Updated May 17, 2023
Introduction to Oracle Data Types
In the Oracle database, you define a data type as a fixed set of properties that associates with every value of every column. In a broader sense, it means that every value has a data type, which is linked to specific storage or memory properties, such as memory space, a particular range that a value associated with that data type can extend to, and a specific set of constraints. It is specified for each column present in a table in a database.
List of Oracle Data Types
Given below is the list of Oracle data types:
1. Character Data Type
Given below are the different character data types.
- Char (size): It is used to store fixed-length character strings. It has a maximum size of 2000 bytes.
- varchar2(size): It is used to store variable-length character strings. It has a maximum size from 1 byte to 4KB.
- nvarchar2(size): It stores variable-length Unicode character strings. The upper limit is 4000 bytes.
- Long: It is also used to store variable-length strings, and it is backward compatible. It can be used to store up to 2 gigabytes.
- raw: It is a variable-length binary string. It has a maximum size of 2000 bytes.
- Long raw: It is variable-length binary strings and backward compatible. It has a maximum size of 2GB.
Example:
In this example, we will create a table t1 with three columns, each with a different character data type, and then insert a row of data into these columns. Once we have done that, we will use DUMP() function to find the details of each column.
Code:
Creating table:
CREATE TABLE t1 (
x CHAR(10),
b VARCHAR2(10),
z raw(10)
);
Inserting values in table:
INSERT INTO t1(x, b, z )
VALUES('Nil', 'Nil', '');
Selecting table:
SELECT
x,
DUMP(x),
b,
DUMP(b),
z,
DUMP(z)
FROM
t1;
Let us execute the queries in SQL developer and check the result.
Output:
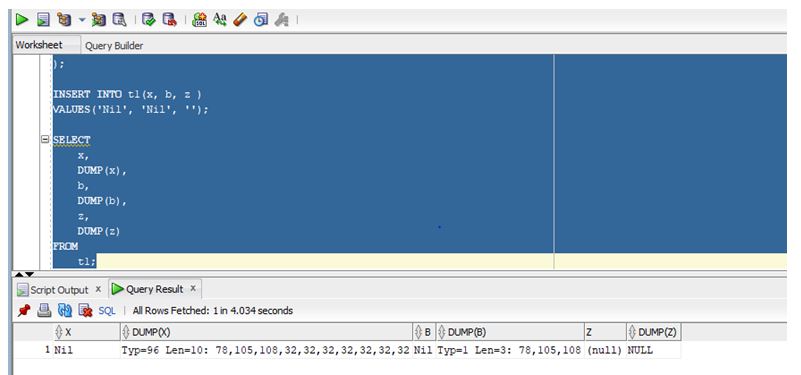
As shown in the above screenshot, the DUMP function returns the detailed information of the x, b, and z columns.
2. Numeric Data Type
Given below are the different numeric data types present in Oracle:
- number(p, s): This is a numeric data type with two arguments ’p’ is for precision, and ‘s’ is scale. For example, if the number(8, 3) means it has five digits before the decimal and three digits after the decimal. The precision range from 1 to 38, and the scale is from range -84 and 127.
- dec(p, s): It is a float type numeric data type where ‘p’ is precision and ‘s’ is scale. The precision ranges from 1 to 38. Here also, dec(3, 1) means 2 digits before the decimal and one digit after the decimal.
Example:
In this example, we are going to create a table named number_example with two columns x and y, which is of data type number and dec. Once the table is created, we are going to insert some data and then check the contents of the table by using a SELECT command.
Code:
Creating table:
CREATE TABLE number_example (
x NUMBER(6, 2), y dec(6,2)
);
Inserting values into the table:
INSERT INTO number_example
VALUES(100.99, 101.99);
INSERT INTO number_example
VALUES(80.552, 11.552);
Selecting table:
select * from number_example;
Let us run the queries in SQL developer and check the result.
Output:
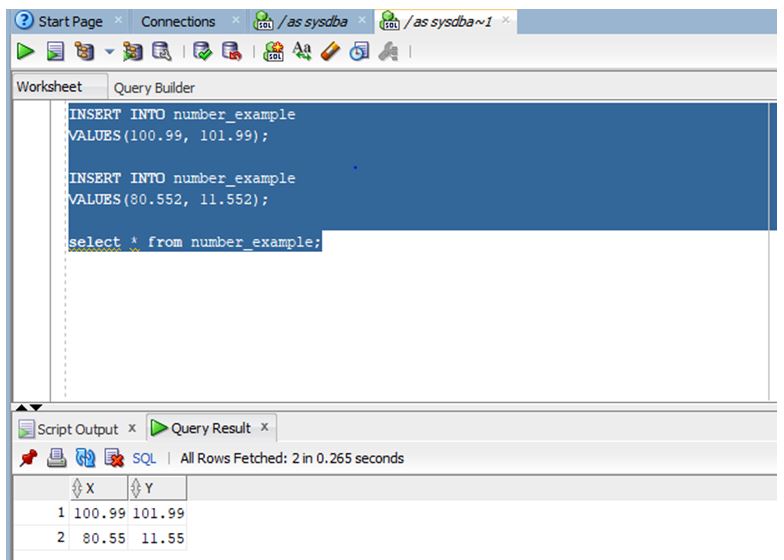
You can see on the screenshot that the size was declared as (6, 2), so it rounded the contents of the second row to two digits after the decimal.
