Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to parseFloat in JavaScript
parseFloat() is a global inbuilt function that accepts a string as an input and converts to floating-point numbers which means the floating-point number is parsed to a point where it encounters a character, a non-digit. Float is a data type for decimal numbers which are often used to calculate analog and continuous values as there calculation is difficult. Floating-point numbers can be a maximum of 3.40282347E+38 and a minimum of -3.40282347E+38. These floating-point numbers are always 64- bit. The floating-point represents a decimal integer with decimal points or fractions. Parsing means analyzing and converting a set of instructions into a format so that a runtime environment can run the program.
Syntax:
Number.parseFloat(value);Or
parseFloat(value);Accept a parameter which is a string and converts to a floating-point number. If the first character of the string cant be converted to a number, then the function returns NaN i.e. Not a Number. Typically returns floating-point number up to the point where a character appears which is not a digit.
Examples of parseFloat in JavaScript
Let us consider an example illustrating the above-mentioned theory,
Example #1
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
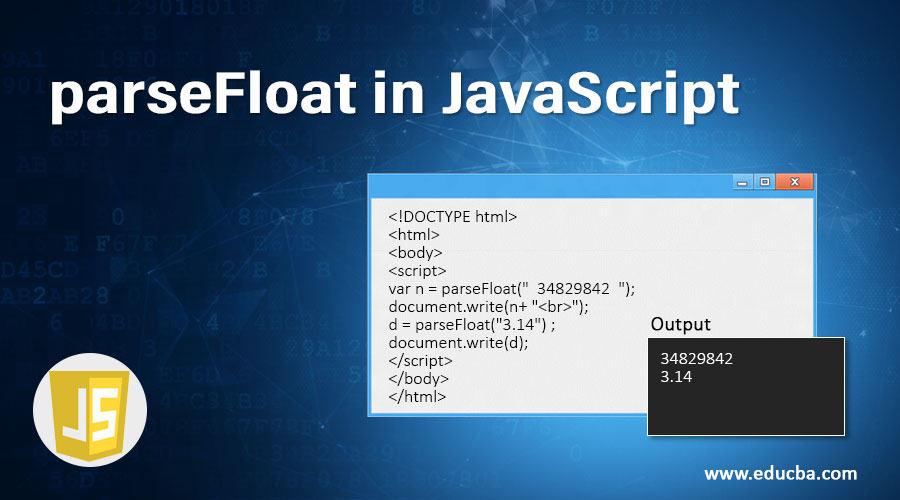
var n = parseFloat(" 34829842 ");
document.write(n+ "<br>");
d = parseFloat("3.14") ;
document.write(d);
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Here, parseFloat() ignores the spaces before and after the input string and only returns the floating-point number i.e 34829842.
Example #2
Using isNaN to check if the input string is a floating digit or character.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
var x = parseFloat("3.45");
if (isNaN(x))
document.write("x is not a number" + "<br>");
else
document.write("x is a number" + "<br>");
var y = parseFloat("howareyou");
if (isNaN(y))
document.write("y is not a number" + "<br>");
else
document.write("y is a number" + "<br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

In Maths, 0/0 is undefined as a real number and is hence represented as NaN. As NaN doesn’t have a value, comparing it to itself returns TRUE. isNaN checks whether a value is NaN (Not – a – Number), returns TRUE if the value is a number and equals to NaN else returns FALSE.
Example #3
Let us see the difference between parseInt() and parseFloat(), using parseInt(), every floating decimal number would be round up to its nearest value i.e if 2.34 would round to 2.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
var x = parseInt("3.67");
var y = parseFloat("3.67");
document.write('Using parseInt("3.67") = ' + x + "<br>");
document.write('Using parseFloat("3.67") = ' + y + "<br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Example #4
Extra-large numbers or extra small numbers can be written with exponential notation.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
var x = parseFloat("432e-4");
var y = parseFloat("432e9");
document.write('Using parseFloat("432e-4") = ' + x + "<br>");
document.write('Using parseFloat("432e9") = ' + y + "<br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
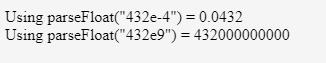
parseFloat() is not a method of any object. If parseFloat() encounters a character but the plus sign (+), minus (-), digits(0-9), decimal or exponent(e or E), parseFloat() returns value up to the character ignoring other invalid characters. Leading and trailing spaces for the values are ignored while parsing. Argument’s first character cant be converted to a digit and returns NaN, can return Infinity, can convert BigInt syntax to numbers as the trailing n character is discarded.
Example #5
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Exploring parseInt() and parseFloat()</title>
<script>
document.write(parseInt( "564.239" ) + "</br>" );
document.write(parseInt( "+564.239" ) + "</br>" );
document.write(parseInt( "-564.239" ) + "</br>" );
document.write(parseInt( "564FGl" ) + "</br>" );
document.write(parseInt( "FGl" ) + "</br>" );
document.write(parseInt( "4px 9px" ) + "</br>" );
document.write(parseInt( "(786)" ) + "</br>" );
document.write(parseInt( "0xF" ) + "</br>" );
document.write(parseInt( "056" ) + "</br>" );
document.write(parseInt( " 564 " ) + "</br>" );
document.write("</br>");
document.write(parseFloat( "564.239" ) + "</br>" );
document.write(parseFloat( "+564.239" ) + "</br>");
document.write(parseFloat( "-564.239" ) + "</br>");
document.write(parseFloat( "564FGl" ) + "</br>");
document.write(parseFloat( "FGl" ) + "</br>");
document.write(parseFloat( "4px 9px" ) + "</br>");
document.write(parseFloat( "(786)" ) + "</br>");
document.write(parseFloat( "0xF" ) + "</br>");
document.write(parseFloat( "056" ) + "</br>");
document.write(parseFloat( " 564 " ) + "</br>");
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Output:

