Updated May 15, 2023
Introduction to Oracle decode
Oracle provides a decode function to the user in which we add procedural if – then – else to the specified query. In the decode function it compares the expression value with each search value one by one. If expression is equal to the search value then it returns the results that correspond to the oracle database. if the expression value does not match with the search value at that time it returns the default value. In another situation if the default value is omitted at that time oracle returns the null value. The decode function is suitable for Oracle 12c, Oracle 11g, Oracle 10g and Oracle 9i.
Syntax:
decode (actual expression, search value, search result [, search value, search result]……….[, default])
Explanation:
- In above syntax we used decode function.
- actual expression: Is value to compare, it is automatically converted to data type that is used for first search value before comparing.
- search value: This is the value we compared with actual expression. Similarly here all search values are automatically converted to the data type that is used for the first search value before comparing.
- search result: It is used to display the search result that means if actual expression is equal to search value then it returns the result.
- default: This is optional keyword, if there is no matches are found the decode function oracle returns the default value, if sometimes default value is omitted then it returns the null value (if decode function does not found any match value).
How decode Function Works in Oracle?
Now let’s see how the decode function works in Oracle:
Basically decode function is used to find any match value by using if – then – else statement.
Different types of arguments that we use in Oracle decode function are as follows:
1. Numeric Types
It is used as a number, binary_float or binary_double. In which if the first search pair is the numeric at that time oracle decode function compares all search result expressions and in first search expression it finds which value is the highest numeric precedence and remaining argument convert to that data type and decode function returns the particular data type.
2. Character Types
If actual expression and search value are the characters at that time oracle decodes function compare them by using the non padded comparison semantics. If search value, actual expression and the result can be any one of the data types such as char, varchar2, nchar or nvarchar. At that time oracle decode function returned string is varchar2 data types and it is the same character set as the first search result parameter. Short – circuit – evaluation is used in Oracle database.
It evaluates the search value before the comparison to the actual expression value rather than all search values. If the previous search result is equal to the actual expression at that time evaluation is terminated. Oracle decode function converts actual expression and search value to the data type of first search value before the comparison and it converts the return value to first search result data type.
Example of Oracle decode
Given below is the example of Oracle decode:
Code:
SELECT
DECODE(2, 2, 'Two')
FROM
dual;
Explanation:
- This is a very simple example of decode function, in which the Oracle decode function compares the first search argument value with the second search argument value.
- Note here both argument values are equal then the decode function in Oracle returns the second argument value which is the string ‘Two’. When we execute the above query then final output we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
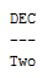
Now let’s create a new table name as college by using the create table statement as follows.
Code:
create table college (college_id int, college_name VARCHAR(20));
Explanation:
- In the above example we created a college table with different attributes as shown in the above statement.
- When we execute the above query then final output we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
![]()
Now we can insert some records into the college by using the insert into statement.
Code:
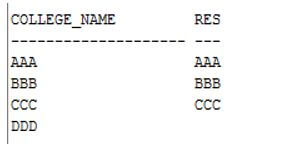
select college_name, DECODE(college_id, 001, 'AAA', 002, 'BBB', 003, 'CCC', ‘GATEWAY’ ) result from college;
Explanation:
- In the above example after inserting records into the college table we apply the decode function on the college table as shown in the above statement. Here we compare the college_id and college_name and we compare the first search value with the next search value.
- When we execute the above query then final output we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Now let’s see how it is equivalent to if – then – else statement as follows.
Code:
if college_id = 001 then
result := ‘AAA’;
elsif college_id = 002 then
result := ‘BBB’;
elsif college_id = 003 then
result := ‘CCC’;
else
result := ‘GATEWAY’;
end if;
Explanation:
- In the above statement the decode function compares each college_id value one by one as shown in the above statement.
- In a similar way we can implement different examples of decode function, suppose users need to compare the two different dates at that time we can use decode function for example if date1 > date2 in this example decode function returns date2 otherwise decode function should return date1.
Rules and Regulations for decode
- Decode function returns the value that has the same data type as the first search result from the list.
- If the first search result is null then its return value is converted to varchar2 data type.
- If the first search result data type is char at that time return value is converted to varchar2.
- If there are no matches found then it returns the default value.
- If default value is omitted and there is no search found at that time oracle decodes returns the null value.
Conclusion
From this article we saw the basic syntax of decode function and we also see different examples of decode function. From this article we saw how and when we use the Oracle decode function.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle decode. Here we discuss the introduction, how decode function works in Oracle? example, rules & regulations for decode. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

