Updated June 3, 2023
Difference Between MySQL Union vs Union All
Mysql union and union all operators are used to get the combined result set two or more tables for two subqueries which involve using a select clause to retrieve the same number and type of columns from both subqueries. Both union and union all clauses have the same requirement and purpose but just with some differences in how both will retrieve the final result set.
In this article, we will study the syntax and usage of unions and all clauses, along with their similarities and differences. We will also learn about the implementation of union and union all in mysql along with the help of an example.
Syntax of Union clause:
The syntax of the union clause in mysql is as shown below:
First select query
UNION
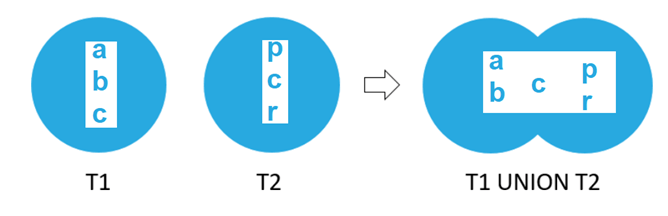
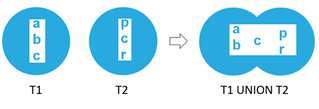
Second select queryThe working of the union operator can be understood from the below Venn diagram example where one of the data set retrieved from the first subquery gives the output a,b,c while the dataset retrieved from the other query is p,c,r and when both these queries are combined with union operator in between the final resultset gives only one occurrence of c which is duplicated in both the resultset. Hence, it can be said that the union operator only combines the result and retrieves the unique values.
Example of Union Operator
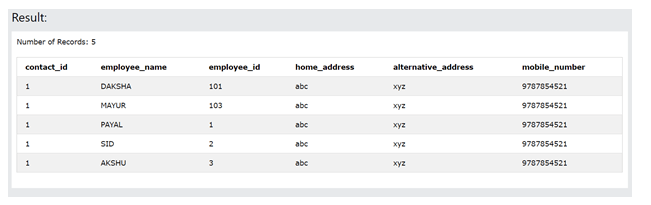
Two tables are considered here, namely employee_details which stores the data related to the employees, and the other one is customer_details which is kept for storing the contact-related information in the table. Both this table contains the names of the employee and the employee id. Let us see what are the contents of each of the tables firstly –
SELECT * FROM [employee_details]SELECT * FROM [contact_details]If we perform union on both the tables using the following query, unique result set data values are retrieved combining data of both the tables as shown below –
SELECT employee_id, f_name FROM employee_details
UNION
SELECT employee_id, employee_name FROM contact_details
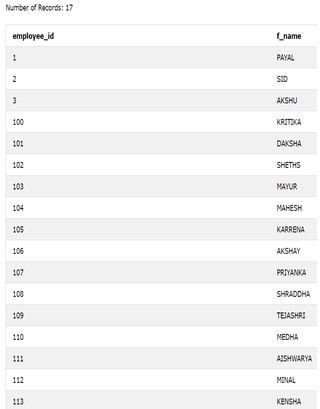
ORDER BY employee_id;The output of the above query statement is as shown below –
Syntax of Union All clause –
The syntax of the union clause in mysql is as shown below –
First select query
UNION ALL
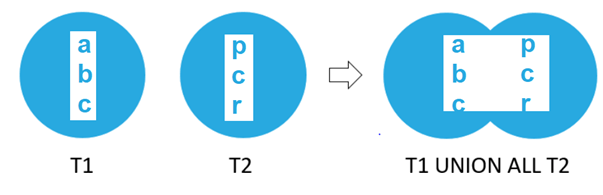
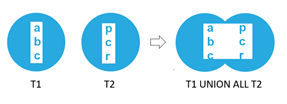
Second select queryWhen the same example is considered, and between the two queries union all operator is applied; it gives the output of elements a,b,c,p,c,r which contains a duplicate occurrence of the c value as it is present in both the data sets. Hence, the union combines the result but also retrieves the duplicate values.
