Updated May 8, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL COALESCE
The PostgreSQL Coalesce function works the same as the IFNULL function in SQL; it is a PostgreSQL function. This function will evaluate values or arguments from left to right for finding the first non-null value or argument; after finding the first argument, it will not evaluate the remaining argument. Coalesce function will accept several arguments or values, but it returns the first argument or values as a non-null result; if all the values are null, then PostgreSQL coalesces function will return the empty result or null value in the result set.
Syntax:
Below given is the syntax as follows:
COALESCE (Value (Any value which we have used with coalesce function) [, ….])COALESCE (Argument1, Argument2,….,ArgumentN);Select column1, column2,…., columnN
COALESCE(description, short_description, '(none)')
From table_name;Parameters:
1. Value: Any value we have used with the coalesce function in PostgreSQL. The coalesce function will return the first non-null value in the result for multiple values.
2. Coalesce: Coalesce states that the function name in PostgreSQL returns as first non-null value as a result. Coalesce function is essential and useful in PostgreSQL.
3. Select: Select is used to fetch data from the table by using a coalesce function in PostgreSQL. We can use multiple column or a single column at one time to fetch data from a table.
4. Argument 1 to Argument N: Argument is nothing but an integer value that we have passed with coalesce function in PostgreSQL. If we are passing three-argument and the first contains a null value, then coalesce function will return the second value in a result.
5. Column 1 to Column N: This is the table’s column name. If we want to fetch data from a table using coalesce function in PostgreSQL, we pass multiple columns simultaneously. Also, we have given column name with coalesce function in PostgreSQL.
6. From: From is a keyword in PostgreSQL used with the table name in the select query.
7. Table name: Table name is used with coalescing function.
8. Description: We are passing the description with coalesce function in PostgreSQL. In the description of coalesce function, we have also passed a column name of a table on which we have used a coalesce function.
9. Shot Description: We have also used a short description parameter while using the coalesce function in PostgreSQL.
10. None: It is the argument passed with coalesce function.
How does the COALESCE Function work in PostgreSQL?
- We have substituted any default value data into null values by using a coalesce function in PostgreSQL.
- It returns the first value, which is not null in the table.
- If the table has multiple values and the column row contains a record with null values, but as a result, we have not required any null value at that time, so we have used this function.
- Coalesce function is essential and useful in PostgreSQL to return the first value, which was not null in the column.
- We have assumed zero or any column row values in PostgreSQL to find the actual result of a table using coalesce function.
- This function will evaluate values or arguments from left to right to find the non-null value or argument. After finding the first argument, it will not evaluate the remaining argument.
- Coalesce function in PostgreSQL will accept several arguments or values, but it returns the first argument or values as a result that is not null. If all the argument is null, then the coalesce function will return the null value (Empty result) in the result set.
- Coalesce functions work is same as the IFNULL function in SQL.
Examples
Given below are the examples:
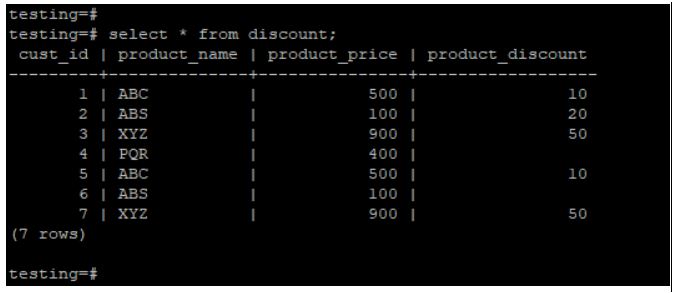
We have used a discount table to describe the example as follows:
Below is the data description of the discount table, which we have used to describe the example.
Code:
select * from discount;Output:
Example #1
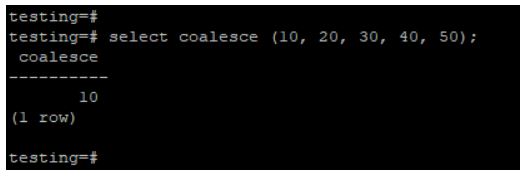
In the below example, we pass values like 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50. The coalesce function will return only first values because it finds non-null values in first place records.
Code:
select coalesce (10, 20, 30, 40, 50);Output:
Example #2
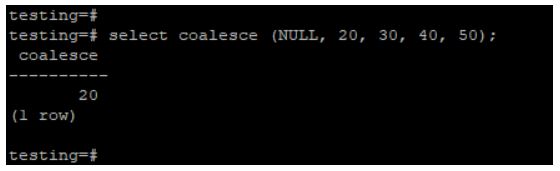
In the below example, we pass values as NULL, 20, 30, 40, and 50. Coalesce function will return the second value because it was not found a non-null value in the first place, so it will go on to the second value, which was 20.
Code:
select coalesce (NULL, 20, 30, 40, 50);Output:
Example #3
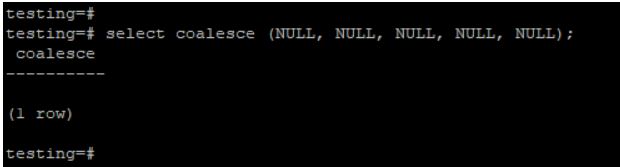
In the example below, we are passing all null values with coalesce function; it will return empty results because all values we pass are null.
Code:
select coalesce (NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);Output:
Example #4
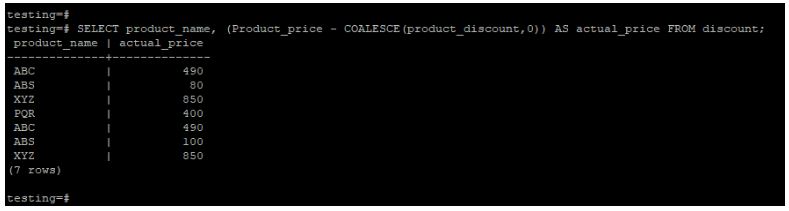
In the below example, we are retrieving the product’s actual price. In the place of a null value, we have to define a zero value using a coalesce function.
Code:
SELECT product_name, (Product_price - COALESCE(product_discount,0)) AS actual_price FROM discount;Output:
Advantages of using COALESCE in PostgreSQL
- The coalesce function evaluates values from left to right to find non-null values from the column.
- In the place of the null value, we have put zero or any value to calculate a result.
- We have substituted any default value data into null values by using a coalesce function in PostgreSQL.
- Coalesce function is essential and useful to return the first value, which was not null in the column.
- It returns the first value, which is not null in the table.
Conclusion
PostgreSQL, coalesce function is used for finding non-null value from the column, which will evaluate from left to right. After finding the first argument, it will not evaluate the remaining argument. We are assuming zero or any column row values to find the actual result of a table using coalesce function.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL COALESCE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

