Updated May 30, 2023

Introduction to PHP mail()
The mail() function helps in allowing the mails to send directly just from the script so easily. It accepts five parameters usually but only the first three of them are mandatory and the other two parameters are optional and not mandatory if all the parameters are mentioned inside of the parenthesis of the mail() function. It helps in sending mail directly from the websites or blogs whenever needed using some form or other. It is a built-in function of the PHP Programming Language which helps in sending some emails from the PHP script or scripts. It is cost-effective when notifying users on important tasks or events.
Syntax and Parameters
Below are the syntax
mail(to1, subject1, message1, headers1, parameters1);Explanation of the parameters of mail() function:
- to1 parameter of mail() function: The “to1” parameter of the mail() function of the PHP Programming language is a mandatory field. It helps in specifying the receiver/receivers of the mail.
- subject1 parameter of mail() function: The “subject1” parameter of the mail() function of the PHP Programming Language is also a mandatory field. It helps in specifying the email’s subject. This parameter may or may not contain any type of newline characters.
- message1 parameter of mail() function: The “message1” parameter of the mail() function of the PHP Programming Language is also a required field just like the above 2 parameters. It helps in defining the message which is going to be sent. Each and every line of it should be separated with some LF (\n). Each Line should not be more than 70 characters. In windows, If FULLSTOP is found at the beginning of a specific line in a message then it may be removed. In order to solve this type of problem, we have to replace the FULL STOP character with the help of the double dot character “..”.
- headers1 parameter of mail() function: The headers1 parameter of the PHP Language is an optional field but it helps in specifying some additional headers which are like Cc, From, Bcc functions. Some of the additional headers will be separated with CRLF – (\r\n). When we are in the process of sending an EMAIL, then it may contain some From header. This can be going to set with this headers1 parameter or in PHP.INI format file.
- parameters1 parameter of mail() function: The parameters1 parameter of the mail function is an optional one. This parameter specifies the additional parameter. It helps in specifying the additional parameter to the email sending program. This setting will be set to the envelope sender address when we use –f send mail option.
How mail() function work in PHP?
The mail() function of the PHP Programming Language works just by helping in sending mails from the PHP script itself directly. It works for PHP 4+ versions. Before PHP 4 version, this mail() doesn’t works so don’t try mail() function if your PHP version is before the PHP 4 version. It works by returning the address parameter’s hash value. But we have to keep in mind that even though the mail is accepted for the delivery but it doesn’t mean that the email is actually received or sent.
The PHP 4.0.5 version is added with the parameter1 parameter. In PHP 4.2.3 PHP version, the parameter1 parameter is disabled in the safe mode. In PHP 4.3.0 version under Windows O.S. accepts some custom headers like Cc, Bcc, From, Date and they are not case-sensitive. In PHP 5.4 version, the header injection protection is added just for the headers parameter purpose. In PHP 7.2 version, the headers1 parameter is also going to accept an array.
Examples
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Here in this example, we are going to implement the mail() function of the PHP Programming Language. Here at first PHP tags are created and inside of it some of the variables are created with some values in it. At first “to_email1” is created with some string value which is the email/gmail address of the specific one which is needed to send the mail. Then the “subject1” variable is created with some string content to display as a subject and then the message variable is created and then it is assigned with some important message text info/other. It is to specify the information to the to_email1 address person. Then header1 variable is created. Then the main PHP function mail() is used. Here 4 parameters are included inside of the mail() function. This function will help in sending a mail with the PHP script itself.
Code:
<?php
$to_email1 = 'name1 @ company .com';
$subject1 = 'Testing the PHP Mail';
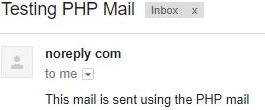
$message1 = 'This mail is sent using the PHP mail function';
$headers1 = 'From: noreply @ company .com';
mail($to_email1,$subject1,$message1,$headers1);
?>Output:
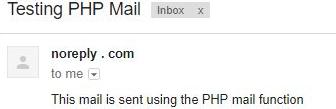
Example #2
This is the example of implementing the custom functions which helps in sending the secure mail to a specific person only with the help of the mail() function inside the PHP script. Here at first a function with some fields are created along with the condition statements. Then “to_email1” variable is created with some email address. Then subject1, messages, and headers1 variables are created. Based on the IF ELSE conditions and the mail() function along with the HTML display elements the program will run and the mail will be sent to the specified email person or other but the PHP.INI file settings should be perfect or use any online compiler if possible.
Code:
<?php
functionsanitize_my_email($field1) {
$field1 = filter_var($field1, FILTER_SANITIZE_EMAIL);
if (filter_var($field1, FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
$to_email1 = 'name @ company .com';
$subject1 = 'Testing PHP Mail';
$message1 = 'This mail is sent using the PHP mail ';
$headers1 = 'From: noreply @ company. com';
//check whether the email address is invalid or not $secure_check
$secure_check1 = sanitize_my_email($to_email1);
if ($secure_check1 == false) {
echo "Invalid input";
} else { //send email
mail($to_email1, $subject1, $message1, $headers1);
echo "This email is now sent using the PHP Mail";
}
?>Output:
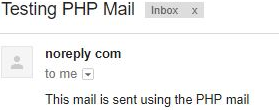
Example #3
This is the example of implementing the PHP mail() function without using the header1 parameter inside of the mail() function of the PHP Programming Language. It is a simple mail but the header1 parameter is not used.
