Updated March 16, 2023
What are Pointers in C++?
Pointers is the most powerful tool in c++; it helps the programmer access and manipulates the memory directly. For instance, when a variable is created, the job of the compiler is to do memory allocation to store the value of the variable. And this value is retrieved using the variable name assigned to the data. C++ has the compatibility to store and retrieve the data from memory, referring to the address of the memory location at which the data is stored. C++ even performs pointers on a pointer.
Syntax:
The general format of the pointer declaration is:
Data_type * pointer -variable-nameNote that the pointer variable should be preceded by an asterisk (*).
Example:
Code:
int * xptr;The variable xptr is a pointer to an integer. Pointer variables can generally point to integer variables, character variables, arrays, files, and functions.
Why do we Need Pointers in C++?
- Dynamic memory allocation is made simple in C++ using pointers, the most prominent importance of pointers is that they are much more efficient in handling the different data types.
- In addition, they increase the execution speed when the function returns one value and give a hand in accessing a variable defined outside the function.
- The most common usage includes data management and accessing class member functions.
How to Create Pointers in C++?
Here are the following steps to create pointers in C++:
Step 1: Initialization of pointers
It is advisable to initialize pointer variables as soon as they are declared. Since pointer variables store addresses, they can address any portion of the memory.
Code:
int *a; // pointer to an integer
double *da; // pointer to a double
float *fa; // pointer to afloat
char *ch // character pointerConsider the following example:
int p, *pi; // This statement instructs the compiler to reserve a space for the variable p in memory to hold an integer value.
pi=&a; // Assigns the address of the integer variable p to the pointer variable. For instance, if the address of p is 4581, then the value in the *pi will be equal to 4581.
Step 2: Pointer void
Here the pointer variable is allowed to point to any data type, and this type is used in passing pointers to functions that work independently of the data type that is pointed to.
Syntax:
void * pointer variable;Example:
Code:
#include<iostream.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int x, *iv;
float f, *fv;
void *vp;
x=3;
f=45.2;
iv=&x;
fv=&f;
vp=&x;
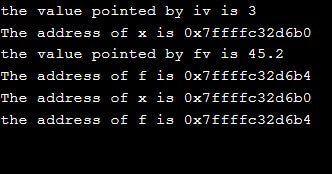
cout<< "the value pointed by iv is "<<*iv<< endl;
cout<< "The address of x is "<<iv <<endl;
cout<< "the value pointed by fv is "<<*fv<< endl;
cout<< "The address of f is "<<fv <<endl;
cout<< "The address of x is "<<vp <<endl;
vp= &f;
cout<< "the address of f is "<<vp<<endl;
}Output:
Step 3: Pointers arithmetic operations in C++
Pointer arithmetic is performed with arrays.
The following operations can be performed on pointers.
- Increment (++)
- Decrement (–)
- Pointer addition
- Pointer subtraction
When we add 1 to the pointer, it specifies adding the size of the pointer pointing at.
The below program specifies pointer arithmetic; it works until it gets at the end of the array.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void pointerarithmetic(int a[], int size)
{
int *e, *t; //Declaring two int pointers variables
e = a; //assigning e to point the arrays initial element a[0]
t = a + size; // assigning variable t to the array last element
while(e != t)
{
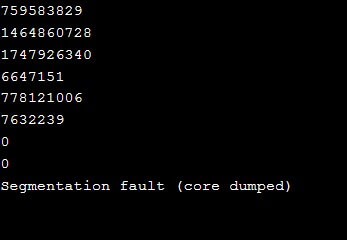
cout << *e << endl; //displays the e
e++; // incrementing ( next element)
}
}
int main()
{
int a[] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20};
pointerarithmetic (a, 20);
return 0;
}Output:
Step 4: Pointer to pointer
- float **fpp;: It denotes two levels of pointers (Multiple indirections). It’s a variable that points to another pointer further points to an object specified in a memory location. For example, fpp be a float pointer currently pointing to memory address 2001, the size of the float is 8 bytes, then by
- fpp++;: indicates fpp pointing to address 2009. Similarly, when the variable is decremented by 1, it will point to the previous location of its base type at address 1993.
Step 5: Pointer to functions
When pointers are passed to a function as arguments, the data items associated with these pointers’ variable are altered within the function and then returned to the calling program; the changes will be retained in the calling program. When a pointer is passed as a parameter, the respective data items are altered globally from within the called function. The pointer is passed by reference.
Functions can be performed in pointers in different ways:
- The function invoked by passing the reference.
- The function invoked by passing a pointer.
Function invoked by passing the reference:
In this, the address is passed as an argument instead of values.
Example:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void changefn(int*, int*);
int main()
{
int n = 5, m = 6;
cout << "Before change" << endl;
cout << "n = " << n << endl;
cout << "m = " << m << endl;
changefn(&n, &m);
cout << "\nAfter change" << endl;
cout << "n = " << n << endl;
cout << "m = " << m << endl;
return 0;
}
void changefn(int* x1, int* x2) {
int s1;
s1 = *x1;
*x1 = *x2;
*x2 = s1;
}Output:
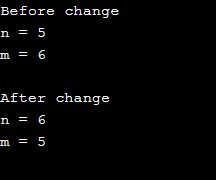
Conclusion
This article intended to refresh the knowledge about how to use pointers in C++ and their basic topics in a simple way with an example. Pointer also is known as a locator, reduces the code statement for higher performance. Pointers plays a vital role in implementing data structures like linked list and programming in the system level. They are a preferable language in embedded systems as they are a good way to access memory directly using pointers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Pointers in C++. Here we discuss the basic concept, why we need it, and how to create pointers in C++ with appropriate examples and output. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


