What is Outsourcing?
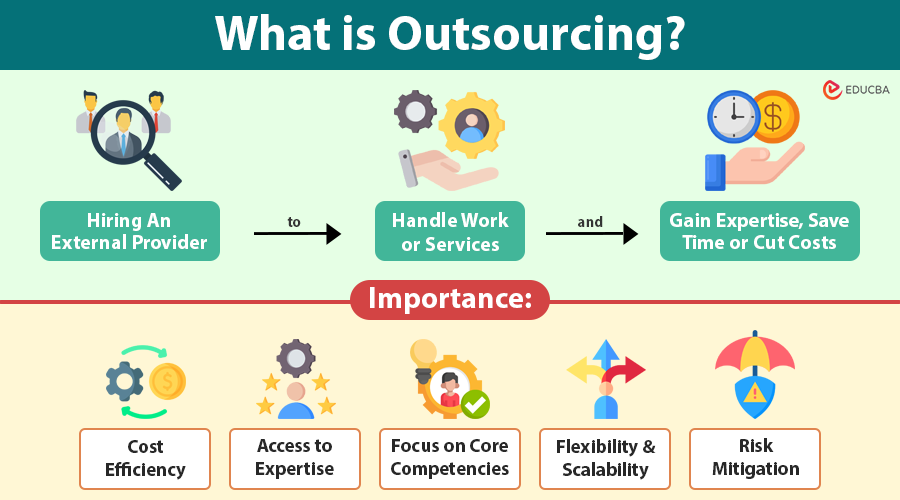
Outsourcing is when a company delegates some of its work or services to an external provider to save time, reduce costs, or access specialized skills. These external providers may be located within the same country or abroad and can offer expertise, resources, or technologies that the company may not possess internally.
Key Points About Outsourcing:
- It can involve core or non-core business functions.
- The outsourcing partner can be another company, a freelance professional, or a specialized agency.
- Services outsourced can range from IT solutions and customer support to payroll management, manufacturing, marketing, and research.
Table of Contents
Importance of Outsourcing
Outsourcing has become a strategic necessity for many businesses due to its multifaceted advantages. It is not just a cost-cutting measure; it is a way to enhance efficiency, competitiveness, and innovation.
Why Outsourcing Matters:
- Cost efficiency: Reduces operational and labor costs by avoiding recruitment, training, and infrastructure expenses.
- Access to expertise: Businesses can leverage global talent pools with specialized skills not available internally.
- Focus on core competencies: Delegating non-core functions allows organizations to concentrate on growth and innovation.
- Flexibility and scalability: It offers the agility to scale operations according to demand, without long-term commitments.
- Risk mitigation: Sharing responsibilities with a specialized provider can reduce operational and compliance risks.
Types of Outsourcing
Outsourcing can be classified based on function, location, and engagement model. Understanding these categories helps businesses choose the most suitable outsourcing strategy.
1. Based on Function
A. IT Outsourcing (ITO)
Involves hiring external vendors for IT services, including software development, cloud services, cybersecurity, application management, and helpdesk support. ITO allows companies to adopt cutting-edge technology without the overhead of an internal IT department.
B. Business Process Outsourcing (BPO)
Delegates non-core functions like customer service, accounting, payroll processing, and data entry. BPO further divides into the following categories:
- Front-Office BPO: Customer-facing operations such as call centers and sales support.
- Back-Office BPO: Internal operations like HR, finance, and accounting.
C. Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO)
Focuses on tasks that require specialized knowledge, such as research, analytics, legal services, and financial consulting. KPO often involves high-level decision-making and complex problem-solving.
D. Manufacturing Outsourcing
Involves contracting production or assembly to third-party manufacturers. This allows companies to focus on product design, marketing, and distribution rather than production logistics.
2. Based on Location
- Onshore outsourcing: Partnering with a vendor within the same country to reduce cultural and language barriers while staying compliant with local regulations.
- Nearshore outsourcing: Outsourcing to nearby countries with similar time zones and cultures helps cut communication delays and lower costs.
- Offshore outsourcing: Contracting work to countries far away, usually to take advantage of lower labor costs, technological expertise, or specialized skills. For example, a U.S.-based company may outsource software development to India or the Philippines.
3. Based on Engagement Models
- Project-based outsourcing: A company outsources a specific project to a vendor, providing a clear timeline, defined deliverables, and a well-defined budget. Ideal for short-term or specialized projects.
- Dedicated team model: A team from the outsourcing provider works exclusively on the client’s projects over a longer period. This model is common in IT and software development.
