Updated May 25, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL ANY
We can compare the particular value with a set of values to validate the query execution to retrieve the matched results. We can use the PostgreSQL ANY operator to achieve the same in PostgreSQL. The PostgreSQL ANY operator compares a value with the result set returned by a subquery.
Syntax:
Consider the following syntax to understand the syntax of the ANY operator:
expression operator ANY(subquery)Explanation:
The result of the subquery should be only one column.
The PostgreSQL, ANY operator, should be preceded by the following:
- =
- <=
- >
- <
- >
- <>
How does ANY Operator Work in PostgreSQL?
The PostgreSQL ANY operator returns true if the result set of subquery contains the required value and meets the specified condition. Otherwise, the result of the ANY operator is false.
As we know the syntax, the right-hand side is a subquery that returns. As a result, the set contains multiple values. On the other hand, the left-hand side of syntax includes an expression that gets evaluated and compared to all values returned from the right-hand side subquery with the help of the specified operator and returns us the boolean value as a result.
Examples to Implement ANY in PostgreSQL?
Consider the tables COUNTRIES and CITIES to understand the PostgreSQL operator’s examples.
Example #1
CREATE table COUNTRIES
(
country_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
country_name VARCHAR (256) NOT null,
last_updated DATE NULL
);
CREATE table CITIES
(
CITY_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
country_id INT NOT NULL,
city_name VARCHAR (256) NOT NULL,
last_updated DATE null,
FOREIGN KEY (country_id) REFERENCES COUNTRIES (country_id)
);Now insert some data in both tables
INSERT INTO COUNTRIES (country_name,last_updated)
VALUES
('India','06-01-2020'),
('US','07-01-2020'),
('CHINA','08-01-2020');
INSERT INTO CITIES (country_id, city_name,last_updated)
VALUES
(1,'Pune','06-02-2020'),
(1,'Mumbai', '07-02-2020'),
(2,'New York', '08-02-2020'),
(2,'Los Angeles', '09-02-2020'),
(3,'Beijing ', '10-02-2020'),
(3,'Shanghai', '11-02-2020');Illustrate both tables and data inserted with the following tables and snapshots.
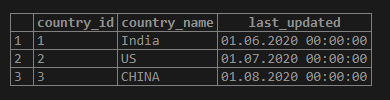
select * from COUNTRIES;Output:
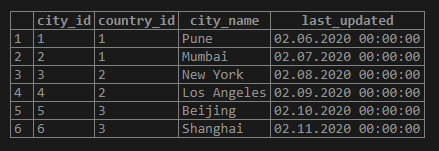
select * from CITIES;Output:
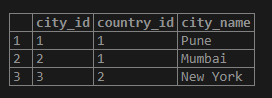
Let’s consider the following example, where we will get records from the cities table where the city names are Pune, Mumbai, and New York.
Example #2
SELECT city_id, country_id, city_name
FROM cities
WHERE
city_id = ANY(
SELECT city_id
FROM cities
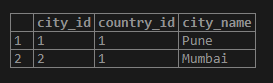
WHERE city_name ='Pune'or city_name ='Mumbai'or city_name ='New York');Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot:
Output:
Let’s consider another example where we will get records from the cities table where the city id is greater than the city id of Pune city.
Example #3
SELECT city_id, country_id, city_name
FROM cities
where city_id > ANY(
SELECT city_id
FROM cities
WHERE city_name ='Pune');Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot:
Output:
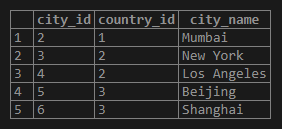
Similar to the above example, we can get records from the cities table where the city id is less than the city id of New York City.
Example #4
SELECT city_id, country_id, city_name
FROM cities
where city_id < ANY(
SELECT city_id
FROM cities
WHERE city_name ='New York');We can use various operators like less than, equal to, greater than, etc.
Output:
Consider the following syntax, which is similar to each other:
exp <> ANY ( A, B, C)Is equivalent to
exp <> A OR exp <> B OR exp <> CAdvantages
Following are the advantages given below:
- This operator compares a value to each value of the result set and returns us true if the result set contains at least one matching row, which helps us to write a single-line statement for multiple values comparison
- This operator can be used with various comparison operators.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL ANY” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.