Updated May 8, 2023

Definition of PostgreSQL Boolean
PostgreSQL Boolean is a simple data type that represents only the structure of true or false data or values. PostgreSQL will support the SQL99 defined Boolean data type of SQL standard; Boolean is also known as “bool”, bool is an alias of Boolean data type in PostgreSQL. We can set the null value of the Boolean data type; if we have set a Null value of the Boolean data type, then it is not interrupted as true or false. In PostgreSQL, the Boolean data type has three states like true, false, and null.
Syntax and Parameter
The syntax and parameter of PostgreSQL Boolean are given below:
Syntax:
Below is the syntax of the Boolean data type as follows. We have defined Boolean data type when table creation and insertion.
CREATE TABLE table_name (Any table name given to the table) (Column_name data
Type NOT NULL, Column_name (Column name to define Boolean data
Type) BOOLEAN NOT NULL (Define not null value of Boolean data type column));Alter table table_name ADD COLUMN column_name BOOLEAN (Define Boolean data
type to the column)Insert into table_name values (true, 't', 'true', 'y', 'yes', '1');Insert into table_name values (false, 'f', 'false', 'f', 'no', '0');Parameter:
Below is the parameter description of the above syntax as follows.
- Create: Create a new table and define a Boolean data type of table column. We have defined the Boolean data type at the time of table creation. Also, we have defined it after table creation using alter command.
- Table name: Create a new table to define the column data type as Boolean in PostgreSQL. We can give any name to a newly created table.
- Column name: Name of the column on which we have defined a Boolean data type. We have set a Boolean value as true, false, and null.
- Data type: Define the data type of the column. We can define any data type of column. Boolean is the most useful and important data type.
- Not Null: We defined a not null value of the column. If we do not set the column’s null value, then inserting a null value in the table is not allowed.
- Boolean is a simple data type used to represent only the structure of true or false data or values. In PostgreSQL, the Boolean data type has three states like true, false, and null.
- Add: Add a new column using alter command and defined Boolean data type to the same column in PostgreSQL.
- Alter: After creating a table and defining a Boolean data type in the same column, we added a column.
- True, t, yes, 1, and y: This is the valid, true value of the Boolean data type.
- False, f, no, 0, and n: This is the valid false value of the Boolean data type.
How does Boolean Data Type Works in PostgreSQL?
Below is the working of the Boolean data type.
- PostgreSQL Boolean in data type has three states like true, false, and null.
- PostgreSQL will support the SQL99 defined Boolean data type of SQL standard; In PostgreSQL, the Boolean data type is also known as “bool”, and “bool” is an alias for the Boolean data type.
- It is a simple data type that represents only the structure of true or false data or values.
- We can set the null value of the Boolean data type; if we have set a Null value of the Boolean data type, then it is not interrupted as true or false.
- In PostgreSQL, we can define a Boolean value as null, true and false. After defining a Boolean data type of true in PostgreSQL, you can retrieve any values that evaluate to true.
- If we define the Boolean value as false, all false values will be retrieved from the table. Defining Boolean value as null is not interrupted as true or false.
- The valid, true value of the Boolean data type is as follows.
- true
- ‘t’
- ‘true’
- ‘y’
- ‘yes’
- 1
- The valid false value of the Boolean data type is as follows.
- false
- ‘f’
- ‘false’
- ‘n’
- ‘no’
- 0
- In PostgreSQL, you need to enclose all Boolean data type values in quotes except for true and false.
- Boolean support the single datatype, but Boolean has three states.
- A boolean data type is a simple data type that only represents a true and false value.
Examples
Below is an example of the Boolean data type as follows.
