Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL datediff
PostgreSQL provides a datediff function to users. The datediff means we can return the difference between two dates based on their specified interval. The datediff Function plays an important role in the database management system because datediff functions as a calendar and is very helpful to users. With the help of the datediff Function, we can determine any previous date or next date similarly, we can determine the previous day and next day, and we can also determine time, week, and minutes. Some functions of datediff use the system’s current date as per query syntax.
Syntax:
select datediff function() date1, interval date2;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use a select clause where the datediff Function means various date-related functions, where date1 is the first specified date, and date2 is the second specified date.
- Here interval is used to determine the difference between the specified dates.
How datediff Function works in PostgreSQL?
- We must install PostgreSQL in our system.
- Require basic knowledge of PostgreSQL.
- We must require the database to apply the datediff Function.
Given below are the different datediff Functions as follows:
First, we see basic functions related to date and time.
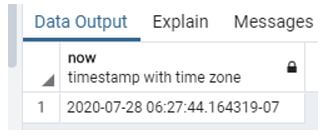
1. now() function
This Function is used to know the current date and time of the system, and this Function is a system defined Function, it gives a result in timestamp.
Example:
Code:
select now();Output:
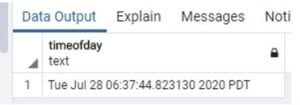
2. Time of day function
This Function shows the date and time in text format.
Example:
Code:
Select timeofday();Output:
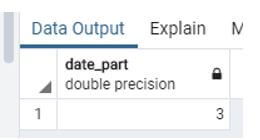
3. Quarter function
This Function is used to know a quarter of a year.
Example:
Code:
select extract (quarter from now());Explanation:
- In this example, we extract a quarter of the current year.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
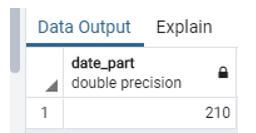
4. Day of the year
This Function calculates the number of days in a single year.
Code:
select extract (doy from now());Output:
Explanation:
- In this example, we use the extract function to know the number of days in a year specific in this example, we use now a function that means it counts days from the system’s current date.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
5. Day of the week
This Function is used to extract days from the week.
Example:
Code:
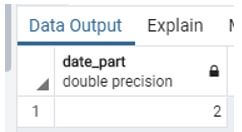
Select extract (dow from now());Explanation:
- In this example, extract the current day in the week it takes the system’s current date to know the day it starts from Monday as 1, Tuesday as 2, and so on. Thus by default, the value of Sunday is 0.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
6. Current month
This Function is used to know the current month.
Example:
Code:
select extract (month from now());Explanation:
- In this example, we extract the current month, where the now() Function takes the system’s current date.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Apart from datediff and extract function, we have another function which we call the date_part Function working of this Function the same as the datediff Function. The datediff Function is not directly supported by PostgreSQL.
Example:
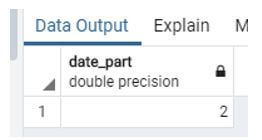
Code:
Select date_part ('dow', now());Explanation:
- In this example, we use the date_part Function instead of extract. Similarly, we implement all the above functions by using the date_part Function.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Now we see the example of the main datediff Function:
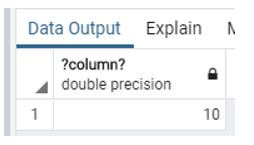
Example #1: Difference between two years
Code:
select date_part ('year', '2020/01/01'::date) - date_part ('year', '2010/01/01'::date);Explanation:
- Suppose we need to know the difference between two dates at that time, we use the above statement, see here, we use date_part instead of datediff because PostgreSQL does not support it directly.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Example #2: Difference between two days
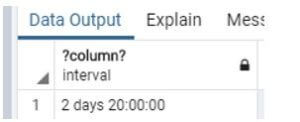
Code:
Select '2020-07-28 22:00:00' :: timestamp - '2020-07-26 02:00:00' :: timestamp;Explanation:
- Suppose we need to determine the difference between two days at that time, we use the above statement.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
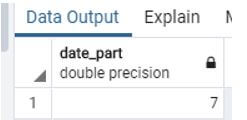
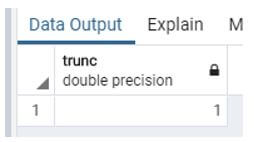
Example #3: Difference between the two week
Code:
Select trunk (date_part ('day', '2020-07-28' :: timestamp - '2020-07-21' :: timestamp) / 7);Explanation:
- Suppose we need to know the difference between the two weeks when we use the above statement.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
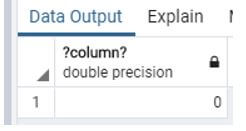
Example #4: Difference between hours
Code:
select date_part('day','2020-07-28 07:55'::timestamp - '2020-07-28 08:05'::timestamp)
* 24+
date_part('hour','2020-07-28 07:55'::timestamp - '2020-07-28 08:05'::timestamp);Explanation:
- Suppose we need to know the difference between two hours at that time. We use the above statement.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
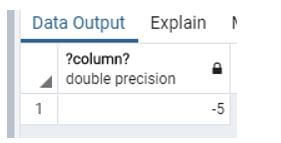
Example #5: Difference between minutes
Code:
select date_part ('hour', '09:40:10'::time - '09:45:50'::time) *60+
date_part ('minute', '09:40:10'::time - '09:45:50'::time);Explanation:
- Suppose we need to know the difference between minutes at that time, we use the above statement.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
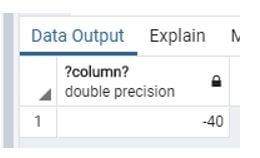
Example #6: Difference between seconds
Code:
select date_part ('hour','09:40:10'::time - '09:40:50'::time)*60+
date_part ('minute','09:40:10'::time - '09:40:50'::time)*60+
date_part ('second','09:40:10'::time - '09:40:50'::time);Explanation:
- Suppose we need to know the difference between the second at that time we use the above statement.
- Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Output:
Conclusion
From the above article, we saw the syntax of datediff and basic functions of datediff as well as some advanced functions like determine the difference between year, month, day, hour, and minutes with multiple examples. From this article, we saw how we could handle different datediff functions.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL datediff” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.