Updated May 30, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL Date Format
Dates are stored using the DATE datatype in the PostgreSQL database. It takes 4 bytes of memory to store any date value in PostgreSQL. The range of DATE datatype is from 4713 BC to 5874897 AD. The format of the date in which it is stored and retrieved in PostgreSQL is yyyy-mm- dd. In this article, we will see how we can store, insert and retrieve the date values and manipulate them according to our requirements and convenience. We will also see the available functions that can help to change the format of the retrieved date and derive periodical parameters like age, day, month, year, and week from a particular date value and to get the current date and assign it as default values for columns that are of DATE datatype.
Syntax of PostgreSQL Date Format
DATE [DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE]Let us create a table named educba containing a date column in it.
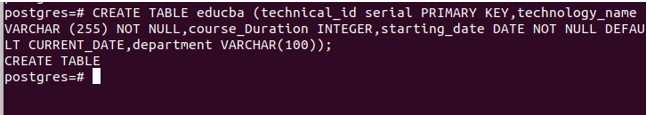
CREATE TABLE educba (technical_id serial PRIMARY KEY,technology_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,course_Duration INTEGER,starting_date DATE NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE,department VARCHAR(100));Firing the above query in our psql terminal command prompt will result in the following output –
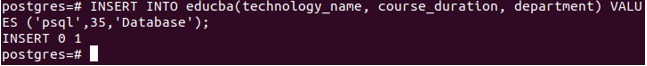
Let us insert the value in the educba table without mentioning the starting_date column’s value while inserting.
INSERT INTO educba(technology_name, course_duration, department) VALUES ('psql',35,'Database');This gives the following output –
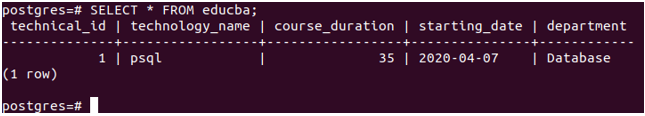
Let us now check the contents of our table educba by firing the following SELECT command – SELECT * FROM educba;
That gives the following output –
We can see that today’s date, i.e, 7th of April 2020, is inserted as the value in the starting_date column of our table even when we haven’t mentioned it while inserting the record. This is because we have mentioned the starting_date column of the DATE datatype and having the default value of CURRENT_DATE, which is the date at the movement when the record will be inserted according to the database server on which the value is inserted.
Functions of PostgreSQL Date Format
Now let us see some of the date-related functions available in PostgreSQL for date retrieval and manipulation.
We can either use the CURRENT_DATE variable and select its value of use Now() function to retrieve the current date, and i,e and further to only retrieve date use Now():: date to retrieve current date value in PostgreSQL in the following way –
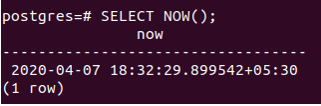
Now() function retrieves the full string of the current date and time. If we fire the SELECT NOW(); command, it will result in –
select now();That gives the following output –
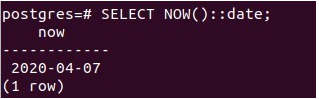
We can use:: double colons to retrieve only the date part from the above output along with the date keyword in the following way –
SELECT NOW()::date;That gives the following output –
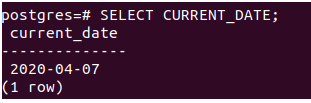
or
SELECT CURRENT_DATE;That gives the following output –
Date Formats
We can get the dates in the format we want by converting the default format value of the date present in yyyy-mm-dd to another format we wish using the to_char function. The following is the syntax of the TO_CHAR method –
TO_CHAR(datetobeConverted, targetTemplate);As shown above, the TO_CHAR method accepts two parameters. The first parameter is the date we want to convert to a certain format, and the second parameter is the template of the target format in which we want the date value to be displayed.
