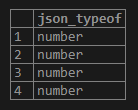
We can get the data type rank field of the nested information JSON object using the following statement:
SELECT
json_typeof (stud_data->'information'->'rank')
FROM
student;Output:
Advantages of using JSON in PostgreSQL
Advantages of using JSON in PostgreSQL are given below:
- Avoid complicated joins.
- Parsing of JSON data is quite easier and faster execution.
- Compatible with various database management systems.
- Javascript Notation Objects are faster and very easy to read and understand.
- The data within the JSON object is separated by a comma, making it easily understandable.
- JSON is lightweight for data exchange.
Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you understand how to use the PostgreSQL JSON data type and how the PostgreSQL JSON data type works to store the data in key-value pair. Also, we have added some examples of PostgreSQL JSON to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL JSON” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.