
Introduction to Nested Structure in C
Any programming language has its own way of defining and describing structures. So Nested structures as its name suggest in C is kind of defining one structure inside another structure. Any member variables can be defined inside a structure and in turn, that structure can further be moved into another structure. The variables inside a structure can be anything like normal or pointer or anything and can be placed anywhere within the structure.
Nested Structure can be accessed in two ways:
- Structure inside a structure in C using the pointer variable.
- Structure inside a structure in C using a normal variable.
Syntax:
Following is the syntax for creating a nested structure:
structure tagname_1
{
var_1;
var_2;
var_3;
.
.
.
.
var n;
structure tagname_2
{
var_1;
var_2;
var_3;
.
.
.
var_n;
}, mem1
} mem2;Working of Nested Structure in C
From the above syntax, we can infer the fact that mem1 structure nested inside member1 structure will contain the member or the variable to be accessed and everyone can be accessed in a nested manner by using. (dot) operator.
- mem2.mem1.var_1: This refers to the first member of the variable of the structure tagname_1.
- mem2.mem1.var_2: This refers to the second member of the variable of the structure tagname_2.
We will take more examples to get clarity on how the syntax satisfies the working of the nested structure.
Examples #1
struct employee
{
struct man
{
char name [20];
int age;
char dob[10];
} d;
int empid;
char desg[10];
} emp;In the above example, man structure is defined inside an employee structure which is a nested structure. Members within the nested structure which is a man can be accessed using the below syntax or format.
Like in the given example
- employee.d .name: It tells about the name of the man inside the employee structure.
- employee.d .age: It will tell about the age of the man as an employee.
It is important to bring into notice one thing like this structure man within employee structure cannot be reused which means it cannot be called again anywhere in the entire code because It is not self-generated.
Instead, a workaround for this can be:
We could have defined the structure outside and then could have declared the variable inside the structure wherever we want to access it throughout the code.
Examples #2
Struct man
{
char name[20];
int age;
char dob [10];
};Also, this structure can be reused by the outer structure.
struct employee
{
struct man info;
int id;
char desg [10];
}The advantage of using this type of structure declaration is that we can declare a variable of type struct man anywhere throughout the program.
Let’s see an example of how nesting of structure within itself is not allowed.
struct teacher
{
char name[20];
char address[100];
int age[];
struct teacher principal; // totally invalid way to create nested structure.
}
Examples of Nested Structures in C
Below are the different examples of nested structure in C:
Example #1 – Initialization of nested structures
Initialization of nested structures is possible at the time of declaration.
Code:
struct student
{
struct person info;
int rollno;
float marks[10];
}
struct student student_1 = {
{"Anji", 26, 1995},
103,
92
};Example
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
struct person
{
char name[20];
int age;
char dob[10];
};
struct student
{
struct person info;
int roll_no;
float marks;
};
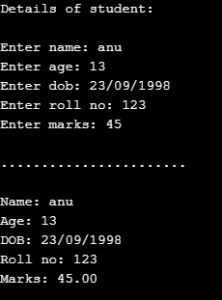
int main ()
{
struct student p1;
printf("Details of student: \n\n");
printf("Enter name: ");
scanf("%s", p1.info.name);
printf("Enter age: ");
scanf("%d", &p1.info.age);
printf("Enter dob: ");
scanf ("%s", p1.info.dob);
printf("Enter roll no: ");
scanf("%d", &p1.roll_no);
printf("Enter marks: ");
scanf ("%f", &p1.marks);
printf("\n.......................\n\n");
printf("Name: %s\n", p1.info.name);
printf("Age: %d\n", p1.info.age);
printf("DOB: %s\n", p1.info.dob);
printf("Roll no: %d\n", p1.roll_no);
printf("Marks: %.2f\n", p1.marks);
return 0;
}Output:
Example #2 – Accessing of members inside nested structure using Pointers
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct student_college_info
{
int college_id;
char college_name[50];
};
struct student_info
{
int id;
char name[20];
float percentage;
struct student_college_info clg_data;
} stu_data, *stu_data_ptr;
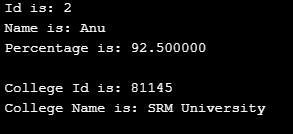
int main()
{
struct student_info stu_data = {2, "Anu", 92.5, 81145,
"SRM University"};
stu_data_ptr = &stu_data;
printf(" Id is: %d \n", stu_data_ptr->id);
printf(" Name is: %s \n", stu_data_ptr->name);
printf(" Percentage is: %f \n\n",
stu_data_ptr->percentage);
printf(" College Id is: %d \n",
stu_data_ptr->clg_data.college_id);
printf(" College Name is: %s \n",
stu_data_ptr->clg_data.college_name);
return 0;
}Output:
Example #3 – Passing structure member as arguments to function
Code:
struct teacher
{
char name [20];
int id;
int marks;
};
void print_struct (char name [], int id, int marks);
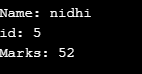
int main ()
{
struct teacher tea = {"nidhi", 5, 52};
print_struct (tea.name, tea.id, tea.marks);
return 0;
}
void print_struct (char name [], int id, int marks)
{
printf ("Name: %s\n", name);
printf ("id: %d\n", id);
printf ("Marks: %d\n", marks);
printf("\n");
}Output:
Example #4 – Structure inside structure using a normal variable
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct student_college_detail
{
nt college_id;
char college_name[50];
};
struct student_detail
{
int id;
char name[20];
float percentage;
struct student_college_detail clg_data;
} stu_data;
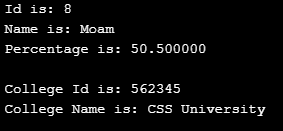
int main()
{
struct student_detail stu_data = {8, "Moam", 50.5, 562345,
"CSS University"};
printf(" Id is: %d \n", stu_data.id);
printf(" Name is: %s \n", stu_data.name);
printf(" Percentage is: %f \n\n", stu_data.percentage);
nbsp;
printf(" College Id is: %d \n",
stu_data.clg_data.college_id);
printf(" College Name is: %s \n",
stu_data.clg_data.college_name);
return 0;
}Output:
Example
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct student
{
int id1;
int id2;
char e;
char f;
float percentage;
};
int main ()
{
int i;
struct student recrd1 = {3, 4, 'C', 'B', 80.5};
printf ("size of structure in bytes: %d\n",
sizeof(recrd1));
printf ("\nAddress of id1 = %u", &recrd1.id1);
printf("\nAddress of id2 = %u", &recrd1.id2 );
printf("\nAddress of a = %u", &recrd1.e );
printf("\nAddress of b = %u", &recrd1.f );
printf("\nAddress of percentage = %u”, &recrd1.percentage);
return 0;
}Output:
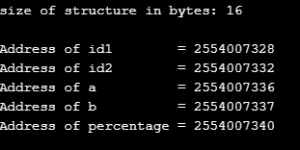
Conclusion
Structures in C is a very interesting way to cluster and group all user-defined member variables and functions into one entity. But still, it has some limitations like it does not allow structure variables and entire structure to contain the build-in datatypes and no use of operators. Therefore in the mere future maybe these features can be taken care of.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Nested Structure in C. Here we discuss the working in Nested Structure in C along with different examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following article to learn more –