Let us see some of the examples of TO_CHAR() method implementations –
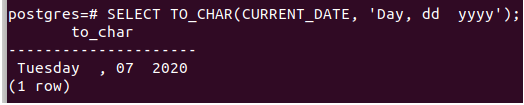
The first template is today’s day, and then the date and year to be displayed after a comma. For specifying today’s date, we will use the CURRENT_DATE variable. We can prepare our query statement for the same in the following way –
SELECT TO_CHAR(CURRENT_DATE, 'Day, dd yyyy');Firing the above statement gives the following output –
Now, if I want to display the day and date without month and year in it. Then my query statement will be –
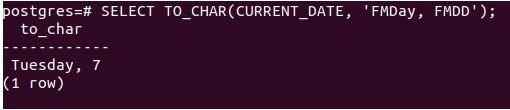
SELECT TO_CHAR(CURRENT_DATE, 'FMDay, FMDD');Firing the above statement gives the following output –
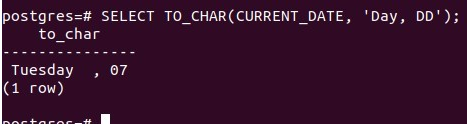
SELECT TO_CHAR(CURRENT_DATE, 'Day, DD');That gives the following output –
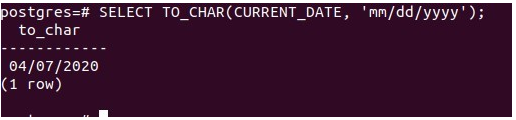
SELECT TO_CHAR(CURRENT_DATE, 'mm/dd/yyyy');That gives the following output –
Finding the difference between the two dates
We can distinguish between two dates by subtracing one from the other using the minus operator (-). Let us consider an example,
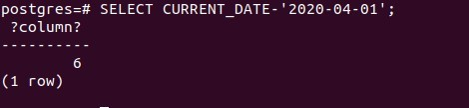
SELECT CURRENT_DATE-'2020-04-01';Firing the above query statement results in the following output –
There is a difference of 6 days between today’s date “2020-04-07” and “2020-04-01”.
Finding out the age
We can even find out the person’s age in terms of days, months, and years from the specified date until today if only one parameter is specified in the AGE() method. If two parameters are specified, the difference between them is given in days, months, and years format. Let us find out, with the help of an example, how it works?
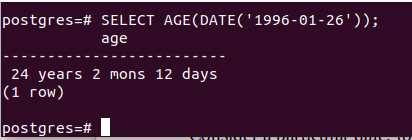
Consider a particular date, for example, “1996-01-26” is the birth date of someone. We have to find out how old that person is. Then we will use the following query statement to find the same.
SELECT AGE(DATE('1996-01-26'));whose output is as follows –
So that person is 24 years, 2 months, and 12 days old.
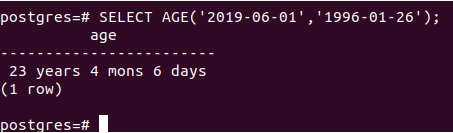
Let us find out how old that person was on the 1st of June 2019, i.e’ 2019-06-01′. Then we can find out the result using the following query statement –
SELECT AGE('2019-06-01','1996-01-26');whose output is as follows –
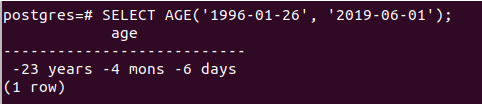
So they were 23 years, 4 months, and 6 days old on the 1st of June 2019 if the birth date is the 26th of January 1996. Note that the first parameter should always be the greater value of a recent date, and the second one should be older and smaller. If not mentioned so, then the result will be negative. Let us confirm the case by just swiping the first and second parameters –
SELECT AGE('1996-01-26', '2019-06-01');whose output is as follows –
Conclusion
DATE datatype stores and manipulates the dates in PostgreSQL, whose format is ‘yyyy-mm-dd.’ However, by using TO_CHAR() method, we can change the format of the date while retrieval. Other than that, many other methods are available to manipulate date values, such as minus operator, AGE(), MONTH(), and YEAR(), that can be used in PostgreSQL while dealing with dates.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Date Format” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.