3. Date Data Type
We are going to declare the Date data types.
- date: As the name suggests, it is used to store date-type string values.
- timestamp: It gives fractional seconds precision, and it will be a number between 0 and 9.
Example:
In this example, we will create a table data_example with columns x and y having data types as DATE and TIMESTAMP, respectively. We will then insert a row with values for both columns and then use the SELECT statement to see the contents of the table.
Code:
Creating table:
CREATE TABLE date_example (
x DATE, y TIMESTAMP(2)
);
Inserting values into table:
INSERT INTO date_example
VALUES(sysdate, LOCALTIMESTAMP(2));
Selecting table:
select * from date_example;
Let us execute the queries in SQL Developer and check the result.
Output:
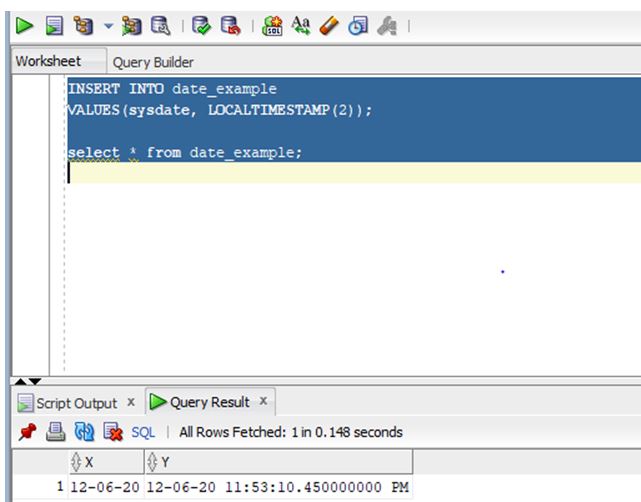
As we can see, the column with the TIMESTAMP data type gives us more accurate fractional time as compared to the Date type.
4. Large Object Data Type
- blob: It is a type of data type that stores large unstructured binary objects, and it can store up to 4 GB of binary data.
- clob: It stores single-byte and multi-byte character data, and it can also accommodate up to 4 GB of character data.
- nclob: It is used to store Unicode data. It can store up to 4 GB of character text data.
- ROWID data types: Rowid is a fixed-length binary data, and the format is BBBBBBB.RRRR.FFFFF, where BBBBBBB is the block in the database file, RRRR is the row in the block, and FFFFF is the database file.
Example:
Each row in an Oracle database has an address. In this example, we will try to get the row address by querying the pseudo column rowid which is of type ROWID.
Code:
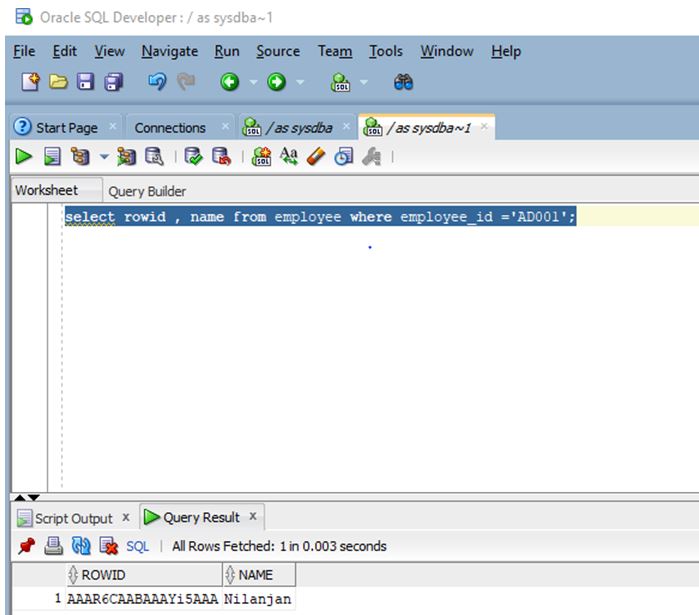
select rowid , name from employee where employee_id ='AD001';
Let us now execute the query in SQL developer and check the result.
Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Oracle Data Types” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

