Updated May 8, 2023

Definition of PostgreSQL EXTRACT()
PostgreSQL extract function() is used to fetch the subfields from a date/time value field, like as in an hour or year, or day. The input field should be a date-time field. The input field is a string of date-time value or interval or timestamp from which we extract the fields like the second, minute, hour, date, etc. There are various units supported by PostgreSQL in which we can extract the input date-time source string. As a return result, the PostgreSQL EXTRACT() function gives a double-precision value.
Syntax:
Consider the following syntax of the PostgreSQL EXTRACT() function:
extract(unit from timestamp)
or
extract(unit from interval)Explanation:
- Timestamp or Interval: It is the input source string from which the unit is gets extracted.
- Unit: This defined the type of the unit to extract like a minute, hour, day, month, and so on.
Consider the following table to understand the possible values of the unit:
| UNIT | TIMESTAMP | INTERVAL |
| CENTURY | A century | The century number |
| DAY | A day of the given month
Numbered like (1-31) |
The day number |
| DECADE | a year which is divided by ten | Similar to TIMESTAMP |
| DOW | Weekday (0) Sunday to (6) Saturday | NIL |
| DOY | A day of the given year numbered like
(1 – 366) |
NIL |
| EPOCH | A second number from ‘1970-01-01 00:00:00’ UTC | The second number |
| HOUR | The hour numbered like (0-23) | The hour number |
| ISODOW | A day of the given week which is defined on ISO 8601 Monday to Sunday | NIL |
| ISOYEAR | ISO 8601 week number of year | NIL |
| MICROSECONDS | seconds with fractional parts, which is multiplied with ‘1000000.’ | Similar to TIMESTAMP |
| MILLENNIUM | The millennium | The millennium number |
| MILLISECONDS | seconds with fractional parts, which is multiplied with ‘1000.’ | Similar to TIMESTAMP |
| MINUTE | A minute numbered like (0-59) | The minute number |
| MONTH | A Month numbered like 1-12 | The month number which is modulo by (0-11) |
| QUARTER | the quarter of the given year | The quarter number |
| SECOND | A second | The second number |
| TIMEZONE | It is in seconds | NIL |
| TIMEZONE_HOUR | The time zone’s hour field. | NIL |
| TIMEZONE_MINUTE | The time zone’s minute field. | NIL |
| WEEK | The week of the giver year as per the ISO 8601 | NIL |
| YEAR | A year
|
Similar to TIMESTAMP
|
How does PostgreSQL EXTRACT() Function Work?
Consider the following pictorial representation for understanding the working of the extract function; as per the unit specified in the EXTRACT syntax, the PostgreSQL EXTRACT function extracts the unit from the input and returns that value.
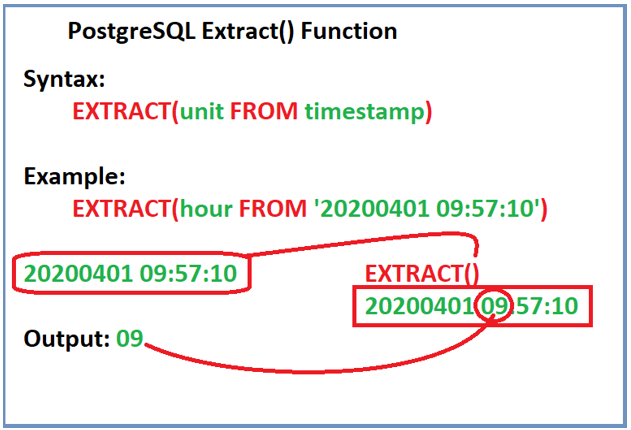
Implementing EXTRACT() Function in PostgreSQL
Let’s consider the following examples for understanding the function examples.
- Consider the following examples to extract date values:
SELECT extract(day from date '2020-04-03');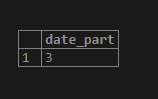
SELECT extract(month from date '2020-04-03') AS MONTH;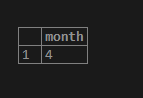
SELECT extract(year from date '2020-04-03') AS year;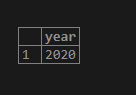
- Consider the following examples to extract timestamp values.
SELECT extract(day from timestamp '2020-04-03 09:57:10'); 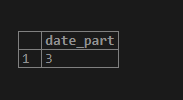
SELECT extract(month from timestamp '2020-04-03 09:57:10');
SELECT extract(minute from timestamp '2020-04-03 09:57:10');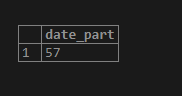
SELECT extract(second from timestamp '2020-04-03 09:57:10');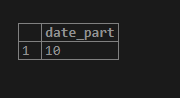
SELECT extract(hour from timestamp '2020-04-03 09:57:10');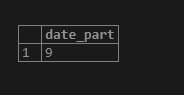
- Use the examples below to extract time values.
SELECT extract(minute from time '09:57:10');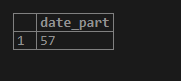
SELECT extract(second from time '09:57:10');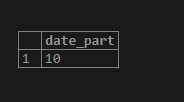
SELECT extract(milliseconds from time '09:57:10.5');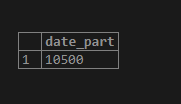
- Use the examples below to extract interval values.
SELECT extract(day from interval '4 days 4 hours');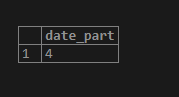
SELECT extract(hour from interval '4 days 4 hours');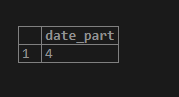
Advantages of using EXTRACT() Function in PostgreSQL
- We can extract the units like a day, month, hour, minute and many more from the source string by using the EXTRACT function.
- This function gives a double-precision value.
- The unit defined to fetch the result is human readable.
- We can extract the input source of type timestamp, interval, and date-time, etc.
Conclusion
We hope from the above article you have understood how to use the PostgreSQL EXTRACT() function and how the PostgreSQL EXTRACT() function works. Also, we have added several examples to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL EXTRACT()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

