Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to Pandas drop_duplicates()
- Pandas drop_duplicates() function helps the user to eliminate all the unwanted or duplicate rows of the Pandas Dataframe.
- Python is an incredible language for information investigation, essentially in view of the awesome biological system of information-driven Python bundles. Pandas is one of those bundles and makes bringing and investigating information much simpler.
- Pandas help us improve data science by teaching us all about different functions like drop_duplicates, which helps us implement mathematical operations using Python code easily.
- One of the normal information cleaning undertakings is to settle on a choice of the most proficient method to manage copy pushes in an information outline. If the entire column is copied precisely, the choice is basic. We can drop the copied line for any downstream examination.
Syntax and Parameters
Dataframe.drop_duplicates(keep='First', subset='None', inplace='False')Where,
- Keep parameter has full control over which duplicate value to consider, and the program always considers the command first by default. Assuming ‘first,’ it thinks about the first incentive as extraordinary and the rest of indistinguishable qualities from the duplicate. Assuming ‘last,’ it thinks about last as an incentive as special and rests of indistinguishable qualities from the duplicate. Assuming False, it thinks about the entirety of indistinguishable qualities from duplicates.
- Subset takes a segment or rundown of the section name. The default esteem is none. Subsequent to passing sections, it will think of them as duplicates.
- Inplace consists of only Boolean values, which help expel rows with duplicates assuming True.
How drop_duplicates() function works in Pandas?
Now we see various program examples of how drop_duplicates() function works in Pandas.
Example #1
Specify rows that are duplicated on the basis of selecting the specific columns.
Code:
import pandas as pd
df = {'S': [3, 3, 3, 4], 'P': [4, 4, 4, 5], 'A': [6, 6, 7, 8]}
main_df = pd.DataFrame(df)
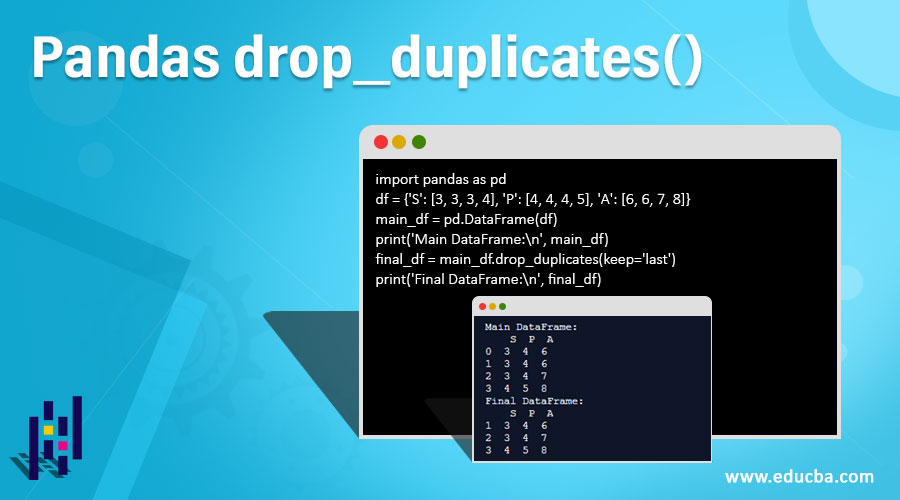
print('Main DataFrame:\n', main_df)
final_df = main_df.drop_duplicates(subset=['S', 'P'])
print('Final DataFrame:\n', final_df)Output:
Explanation: In the above program, we first initialize the dataframe and sort them as different rows and columns. This will be our main dataframe, and we will define various subclasses of this particular dataframe. Here, we define only one sub dataframe which is the final dataframe. We define these 2 dataframes, and using drop_duplicates(), we have to eliminate the values in the specific columns which are duplicates. Here, we define a subset in the final dataframe, and we define 2 columns where the values are repeated. We delete them so that in the final dataframe, only unique values are shown for that particular column.
Example #2
To eliminate the rows using the inplace parameter
Code:
import pandas as pd
df = {'S': [3, 3, 3, 4], 'P': [4, 4, 4, 5], 'A': [6, 6, 7, 8]}
main_df = pd.DataFrame(df)
main_df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True)
print(main_df)Output:

Explanation: In the above program, similarly to before, we define the dataframe, but here, we only work with the main dataframe and not the final dataframe. Here, we eliminate the rows using the drop_duplicate() function and the inplace parameter. We have deleted the first row here as a duplicate by defining a command inplace = true which will consider this particular row as a duplicate and delete it, and produces the output with the rest of the row values.
Example #3
Saving the last row by dropping the other duplicates
Code:
import pandas as pd
df = {'S': [3, 3, 3, 4], 'P': [4, 4, 4, 5], 'A': [6, 6, 7, 8]}
main_df = pd.DataFrame(df)
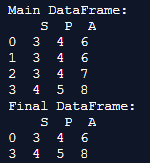
print('Main DataFrame:\n', main_df)
final_df = main_df.drop_duplicates(keep='last')
print('Final DataFrame:\n', final_df)Output:
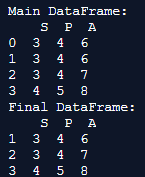
Explanation: Here, we first create the dataframe and call it the main dataframe. The motive here is to eliminate the other duplicates and keep the last row in the output. Hence, we provide the parameter keep = last. This helps in saving the last row and deletes the first row values, and the rest other duplicates are also shown in the output when the code is implemented.
Example #4
Eliminating all the duplicate rows
Code:
import pandas as pd
df = {'S': [3, 3, 3, 4], 'P': [4, 4, 4, 5], 'A': [6, 6, 7, 8]}
main_df = pd.DataFrame(df)
print('Main DataFrame:\n', main_df)
final_df = main_df.drop_duplicates(keep=False)
print('Final DataFrame:\n', final_df)Output:
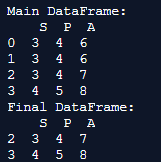
Explanation: Here, we create the dataframe and initialize bother main dataframe and the final dataframe in the program. The main motive is to delete all the rows which have duplicate values and keep the rows that consist of only unique values. To eliminate rows 0 and 1 from the data, where all the values in these rows are duplicates, you can use the functional parameter “keep = false.” This parameter ensures that only rows 2 and 3, which have unique values, are displayed in the output.
Conclusion
A significant piece of Data investigation is breaking down Duplicate Values and expelling them. Pandas drop_duplicates() strategy helps in expelling duplicates from the information outline. Thus, it returns all the arguments passed by the user.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Pandas drop_duplicates()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


