Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction on Object in C++
C++ is an object-oriented programming language; everything in it is correlated with the class and object. The class will correspond to the blueprint of something similar to the real-life entity, and it will define it. The object can be considered as the actual real-life entity of the blueprint. An object plays a very important role in the C++ language; it will be used almost everywhere while programming. Everything in C++ plays around the Object; hence it is necessary to understand the object in C++.
How to Create an Object in C++?
Before we create an actual object, it is necessary to have its class to be already created. As mentioned above, a class is like a blueprint, and an object will be instantiated using that class. A class will define what will be there in and for the object. Basically, the class defines two main things. First is the attributes or a thing that can be expressed as some quantity or anything; it is known as a data member in C++ analogy. The second thing defined will be of some kind of verb or action or anything we can perform; this is known as a member function. The member function (second term) will act upon the data members (first term) defined in a class.
Now we will see how can we create an object in C++.
First, Let’s see the example where we will define the simple class.
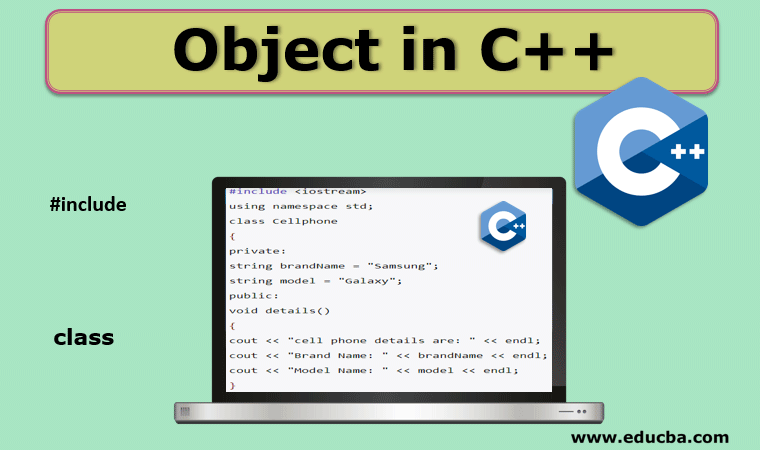
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cellphone
{
private:
string brandName = "Samsung";
string model = "Galaxy";
public:
void details()
{
cout << "cell phone details are: " << endl;
cout << "Brand Name: " << brandName << endl;
cout << "Model Name: " << model << endl;
}
};As can be seen, for example, that we have defined a class with the name Cellphone.
Let’s create an object of this class; an object is an actual instantiation of a class. Below is an example of creating an object. Creating an object of a class is very simple.
int main()
{
Cellphone obj; //defining an object of type Cellphone
return 0;
}The class is a user-defined datatype, and in our example, it is a Cellphone. As you can see, the syntax of defining an object is simple in a manner. It starts with the name of the class for which we are creating an object, followed by the name of an object which is of user choice. In this example, we have defined the object of class Cellphone with the name as an obj in the main method. We can also define the object anywhere else in the program following the scope.
Properties of an Object in C++
In the above section, we said that we define two things while defining a class; the first one is the attributes. These attributes or values declared specifically in class are known as “properties”. Every class or object will have corresponding properties related to it. In our example of class Cellphone, we already have defined properties as brandName and model. The properties will be related to the class; this makes it easy to understand the code.
Let’s add one more property named cellNo in our example.
class Cellphone
{
private:
string brandName = "Samsung";
string model = "Galaxy";
int cellNo = 123;
public:
void details()
{
cout << "cell phone details are: " << endl;
cout << "Brand Name: " << brandName << endl;
cout << "Model Name: " << model << endl;
}
};As you can see, we have added a new property cellNo with the data type of it as Integer.
Properties in C++ achieves data encapsulation and data hiding. As the properties correspond to data, we are wrapping it up into the defined class, which means data is encapsulated. And in our example, we have declared data fields in private modifiers; due to this, nobody outside this class can access the fields defined. This achieves data hiding in C++.
Methods of an Object in C++
The second thing which we declare in class is methods. Anything that relates to action or activity can be defined in the methods of the class. In our example, we have defined one method called details. It’s a public method that prints the details of the Cellphone. Methods are nothing but functions that are defined in a class. Methods are used to perform actions specifically related to the class. We can perform anything as per requirement in the methods. The class methods can access the public as well as privately defined data members.
Let’s add one more method to our example. This method will display the cell number of the Cellphone.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cellphone
{
private:
string brandName = "Samsung";
string model = "Galaxy";
int cellNo = 123;
public:
void details()
{
cout << "cell phone details are: " << endl;
cout << "Brand Name: " << brandName << endl;
cout << "Model Name: " << model << endl;
}
void cellNumber()
{
cout << "Cell Number: " << cellNo << endl;
}
};We have added one new method, cellNumber(). This method will display the cell number on the screen. As we have declared an object already, we will call both the methods and will see the output. Calling the method using the object is an easy task.
int main()
{
Cellphone obj; // defining an object of type Cellphone
obj.details(); // call method details() of class
obj.cellNumber(); // call method cellNumber() of class
return 0;
}Output:
cell phone details are:
Brand Name: Samsung
Model Name: Galaxy
Cell Number: 123
Conclusion
So, an object plays an important role in C++. Everything in C++ revolves around an Object. To declare an object, it is necessary to define the class of it. Each object will have two types of fields properties and methods. Properties correlate to data variables/members, and methods correlate to functions acting upon the data members. Data members and methods together provide data encapsulation and data hiding features easily.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Object in C++. Here we discuss How to Create an Object in C++ with the Properties and Methods of an Object. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


