Updated June 8, 2023

Introduction to Operator Precedence in C++
The operator precedence determines which operator is to be first evaluated and which next in expression when one or more operators present in an expression. the other term which is related to expression is operator associativity. Operator associativity which determines the direction of operator evaluation of the same operator precedence, associativity can be left to right or right to left.
Lets take an example: x = 10 + 22 / 2.
In the above example, the result is 21, not 16 because the ‘/’ operator has higher precedence than the ‘+’ operator.
Lets take an example: x = 10 -20+ 22 / 2.
In the above example, the result is 1, not 19 because the same as above ‘/’ operator has higher precedence than the ‘+’ operator and ‘+’ and ‘-‘ operator is of the same precedence and their associativity is left to right so the expression evaluates as –
- x = 10 – 20+ 22 / 2
- x=10 – 20+11
- x=-10+11
- x=1
So, Operators Precedence and operator Associativity are two characteristics of operators that specify the order of evaluation in an expression.
Top 15 Operator Precedence in C++
Next, we see the operator precedence and associativity in C++ in the below table where the highest operators are at the top and lowest precedence operator at the bottom:
|
Category |
Operator |
Associativity |
| Postfix | ‘()’,‘[]’, ‘.’, ‘->’,‘++’,‘- -‘ | L -> R |
| Unary | ‘-‘, ‘+’,‘~’, ‘!’,‘–‘, ‘++’,‘&’, ‘*’, ‘(type)’, ‘sizeof’ | R -> L |
| Multiplicative | ‘/’, ‘*’, ‘ %’ | L -> R |
| Additive | ‘-‘, ‘+’ | R -> L |
| Shift | ‘>>’, ‘<<’ | L -> R |
| Relational | ‘>’, ‘>=’, ‘<’,‘<=’ | L -> R |
| Equality | ‘!=’, ‘==’ | R -> L |
| Bitwise AND | ‘&’ | L -> R |
| Bitwise XOR | ‘^’ | L -> R |
| Bitwise OR | ‘|’ | R -> L |
| Logical AND | ‘&&’ | L -> R |
| Logical OR | ‘||’ | L -> R |
| Conditional | ‘?:’ | R -> L |
| Assignment | ‘=’,‘+=’,‘-=’,‘*=’,‘/=’, ‘%=’, ‘>>=’, ‘<<=’, ‘&=’,‘^=’, ‘|=’ | R -> L |
| Comma | , | L -> R |
Examples to Implement Operator Precedence in C++
Below are mentioned the examples:
Example #1
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// declare variables
int a = 10, b=22, c=2, x;
// expression
x= a + b / c;
// display result
cout<<"The result of the expression is = "<<x;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
Explanation: As in the code, the expression is evaluated and output is 21, not 16 because the ‘/’ operator is first performed and then ‘+’ operator performed, so expression is solved as x = a + ( b / c ).
Example #2
Next, we rewrite the above c++ code to understand the operator precedence overload with the following example:
Code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// declare variables
int a = 10, b=22, c=2, x;
// expression
x = ( a + b ) / c;
// display result
cout<<"The result of the expression is = "<<x;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
Explanation: As in the code, the expression is evaluated and output is 16, not 16 because the ‘( )’ is first performed ( as subexpression) which is having ‘+’ operator so it is performed’ and then ‘/’ operator is performed.so an expression is solve as x = ( a + b ) / c.
Example #3
Next, we write the c++ code for operator associativity with the following example:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// declare variables
int a = 10, b=22, c=2, x;
// expression
x = a == b != c;
// display result
cout<<"The result of the first expression is = "<< x <<endl;
x = a == ( b != c );
cout<<"The result of the second expression is = "<<x <<endl;
return 0;
}Output:
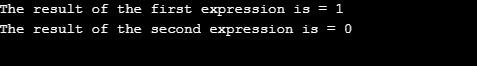
Explanation: As in the above code the first expression operators == and != have the same precedence and the associativity is left to right so first == and then != operator performed. And in the second expression first != and then == operator performed. So first expression is solve as:
- x = a == b != c
- x = 10 == 22 != 2
- x=0 != 2
- x=1
- and second expression is solve as –
- x = a == (b != c)
- x = 10 == (22 != 2)
- x=10 == 1
- x=0
Example #4
Next we write the c++ code for operator associativity with the following example:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// declare variables
int a = 10, b=22, c=2, x;
// expression
x = a > b > c;
// display result
cout<<"The result of the first expression is = "<< x <<endl;
x = a < b < c;
cout<<"The result of the second expression is = "<<x <<endl;
return 0;
}Output:
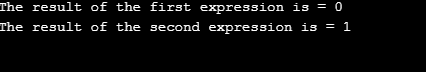
Explanation: As in the above code, the first expression contains>operator whose associativity is left to right. Therefore the expression becomes ((a > b) > c), which becomes (0 > 2), so output is 0. And the second expression contains>operator whose associativity is left to right. Therefore the expression becomes ((a< b) < c), which becomes (1 < 2), so output is 1.
Conclusion
Operator precedence is the main characteristic of operators, which determines which operator is to be first evaluated and next in expression when one or more operators present in an expression and the associativity of the operator determine the direction of operator evaluation of the same operator precedence in an expression.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Operator Precedence in C++. Here we discuss the operator precedence and associativity in C++ and examples to implement. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


