Updated May 18, 2023
Introduction to Postgres add a user.
The default user in PostgreSQL after installing it is a Postgres user. In real-time scenarios, creating multiple users is often necessary to assign access privileges and maintain database security effectively. In this article, we will learn how to create new users in PostgreSQL.There are two methods to do so. The first method involves using the CREATE query statement to create a new user, and the second method uses the meta-command to create the user in PostgreSQL’s psql utility. We will study the syntax and options provided in both the methods and see an example of creating a new user in PostgreSQL using each of the above-mentioned methods.
Syntax:
Format 1 –
CREATE USER name [ [ WITH ] option [ ... ] ]where option can be:
SYSID uid
CREATEDB | NOCREATEDB
| CREATEUSER | NOCREATEUSER
| [ ENCRYPTED | UNENCRYPTED ] PASSWORD 'newPassword'
| VALID UNTIL 'expirytime'Using the above create command, the new user can be created, and other options can also be assigned.
- Name – It is the name of the user or role whose properties or password you want to change.
- Option – We can change multiple parameters and privileges associated with the user using this format. The following section lists some of the option properties.
- SYSID uid – The SYSID UID represents the user ID assigned to uniquely identify the user in the database server during the creation process. It is not necessary to mention. If you do not explicitly specify a value, the system will automatically assign a value equal to the maximum user ID plus one to the current user ID being created.
- CREATEDB – This can be specified if you want to give the privilege to the user to create a new database
- NOCREATEDB – The NOCREATEDB option can be specified to restrict the user from creating any new databases.
- CREATEUSER – This property can be specified to allow the user to create new users.
- NOCREATEUSER – When you include the NOCREATEUSER property in the query, as mentioned above, it restricts the user from creating new users.
- ENCRYPTED – The ENCRYPTED property determines if the password stored in the pg_catalog’s pg_shadow table is in MD5 encrypted format.
- UNENCRYPTED – The pg_catalog does not store the password in an encrypted format. If the ENCRYPTED or UNENCRYPTED property is not specified during user creation and no default password storing mechanism is set, the password encryption method will be determined by the password_encryption configuration variable.
- PASSWORD – The new Password is the string that you want to set as the password for the user. If this field is not specified and the user has no previously set password, the user will not require authentication. They will be able to log into the system without providing a password. But if you switch to a password authentication system, the user won’t be able to log in.
- VALID UNTIL expirytime – This field can be used if you want to allow the set password up to some specific period. This field if the timestamp up to which you want to permit the assigned password to work.
Example of Postgres add a user.
We will firstly login to the system by Postgres default user. Here we have my password assigned to the Postgres role already. So, we will enter the password.
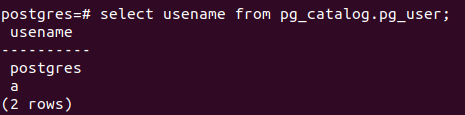
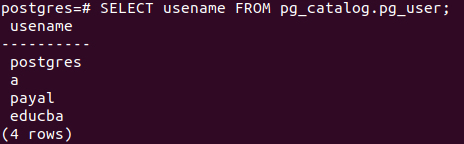
sudo su - postgresFurther, Let us check all the users which are present in the database server by firing the command using psql promp –
select usename from pg_catalog.pg_user;Alternatively, you can use meta-command \du to retrieve the user details that give the same results.
Now, we will create a new user named payal in the current database server using the CREATE USER format mentioned above with the help of the following query –
CREATE USER payal WITH ENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'payal@123';that gives the following output –
As the output is CREATE ROLE. The user has been created successfully.
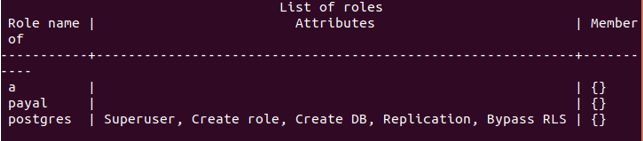
Let us check by using the \du metacommand that results in the following output –
\duFormat 2 –
createuser [options...] [nameofuser]The superusers can only use this command to create a new user in PostgreSQL.
- Nameofuser – It is the name of the user that you wish to create.
- Options – There are several options available for creating a user, such as a, A, e, E, d, D, i, q, N, P, etc. When using the user creation command, these options are preceded by a hyphen (-).
While creating the users remotely, some of the connection related options that can support the operation are mentioned below –
-h nameOfHost or –host nameOfHost
It helps us specify the host’s name on which the server is running.
-p nameOfPort or –port nameOfPort
It allows us to specify the port of the TCP or socket of the local UNIX domain that the server listens to for connections.
-U nameOfUser or –username nameOfUser
It helps us to specify the name of the user with which you want to connect as.
-W or –password
It helps us to specify whether to ask for the password prompt for new users.
For example –
Let us create a new user named educba by using the above syntax –
createuser educba;that gives the following output and password is being asked to enter for the educba user-
Please note that you can execute this command only on the postgres shell, not on the psql command prompt.
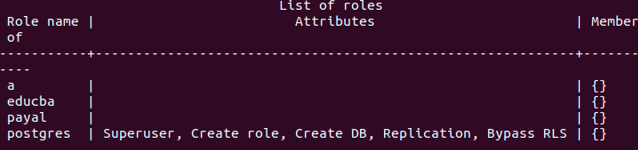
To verify if the educba user has been created, you can log into the psql command prompt and execute the meta command \du.
Psqlfiring the \du commands gives the following output containing the educba user that we created.
\duSELECT usename FROM pg_catalog.pg_user;gives the following output –
Conclusion
We can create multiple new users by either using the CREATE query on the psql terminal or the createuser command that can be used on the psql shell. Both these methods provide flexibility to specify user-related properties and other details required while user creation in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Postgres add user” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.