Updated May 3, 2023
Introduction to INTERSECT in PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL INTERSECT will combine the result of two or more select statements, like union and except operation. It will combine the result of two or more select statements. It will combine two or more select statement results set into a single result set.
This operator returns rows that were available in both the result set. We can combine one or more select query results set into a single result set by using this operator, and it is more useful and important in PostgreSQL.
Syntax 1
Select Column_name1, Column_name2, …, Column_nameN from table1
INTERSECT
Select Column_name1, Column_name2, …, Column_nameN from table2
Where conditionSyntax 2
Select expression1, expression2, …, expressionN from table1
INTERSECT
Select expression 1, expression 2, …, expressionN from table2
Where conditionSyntax 3
elect * from table1
INTERSECT
Select * from table2
Where conditionBelow is the parameter description of the above syntax are as follows:
- Select: Select statement is used to select no of the column from tables.
- Column1 to ColumnN: Column used in the select statement to fetch results using
- intersect in PostgreSQL.
- Expression1 to ExpressionN: Column used in the select statement to fetch results using
- intersect in PostgreSQL.
- .Table1 and Table2: Table used to retrieve data using the operator in PostgreSQL.
- Intersect: This operator used to combine the result of two or more select queries into a single result set.
- From: Keyword to define table from which we have fetching data.
- Where condition: Where the condition is used to fetch a specific condition of data.
- Asterisk (*): Retrieve all columns in the result set from the specified table.
How does the INTERSECT Operator work in PostgreSQL?
- One can merge multiple select statements into one query and collect corresponding rows from the dataset using it.
- Below is the picture representation of INTERSECT as follows:
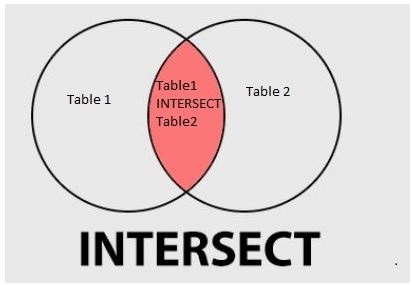
- The above figure shows the INTERSECT of table 1 and table 2. The result of the INTERSECT of table 1 and table 2 was combined with a single result set.
- The operator is only used in condition if we only have duplicate data from both the result set.
- INTERSECT only fetch those available data in both the result set, duplicate data fetched using intersect in PostgreSQL.
- We have not used the order by clause in the INTERSECT operator to fetch data in ascending or descending order.
- This operator will return the intersection of two or more data set into the single resultant data set.
- We will define each data set in INTERSECT by using a select statement that includes the shared record to create the resultant set.
Examples
To use the INTERSECT operator in PostgreSQL, we have using the emp_test1 and emp_test2 table.
Table1: emp_test1
CREATE TABLE emp_test1 ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, date_of_joining date NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (emp_id));Output:
![]()
INSERT INTO emp_test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');Output:
![]()
INSERT INTO emp_test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (2, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');Output:
![]()
INSERT INTO emp_test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (3, 'XYZ', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 35000, '02-01-2020');Output:
![]()
INSERT INTO emp_test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (4, 'BBS', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 45000, '02-01-2020');Output:
![]()
INSERT INTO emp_test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (5, 'RBS', 'Delhi', '1234567890', 50000, '03-01-2020');Output:
![]()
select * from emp_test1;Output:
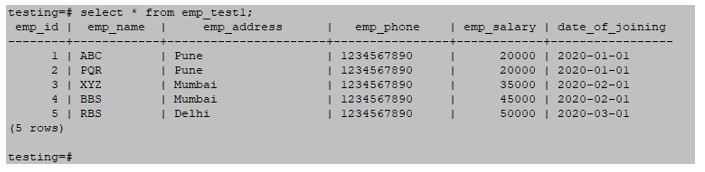
Table 2: emp_Test2
CREATE TABLE emp_test2 ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, date_of_joining date NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (emp_id));Output:

INSERT INTO emp_test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (6, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');Output:
![]()
INSERT INTO emp_test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (7, 'XYZ', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 35000, '02-01-2020');Output:
![]()
INSERT INTO emp_test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (8, 'BBS', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 45000, '02-01-2020');Output:
![]()
INSERT INTO emp_test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (9, 'RBS', 'Delhi', '1234567890', 50000, '03-01-2020');Output:
![]()
INSERT INTO emp_test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (10, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');Output:

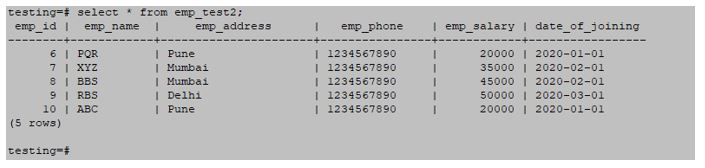
select * from emp_test2;Output:
Please find below an example of INTERSECT operator :
Example #1
Intersect operator using all columns from both the table:
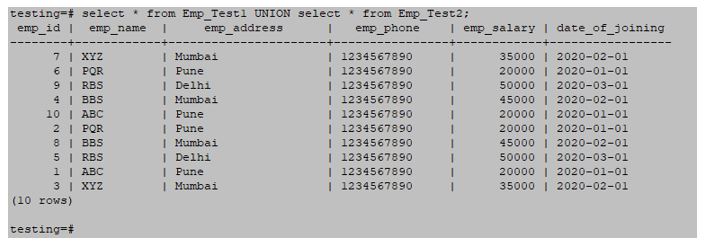
- We must retrieve data from every column in the example below. All data is then combined with the tables emp_test1 and emp_test2 in this scenario.
- In this scenario, all records will be retrieved from both tables.
select * from Emp_Test1 INTERSECT select * from Emp_Test2;Output:
Example #2
Intersect operator using a specific column from both the table:
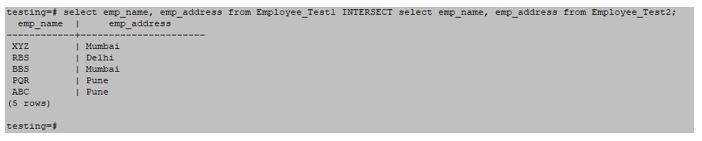
- In the below example, we have to retrieve data from specific columns. In such a case, only matching records from both the tables are fetched.
- To retrieve duplicate records from two tables in PostgreSQL, you can use the intersect function.
- When using “INTERSECT” in PostgreSQL, only the matching records from both tables will be retrieved.
select emp_name, emp_address from Employee_Test1 INTERSECT select emp_name, emp_address from Employee_Test2;Output:
Rules and Regulation
- Intersect in PostgreSQL will return those rows which were common from both the datasets.
- Intersect operator in PostgreSQL doesn’t manage data in ascending or descending order.
- It only retrieves matching records from both the dataset.
- If we only required a matching record from two different tables simultaneously, we have used intersect in PostgreSQL.
- This operator is handy and important in PostgreSQL to retrieve matching data from two or more data sets.
- In PostgreSQL, the “INNER JOIN” operator returns only those rows that are available in both datasets.
Conclusion
It is essential in PostgreSQL. To retrieve matching data from two or more datasets simultaneously in PostgreSQL, you can use the INTERSECT operator. This operator only retrieves matching records from both the dataset. If we required matching records data set at the same time, we used intersect in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL INTERSECT” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