1. We have defined the Boolean data type as a column at the time of table creation. We have created a product table, and we have to define the Boolean data type on the availability column as follows.
testing=# CREATE TABLE product (prod_id INT NOT NULL, prod_name character(10) NOT NULL, delivery_address character(20) NOT NULL, delivery_phone character(14), prod_availability BOOLEAN NOT NULL, delivery_date timestamp NOT NULL);
2. We have defined the Boolean data type after creating the table. Below is an example of the same is as follows.
testing=# ALTER table product ADD COLUMN prod_delivery_status BOOLEAN;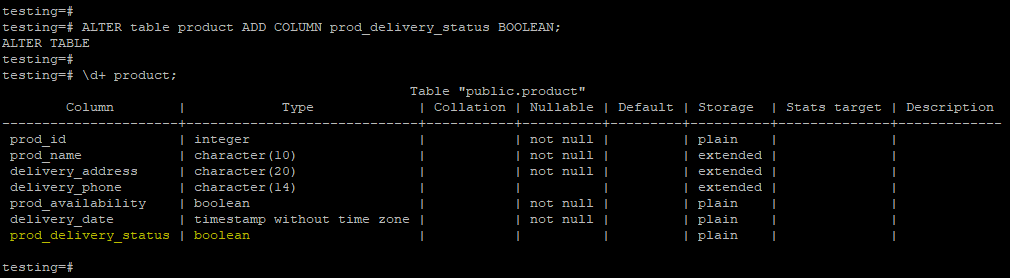
3. Insert Boolean data into the table.
testing=# Insert into product values (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 'yes', 'true');
testing=# Insert into product values (2, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 'no', 'false');
testing=# Insert into product values (2, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', '1', '0');
testing=# select * from product;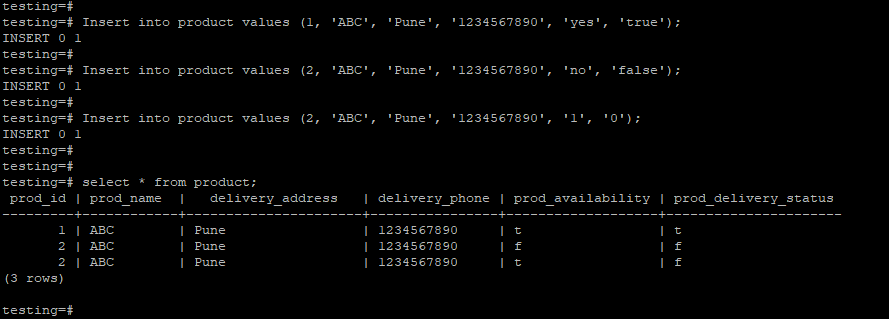
4. Retrieve data from a table in which product availability is true.
testing=# select prod_id, prod_name, delivery_address, delivery_phone, prod_availability from product where prod_availability = true;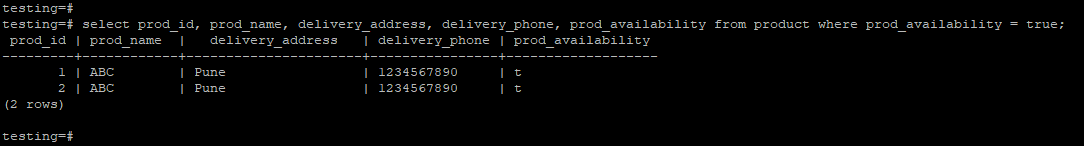
5. Retrieve data from a table in which product availability is false.
testing=# select prod_id, prod_name, delivery_address, delivery_phone, prod_availability from product where prod_availability = false;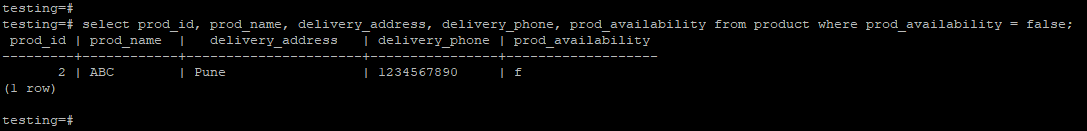
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Boolean” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