- Managed services: The outsourcing partner manages an entire business function from end to end, including staffing, operations, quality, and reporting. Commonly used in IT infrastructure management.
Benefits of Outsourcing
Outsourcing offers a competitive advantage by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling businesses to concentrate on their strategic objectives.
- Cost reduction: Reduces the need for full-time staff, training costs, and infrastructure investments.
- Efficiency and productivity: External providers bring experience, processes, and tools that improve output quality and speed.
- Access to global talent: Organizations can work with specialists worldwide, gaining access to skills they lack internally.
- Flexibility and scalability: Companies can quickly scale operations up or down depending on business demands.
- Focus on core business: Frees internal resources to concentrate on growth, product development, and customer engagement.
- Innovation: Outsourcing partners often introduce new technologies, processes, and creative solutions.
Challenges of Outsourcing
While it offers numerous advantages, it is not without risks. Organizations must carefully evaluate potential pitfalls:
- Quality control issues: Ensuring the outsourced work meets company standards can be difficult.
- Communication barriers: Time zone differences, language, and cultural variations can lead to misunderstandings.
- Security risks: Sharing sensitive information with external companies can increase the risk of data breaches and leaks.
- Dependency on vendors: Over-reliance on external providers may hinder internal skill development.
- Hidden costs: Poorly managed contracts, revisions, or delayed deliverables can lead to increased overall costs.
Best Practices for Effective Outsourcing
To achieve successful outcomes, companies should follow best practices:
- Define clear objectives: Clearly define why you are outsourcing, the specific tasks you will delegate, and the expected outcomes.
- Select the right partner: Assess vendors based on their expertise, reliability, compliance, and cultural alignment.
- Maintain strong communication: Utilize meetings, project management tools, and updates to maintain transparency.
- Implement effective security measures: Ensure data protection and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Monitor performance: Utilize KPIs, SLAs (Service Level Agreements), and performance reports to measure results effectively and efficiently.
- Start small: Pilot projects can help assess vendor capabilities before scaling up.
- Foster collaboration: Encourage integration between internal teams and outsourced teams for better results.
Future Trends in Outsourcing
Outsourcing is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, globalization, and shifting business demands. Emerging trends include:
- Automation and AI integration: Companies are automating routine tasks in BPO and KPO to reduce human error and increase efficiency.
- Remote work integration: It increasingly leverages remote work models for flexible staffing solutions.
- Strategic outsourcing: Companies are moving beyond cost reduction to outsourcing high-value, knowledge-intensive functions.
- Sustainable outsourcing: Focus on ethical practices, environmental responsibility, and social compliance.
- Data-driven outsourcing: Outsourcing partners are increasingly using analytics to drive insights and improve business outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Outsourcing has become a cornerstone strategy for businesses seeking to remain competitive in a global marketplace. When implemented effectively, it enables organizations to reduce costs, enhance efficiency, access specialized expertise, and concentrate on their core business objectives. However, success requires careful planning, strong partnerships, and robust performance management. By understanding the types, benefits, challenges, and best practices of outsourcing, businesses can leverage it as a powerful tool for growth, innovation, and strategic advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How do companies choose what to outsource?
Answer: Companies typically outsource non-core activities or tasks requiring specialized skills, such as IT support, payroll, customer service, or manufacturing, while retaining strategic and critical business functions in-house.
Q2. What legal considerations should companies keep in mind when outsourcing?
Answer: Companies should address intellectual property protection, confidentiality agreements, compliance with local and international regulations, and clearly defined service-level agreements (SLAs) in outsourcing contracts.
Q3. How do companies measure the success of outsourcing?
Answer: Success is measured using KPIs, SLAs, performance metrics, cost savings, quality of service, customer satisfaction, and adherence to timelines and project objectives.
Q4. Can outsourcing be used for short-term projects?
Answer: Absolutely. Project-based outsourcing is ideal for short-term, specialized tasks that require external expertise, without the need for long-term commitments.
Q5. How do companies manage the cultural and language barriers in outsourcing?
Answer: Effective strategies include selecting vendors with compatible cultures, offering cross-cultural training, scheduling overlapping work hours, and utilizing collaboration tools to ensure clear communication.
Q6. Is outsourcing secure for handling sensitive data?
Answer: Outsourcing can be safe if companies use NDAs, encrypt data, control access, and follow rules like GDPR or HIPAA.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on outsourcing helped you understand its significance and practical applications. Explore our related articles on: