Updated May 17, 2023
Definition on PostgreSQL escape single quote.
Normally single and double quotes are commonly used with any text data in PostgreSQL. To ignore or escape the single quote is a common requirement of all database developers. By using double quotes and backslash, we can avoid the complexity of single quotes as well as it is easy to read and maintain. Basically, in PostgreSQL single quote is used to define string constant when a string has a single quote at that time, you need to replace it by a double quote, and the main thing about escape a single quote depends on the version of PostgreSQL that means you can use a different notation to escape single quote from database.
Syntax:
select 'Text' 'Text';Explanation:
In the above syntax, we use a select statement to escape a single quote with a double-quote, as shown in the above statement.
Another way to escape a single quote is as follows.
select E 'Text\'Text';Explanation:
In the above syntax, we use a select statement, but this syntax is applicable for old versions of PostgreSQL string constants with E and backslash \ to escape single quotes. But the main problem with a backslash is that when we replace a single quote with a double-quote and multiple backslash \ it is difficult to read and maintain, so PostgreSQL version 8.0 introduces dollar quoting to avoid the complexity of the developer.
How to escape a single quote in PostgreSQL?
Let see how we can escape the single quote in PostgreSQL as follows.
Basically, a single quote is used to define a token as a string; this is the context used in PostgreSQL for different purposes. When we write any text in a single quote, it is treated as a reference object, and the identifier is represented by using double-quoted text. For example, suppose our statement is like
select 'Welcome in PostgreSQL';in which we use a single quote so how we can escape a single quote is as follows
select ‘I’ ‘m also welcome in PostgreSQL’;
in this statement, we escape a single quote by replacing a double quote, as shown in the above statement.
Examples
Let’s try to understand how we can escape single quotes with the help of different examples as follows.
PostgreSQL has provided a $ dollar feature without escape a single quote, so we can define a function or create a function as follows.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION sample_function(insert_text_asname text)
RETURNS text AS
$$
SELECT 'sample_function. my full name is ' || insert_text_asname || '.';
$$
language SQL strict;Explanation:
In the above example, we create a function name as a sample_function with different parameters, such as your name, as shown in the above statement, and it returns by using a select statement with the same parameter. Illustrate the remaining end result of the above announcement by way of the usage of the following snapshot.
The same function we write, or we can say that it is equivalent to a single escape quote.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION sample_function(insert_text_asname text)
RETURNS text AS
'
SELECT ''sample_function. my full name is '' || insert_text_asname || ''.'';
'
language sql strict;Explanation:
See here in the above example, we create the same function with the same parameter by using double-quotes. But when we compare both statements, then we realize $$ dollar is better to read and understand.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION sample_demo(insert_pgsql text)
RETURNS text AS
$$
DECLARE var_result text;
BEGIN
EXECUTE insert_pgsql INTO var_result;
RETURN var_result;
END;
$$
language 'plpgsql' STRICT;Explanation:
In the above example, we created one more example name as sample_demo, with different parameters, as shown in the above statement, and it returns the resulting text. Illustrate the remaining end result of the above announcement by way of the usage of the following snapshot.
When we use the above-created functions, then let’s see how we can escape single quotes from the string as follows.
Example #1
SELECT sample_demo($sql$SELECT sample_function($phrase$John's home's ground$phrase$)
|| $phrase$ hi myself Simran and today is birthday and want to invite’s all my school friend’s today.$phrase$ $sql$);Explanation:
In the above example, we use both function sample_demo and sample_function constant string see here, we use the dollar $ symbol to escape a single quote. Illustrate the remaining end result of the above announcement by way of the usage of the following snapshot.
Let’s compare it with a single quote.
SELECT sample_demo('SELECT sample_function("John""s home""s ground$phrase$)
|| "hi myself Simran and today is birthday and want to invite"s all my school friend”s."');Explanation
See in the above statement, we use a double quote to escape single quotes, but it isn’t easy to read and maintain the string it also increases the complexity of coding, but when we specify the dollar $ so it could be better to compare double quotes as shown in the above example.
Let’s see another example to escape single quotes by using double quotes as follows.
Example #2
First, create a table by using the create table statement as follows.
CREATE TABLE sample_quote
(
ID int
, Title TEXT
);Explanation:
In the above example, we created a table name as sample_quote with two attributes, as shown in the above statement. Illustrate the remaining end result of the above announcement by way of the usage of the following snapshot.
Now we insert some records by using insert into statements as follows.
INSERT INTO sample_quote
VALUES
(1,E'Simaran\'s rdbms database')
,(2,E'sample\'s different properties')
,(3,'john blog''s for different Reviews');Explanation:
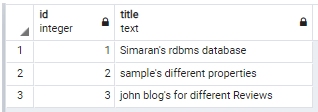
With the help of the above statement, we insert some records as shown in the above statement. See here we use both double quote and E\ backslash in the above statement. Illustrate the remaining end result of the above announcement by way of the usage of the following snapshot.
To see all data from sample_quote those with a (r) by, use the following statement.
select * from sample_quote where Title like E'%\'s%';Explanation
With the help of the above statement, we can see those titles that have a character in a string. Illustrate the remaining end result of the above announcement by way of the usage of the following snapshot.
Conclusion
We hope you understand the PostgreSQL escape single quote from this article. The above article taught us the basic syntax of PostgreSQL escape single quote. We have also discovered how to enforce them in PostgreSQL with different examples of every technique. From this article, we have learned how we can handle escaping single quotes in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL escape single quote” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.