‘0x’ and ‘056’, as we are not treating as base 16 and base 8 respectively, the only difference is parseFloat() returns decimal for values like 564.239 whereas parseInt() returns 564.
Example #6
If there are two decimals, the second decimal is invalid and the parseFloat() method converts string up to that position. String 22.45.32 will be parsed to 22.45.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
document.write(parseFloat( "22.45.32" ) + "</br>" );
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
Example #7
Using Number.parseFloat(strng_value).
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
var a="25";
var b="25.75"
var c="How are you";
var d="25How are you";
var e="25.75How are you"
document.writeln(Number.parseFloat(a)+"<br>");
document.writeln(Number.parseFloat(b)+"<br>");
document.writeln(Number.parseFloat(c)+"<br>");
document.writeln(Number.parseFloat(d)+"<br>");
document.writeln(Number.parseFloat(e));
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Example #8
Before parsing and after parsing the value.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>area of a circle</title>
</head>
<script>
var a="10.67";
var b="23.51";
var c=a+b;
document.writeln("Before invoking parseFloat(): "+c+"<br>");
var c=Number.parseFloat(a)+Number.parseFloat(b);
document.writeln("After invoking parseFloat(): "+c);
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Example #9
Let us see how to calculate simple interest using parseFloat.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Simple Interest</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function simpleInterest()
{
var pa,rate,time;
pa=parseFloat(prompt("Enter Principle Amount"));
rate=parseFloat(prompt("Enter Rate Amount"));
time=parseFloat(prompt("Enter Time(year)"));
document.write(pa + "</br>");
document.write(rate + "</br>");
document.write(time + "</br>");
var si=(pa*rate*time)/100;
document.write("Simple Interest anually is: "+si);
}
</script>
<body>
<center>
<input type="button" value="Calculate Simple Interest" onclick="simpleInterest()" />
</center>
</body>
</html>Output:

On clicking on the button:
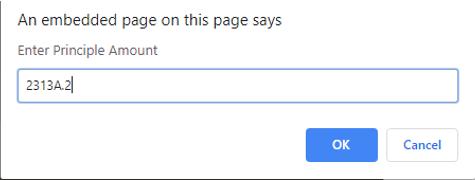
We need to enter the principal amount, similarly have to enter the rate of interest and time.
Principal amount: 2313A.2
Rate: 2.A
Time: 1.2A

Example #10
Calculation of circle radius.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>area of a circle</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function area()
{
var radius;
radius=parseFloat(prompt("Enter radius"));
document.write(radius + "</br>");
var area = 3.14 * radius * radius;
document.write("Area of circle is is: "+area);
}
</script>
<body>
<center>
<input type="button" value="Calculate Area" onclick="area()" />
</center>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
Radius: 3DF.4A

Conclusion
Finally, we can conclude by saying that parsing these float digits can be helpful for complex calculations, as even though the user enters any character, parseFloat restricts only numbers and takes only the number as an input, which is parsing and returns floating value. This javascript function is not vigorous as parseInt() function as it parses the incoming string values to floating-point numbers instead of decimal but can only work with base 10 decimal values, not octal or hexadecimal.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to parseFloat in JavaScript. Here we discuss the basic concept along with top 10 simple examples with code implementation and output. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