Code:
<?php
$to1 = '[email protected]';
$subject1 = 'The Marriage Proposal';
$message1 = 'Hi Radha, will you marry me? Say Yes or No';
$from1 = '[email protected]';
// Sending email
if(mail($to1, $subject1, $message1)){
echo 'Now Your mail will be sent automatically and successfully.';
} else{
echo 'Now it is Unable to send the email/gmail. Please try again.';
}
?>Output:
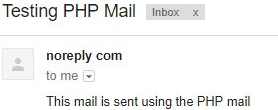
Example #4
This is the example of implementing the PHP mail() function in order to send an attachment file along with the mail. Here at first HTML form is created for some variable values and to get the attachment file. After clicking the submit button the PHP mail() function works with the help of the PHP mail function code. Then the output text will be displayed as shown in the output section below.
HTML File Code:
<html>
<body>
<form enctype="multipart/form-data" method="POST" action="string22.php">
<label>Your Name1 <input type="text" name="sender_name1" /></label><br>
<label>Your Email1 <input type="email" name="sender_email1" /></label><br>
<label>Subject1 <input type="text" name="subject1" /></label><br>
<label>Message1 <textarea name="message1"></textarea></label><br>
<label>Attachment1 <input type="file" name="attachment1" /></label><br>
<label><input type="submit" name="button" value="Submit" /></label><br>
</form>
</body>
</html>PHP File Code:
<?php
if($_POST['button'] &&isset($_FILES['attachment1']))
{
$from_email = '[email protected]'; //from mail, sender email addrress
$recipient_email = '[email protected]'; //recipient email addrress
//Load POST data from HTML form
$sender_name1 = $_POST["sender_name1"] //sender name1
$reply_to_email = $_POST["sender_email1"] //sender email1, it will be used in "reply-to" header
$subject1 = $_POST["subject1"] //subject1 for the email
$message1 = $_POST["message1"] //message1 body1 of the email
//Get uploaded file data using $_FILES array
$tmp_name = $_FILES['my_file']['tmp_name']; // Now get the temporary file name1 of the file on the server
$name = $_FILES['my_file']['name']; // Now get the name of the file1
$size = $_FILES['my_file']['size']; // Now get size of the file1 for size validation
$type = $_FILES['my_file']['type']; // Now get type of the file1
$error = $_FILES['my_file']['error']; // Now get the error (if any)
//It is a validating form field which helps in attaching the file
if($file_error> 0)
{
die('Upload error or No files uploaded');
}
//It is like reading from a specific uploaded file and also the base64_encode content1
$handle1 = fopen($tmp_name, "r"); // Now setting the file handle1 only for reading the file
$content1 = fread($handle1, $size); // Now reading the file
fclose($handle1); // Now close upon completion
$encoded_content11 = chunk_split(base64_encode($content1));
$boundary1 = md5("random"); // Now defining the boundary1 with a md5 hashed value
//Now header
$headers1 = "MIME-Version: 1.0\r\n"; // Now Defining the MIME version
$headers1 .= "From:".$from_email."\r\n"; // Now the Sender Email
$headers1 .= "Reply-To: ".$reply_to_email."\r\n"; // Now Email addrress to reach back
$headers1 .= "content1-Type: multipart/mixed;\r\n"; // Now Defining content1-Type
$headers1 .= "boundary1 = $boundary1\r\n"; // Now Defining the boundary1
//Now this is about plain text
$body1 = "--$boundary1\r\n";
$body1 .= "content1-Type: text/plain; charset=ISO-8859-1\r\n";
$body1 .= "content1-Transfer-Encoding: base64\r\n\r\n";
$body1 .=chunk_split(base64_encode($message1));
//NOw attachment1
$body1 .= "--$boundary1\r\n";
$body1 .="content1-Type: $file_type; name=".$file_name."\r\n";
$body1 .="content1-Disposition: attachment1; filename=".$file_name."\r\n";
$body1 .="content1-Transfer-Encoding: base64\r\n";
$body1 .="X-attachment1-Id: ".rand(1000, 99999)."\r\n\r\n";
$body1 .= $encoded_content11; // NOw Attaching the encoded file with email
$sentMailResult1 = mail($recipient_email, $subject1, $body1, $headers1);
if($sentMailResult1 )
{
echo "This mail is sent using the PHP mail function"; // Now it will be printed only if the file is going to be sent successfully
unlink($name); // Now deleting the file just after the attachment1 is sent.
}
else
{
die("Sorry attachment mail not sent");
}
}
?>Output of HTML Code:
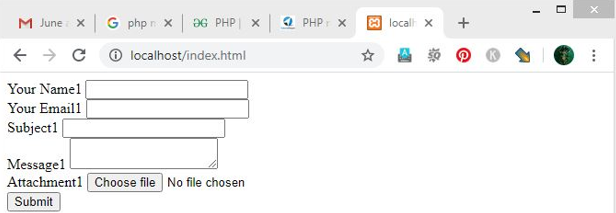
Output of PHP Code:
Conclusion
We hope you learned what is the definition of PHP mail() function along with its syntax and explanation of the parameter of the mail() function, How the mail() function works in PHP along with various examples to under mail() concept better and so easily.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PHP mail(). Here we discuss an introduction to PHP mail(), syntax, parameters with how does it work and examples to implement, You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


