Updated May 17, 2023

Introduction to Oracle SYS_CONTEXT()
SYS_CONTEXT is nothing but an Oracle function that returns relevant information of the current Database session. This function helps to retrieve information about Oracle Environment. This is a parameter based function that accepts parameters and returns the corresponding value of that parameter.
Points of Concentration:
- This function returns information about the current instant.
- This function can be used in SQL or PL / SQL statements.
- It must be executed locally
- SYS_CONTEXT function evaluates once per SQL statement execution.
- The Function returns the output as a VARCHAR2 data type.
- The default length of the output is 256 bytes.
Syntax
Oracle SYS_CONTEXT function syntax is as follow
SYS_CONTEXT (Namespace, Parameter, [, Length])
Explanation:
- Namespace: It is a valid ORACLE SQL Identifier. It must be already created.
- Parameter: It can be any string. It’s not case sensitive. The length of the parameter must be less than or equal to 30 bytes (length <= 30 bytes). An attribute or value of this parameter must be already set using the DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT procedure.
- Length: It is optional. It is used to change or override the length using the ‘length’ parameter. The valid range of length parameter is 1 to 4000 bytes. Oracle ignores invalid length range and uses the default range. The default range of return value is 256 bytes.
Operators used with Oracle SYS_CONTEXT()
‘USERENV’ is an Oracle’s built-in Namespace. It is an SQL identifier and is used to retrieve the information of the current database session. The associated parameters with the namespace are information variables.
The parameters are listed below which are associated with namespace ‘USERENV’ are useful to retrieve current session information in the database: All listed parameters are available in Oracle 11g version.
| Parameter | Description |
Length (bytes) |
| ACTION | It returns application name | 32 |
| AUDITED_CURSORID | It returns the cursor id of the SQL | NA |
| AUTHENTICATION_DATA | Returns Authentication data that are being used for login | 256 |
| AUTHENTICATION_TYPE | Returns type of user’s authentication i.e. Database, OS, Network, etc. | 30 |
| BG_JOB_ID | Returns the job id of the current session if Oracle establishes background process, else returns NULL | 64 |
| CLIENT_IDENTIFIER | Returns client identifier is set by the application through DBMS_SESSION.SET_IDENTIFIER procedure | 64 |
| CLIENT_INFO | Returns the user’s session info that is stored using the DBMS_APPLICATION_INFO package. | 64 |
| CURRENT_SCHEMA | Returns the name of the default schema of the current schema | 30 |
| CURRENT_SCHEMAID | Returns ID of the default schema of the current session | 30 |
| CURRENT_SQL
CURRENT_SQLn |
It returns the first 4k bytes SQL that triggered for audit and n is an integer from 1 to 7 that return subsequent 4k bytes increment. If n=2 then it returns 8k to 12k bytes. | 4 |
| CURRENT_USER | Returns the current user name | 30 |
| CURRENT_USERID | Returns current user-id | 30 |
| DB_DOMAIN | Returns database domain name that is specified in the DB_DOMAIN initialization parameter. | 256 |
| DB_NAME | Returns database name that is specified in the DB_NAME initialization parameter. | 30 |
| DB_UNIQUE_NAME | Returns database name that is specified in the DB_UNIQUE_NAME initialization parameter. | 30 |
| ENTRYID | Returns current audit entry number | 30 |
| EXTERNAL_NAME | Returns the external name of the DB user | 256 |
| FG_JOB_ID | Returns job id that establishes by the client foreground process in the current session else NULL. | 30 |
| GLOBAL_CONTEXT_MEMORY | Returns number that is being used by the globally accessed context in the system global area | NA |
| HOST | Returns client’s machine name | 54 |
| INSTANCE | Returns current instance identification number | 30 |
| IP_ADDRESS | Returns client’s machine IP address | 30 |
| ISDBA | Returns TRUE if a user is DBA else FALSE | 30 |
| LANG | Returns ISO abbreviation for the language | 62 |
| LANGUAGE | Returns the language, territory of the current session in this form:language_territory.characterset | 52 |
| MODULE | Returns application name | 48 |
| NETWORK_PROTOCOL | Returns communication network protocol | 256 |
| NLS_CALENDAR | Returns calendar of the current session | 62 |
| NLS_CURRENCY | Returns currency of the current session | 62 |
| NLS_DATE_FORMAT | The returns date format of the current session | 62 |
| NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE | Returns language for expressing dates | 62 |
| NLS_SORT | Returns type of sorting Binary or Linguistic | 62 |
| NLS_TERRITORY | Returns Territory name of the current session | 62 |
| OS_USER | Returns OS user name who initiated database session | 30 |
| PROXY_USER | Returns user name who initiated database session on behalf of SESSION_USER | 30 |
| PROXY_USERID | Returns the ID of the PROXY_USER | 30 |
| SERVICE_NAME | Returns the service name which is connected in the given session | 64 |
| SESSION_USER | Returns database user name who authenticated current user | 30 |
| SESSION_USERID | Returns the ID of the SESSION_USER | 30 |
| SESSIONID | Returns identifier of an auditing session | 30 |
| STATEMENTID | Returns number of SQL statements that audited in a given session | NA |
| TERMINAL | Returns OS identifier for the client of the current session. | 10 |
Examples to Implement Oracle SYS_CONTEXT() function
Below are some examples mentioned:
Example #1
In this section we’ll see the implementation of Oracle SYS_CONTEXT ( )function and its behavior.
Code:
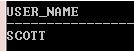
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','CURRENT_USER') User_name FROM DUAL;
Output:
Explanation: In the above example parameter, ‘CURRENT_USER returns the user name of the session in which the SQL statement gets executed. But this parameter is being deprecated, so it won’t be available for the use. Use the SESSION_USER parameter instead.
Example #2
Code:
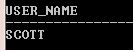
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','SESSION_USER') User_name FROM DUAL;
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, parameter ‘SESSION_USER’ being used instead of ‘CURRENT_USER and it returns the same output.
Example #3
Code:
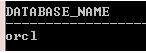
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','DB_NAME') Database_Name FROM DUAL;
Output:
Explanation: In the above example parameter, ‘DB_NAME’ returns the Database name of the current session in which the SQL statement gets executed.
Conclusion
Oracle SYS_CONTEXT () function is a very useful function to retrieve the relevant information about the current database session. By using Oracle Regular Expressions various useful or important information about the current session can be retrieved that helps us to find out where the SQL is running who or how many users are logged on, the status of the session, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle SYS_CONTEXT(). Here we discuss an introduction to Oracle SYS_CONTEXT(), syntax, operators, examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –