Updated March 8, 2023
Difference Between Naive Bayes vs Logistic Regression
The following article provides an outline for Naive Bayes vs Logistic Regression. An algorithm where Bayes theorem is applied along with few assumptions such as independent attributes along with the class so that it is the most simple Bayesian algorithm while combining with Kernel density calculation is called Naive Bayes algorithm. We can scale Naive Bayes based on our requirements. Probability of certain behavior or class based on the available data is determined with the help of regression analysis otherwise called Logistic regression. The data is predicted and the relationship between given data is explained with the help of logistic data.
Head to Head Comparison Between Naive Bayes vs Logistic Regression (Infographics)
Below are the top 5 differences between Naive Bayes vs Logistic Regression:
Key Difference Between Naive Bayes vs Logistic Regression
Let us discuss some of the major key differences between Naive Bayes vs Logistic Regression:
- When we have correlated features for both Naive Bayes and logistic regression, correlation happens with labels by making predictions so that when the labels are repeating, there are more chances for making the repetitive features the prominent ones in the Naive Bayes algorithm. This will not happen in Logistic regression as the repeating features are counted less number times making it compensate with the repetition. There is no optimization in Naïve Bayes making it to calculate the entries of features directly. But we cannot add different features for the same problem here.
- Naive bayes calculates directly from the features aiming in more perfection but gives poor results if the features are more. It does not consider the calibrations and if there are dependency in the features, it will consider that and add into the feature making it more prominent. If the feature is giving negative impact, this will give poor results. This is not a problem in Logistic regression as calibration of the features happen on time when the features are added more number of times giving exact results. Naïve bayes individually counts the classes and gives result based on the more number of feature count in a particular class. The classes are separated in Logistic regression making it to identify the prominent feature based on calibration.
- Naive Bayes is mostly used to classify text data. For example, to identify whether the mailbox has spam, this algorithm can be used to find spam emails based on some terms within the mail. Email text is taken as input where there are no dependent features to be considered. Linear combination of inputs is considered to give binary output where features to be dependent or independent is not considered as a point to classify the data.
- The error is higher in Naive Bayes making it a grave mistake if the classification is done on a small amount of data and if there are dependent features which were ignored while doing the algorithmic calculation. Hence, Naïve Bayes is not a go-to solution always for any classification problems. The error is less in Logistic regression where we can find the answers easily for dependent or independent features with large data.
- Training data is directly taken into consideration while making assumptions in Logistic regression. Training data is not considered directly but a small sample is taken in Naïve Bayes classification. Logistic regression discriminates the target value for any input values given and can be considered as a discriminative classifier. All the attributes are accounted for in the Naive Bayes algorithm.
Naive Bayes vs Logistic Regression Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Naive Bayes vs Logistic Regression:
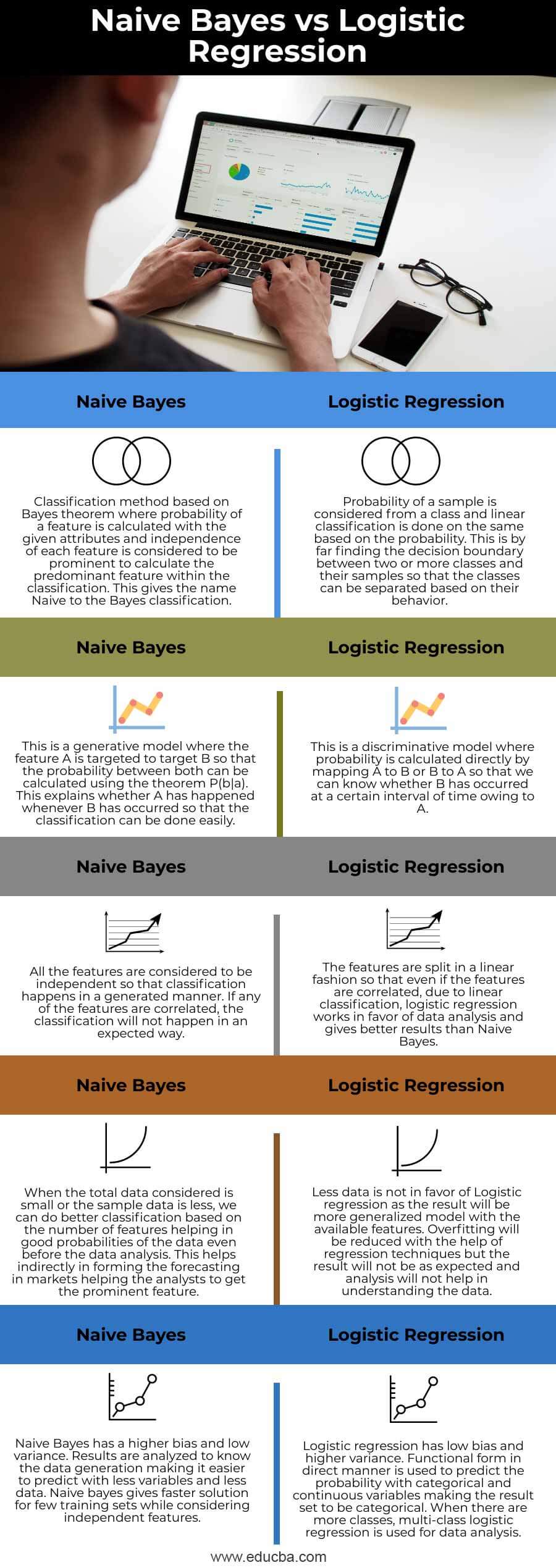
| Naive Bayes Classification | Logistic Regression |
| Classification method based on Bayes theorem where the probability of a feature is calculated with the given attributes and independence of each feature is considered to be prominent to calculate the predominant feature within the classification. This gives the name Naive to the Bayes classification. | Probability of a sample is considered from a class and linear classification is done on the same based on the probability. This is by far finding the decision boundary between two or more classes and their samples so that the classes can be separated based on their behavior. |
| This is a generative model where feature A is targeted to target B so that the probability between both can be calculated using the theorem P(b|a). This explains whether A has happened whenever B has occurred so that the classification can be done easily. | This is a discriminative model where probability is calculated directly by mapping A to B or B to A so that we can know whether B has occurred at a certain interval of time owing to A. |
| All the features are considered to be independent so that classification happens in a generated manner. If any of the features are correlated, the classification will not happen in an expected way. | The features are split in a linear fashion so that even if the features are correlated, due to linear classification, logistic regression works in favor of data analysis and gives better results than Naive Bayes. |
| When the total data considered is small or the sample data is less, we can do better classification based on the number of features helping in good probabilities of the data even before the data analysis. This helps indirectly in forming the forecasting in markets helping the analysts to get the prominent feature. | Less data is not in favor of Logistic regression as the result will be a more generalized model with the available features. Overfitting will be reduced with the help of regression techniques but the result will not be as expected and analysis will not help in understanding the data. |
| Naive Bayes has a higher bias and low variance. Results are analyzed to know the data generation making it easier to predict with less variables and less data. Naive bayes give a faster solution for few training sets while considering independent features. | Logistic regression has low bias and higher variance. Functional form indirect manner is used to predict the probability with categorical and continuous variables making the result set to be categorical. When there are more classes, multi-class logistic regression is used for data analysis. |
Conclusion
Both the classifiers work in a similar fashion but the assumptions considered along with the number of features differ. We can do both the classifications on the same data and check the output and know the way how data performs with both the classification. These are the two most common statistic models used in machine learning.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Naive Bayes vs Logistic Regression. Here we discuss key differences with infographics and comparison table respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

