Updated April 19, 2023

Introduction to NumPy stack
The following article provides an outline for NumPy stack. Python provides different functions to the users. To work with arrays, the python library provides a NumPy function. The stack() characteristic is used to be a part of a sequence of equal dimension arrays alongside a new axis. The axis parameter of array specifies the sequence of the new array axis in the dimensions of the output. For example, suppose axis=0 that means it determines the first dimension and if axis=-1 that means it determines the last dimension. NumPy is an acronym for numerical python. Basically, NumPy is an open source project. NumPy performs logical and mathematical operations of arrays. Therefore, processing and manipulating can be done efficiently.
Syntax:
numpy.stack(Arr, Axis)Explanation:
- Arr: In the above syntax the first parameter is Arr means array, it is used to define a sequence of equal dimension arrays with the same shape of array.
- Axis: It is the final output array along with the input array.
How stack Function work in NumPy?
- We must install Python on our system.
- We must install numpy using the pip command.
- We required basic knowledge about Python.
- We required basic knowledge about stack function with parameters.
- We required basic knowledge about arrays.
- We can perform different operations using a numpy stack function.
Examples of NumPy stack
Given below are the examples of NumPy stack:
Example #1
For if Axis=0 and Axis=1.
Code:
import numpy as snp
A_x = snp.array([ 2, 3, 4] )
print ("First Input Array: \n", A_x)
A_y = snp.array([ 5, 6, 7] )
print ("Second Input array : \n", A_y)
A = snp.stack((A_x, A_y), axis = 0)
print ("\n ", A)
B = snp.stack((A_x, A_y), axis = 1)
print ("\n ", B)Explanation:
- We import NumPy functions and use them as snp.
- We declared variable two input arrays such as A_x and A_y with array values.
- We tried to print the value of the input array with their values respectively.
- Then we used a stack function with both input arrays along with axis values 0 and 1 respectively.
- Finally we have printed both resultant output arrays with axis value.
- In the above example we implemented a stack function with axis values 0 and 1.
Output:

Example #2
For if Axis= 0, Axis=1 and Axis=-1.
Code:
import numpy as snp
A_x = snp.array([[ 2, 3, 4], [ -2, -3, -4]] ) #input array
print ("First Input Array : \n",A_x)
A_y = snp.array([[ 5, 6, 7], [ -5, -6, -7]] ) #input array
print ("Second Input array : \n", A_y)
A = snp.stack((A_x,A_y), axis = 0) # Array with axis=0
print (" 0: \n ", A)
B = snp.stack((A_x, A_y), axis = 1) # Array with axis=1
print (" 1: \n ", B)
C = snp.stack((A_x, A_y), axis = -1) # Array with axis=-1
print (" -1: \n ", C)Explanation:
- We import NumPy functions and use them as snp.
- We declared variable two input arrays such as A_x and A_y with array values.
- We tried to print the value of the input array with their values respectively.
- Then we used a stack function with both input arrays along with axis value 0, 1 and -1 respectively.
- Finally we tried to print both resultant output arrays with axis value.
- In the above example we implemented a stack function with axis values 0, 1 and -1.
Output:
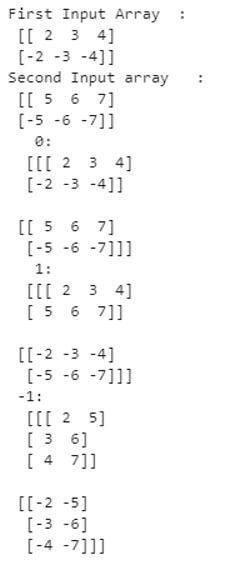
Example #3
For if Axis = 1 and Axis = 2.
Code:
import numpy as snp
A_x = snp.array([ 1, 2, 3] ) #input array
print ("First Input Array : \n",A_x)
A_y = snp.array([ 4, 5, 6] ) #input array
print ("Second Input array : \n",A_y)
A = snp.stack((A_x, A_y), axis = 1) # Array with axis=1
print (" \n ", A)
B = snp.stack((A_x, A_y), axis = 2) # Array with axis=2
print (" \n ", B)Explanation:
- We import NumPy functions and use them as snp.
- We declared variable two input arrays such as A_x and A_y with array values.
- We try to print the value of the input array with their values respectively.
- Then we used a stack function with both input arrays along with axis values 1 and 2 respectively.
- Finally we try to print both resultant output arrays with axis value.
- In the above example we implemented a stack function with axis values 1 and 2. See in this example it only executes an array with axis 1 and when we assign axis 2 at that time it shows an error message as axis 2 is out of bounds for array dimension 2.
Output:

![]()
Example #4
For if Axis= 1 , Axis=2 and Axis=-1 with shape function.
Code:
import numpy as np
arrays = [np.random.randn(4, 5) for _ in range(10)] #input array
A_x = snp.stack(arrays, axis=0).shape #Array with axis=0
print("\n", A_x)
A_y = snp.stack(arrays, axis=1).shape #Array with axis=1
print("\n", A_y)
z = np.stack(arrays, axis=2).shape #Array with axis=2
print("\n", z)Explanation:
- We import numpy functions and use them as snp.
- We declared a random array.
- We try to print the value of the input with their array values respectively.
- Then we used a stack function with both input arrays along with axis values 1 and 2 respectively.
- Finally we try to print both resultant output arrays with axis value.
- In the above example we implemented numpy stack with shape function.
Output:

Conclusion
From the above article we saw basic syntax of NumPy stack functions. We also saw how we can implement them in python with different examples. From this article we also saw how we can handle NumPy stack functions in python.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to NumPy stack. Here we discuss the introduction and working of NumPy stack along with different examples and code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