Example of Union All Operator
One of the examples where we have implemented a union operator is as shown below –
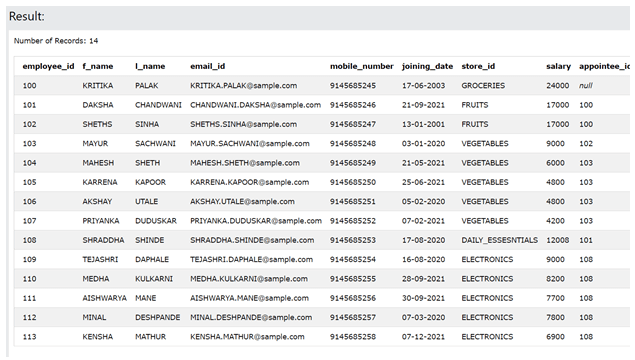
SELECT employee_id, f_name FROM employee_details
UNION ALL
SELECT employee_id, employee_name FROM contact_details
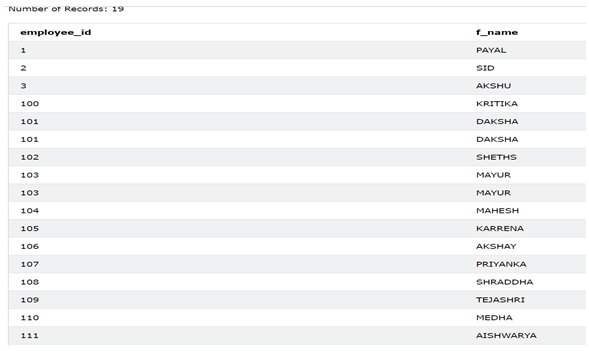
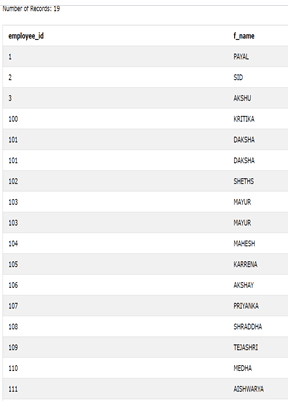
ORDER BY employee_id;The output of the above query statement is as shown below –
The records of employee id with 101 and 103 have the same employee_id in both the tables and the same f_name column value; that’s why both occurrences of it persist in the output of the union of all operators.
Head to Head Comparison between MySQL Union vs Union All (Infographics)
Below are the top 8 differences between MySQL Union vs Union All:
Key Differences between MySQL Union vs Union All
Some of the key differences between MySQL Union vs Union All are:
The most critical feature that needs to be pointed out over here is that in case of a union operator, combining the data from two sources eliminates the duplicate entries retrieved from both datasets and keeps only one of its entries. In the case of the union of all operators, none of the elimination is performed, and the duplicate values are held in the final result set.
MySQL Union vs Union All Comparison Table
Let us discuss the top comparison between MySQL Union vs Union All:
| Union | Union All |
| When applied to the two subqueries retrieving a particular data set, the UNION operator combines them and returns the final result set containing unique occurrences of data retrieved from both tables. | When applied to the two subqueries retrieving a particular data set, the UNION ALL operator combines them. It returns the final result set, which may contain any occurrences of data values retrieved from both tables. |
| The default behavior of the UNION operator involves eliminating all the duplicate values from the combined data set retrieved from both datasets. | There is no such default behavior in the case of the UNION ALL operator. |
| The working of the UNION operator is much slower because after combining the data from the two tables, it also has one more step to perform: eliminating all the duplicate values. | The execution of the UNION ALL operator is comparatively faster because it only carries out a combination of two data sets. |
| Database designers and users prefer to use the union operator as it retrieves unique results. Most frequently used as compared to UNION ALL. | Database designers and users do not much prefer them. However, it depends upon the requirement of which operator will be used. |
The syntax of the UNION operator is –
|
The syntax of the UNION ALL operator is –
|
| Venn diagram for representing the working of union operator is as shown below –
The c data value is present in both data sets. Hence, the final result considers only one occurrence of it. |
Venn diagram for representing the working of union all operator for same data sets is as shown below –
Even though c is present in both data sets, both occurrences are retained in the final result set. |
One of the examples where we have implemented a union operator is as shown below –
The output of the above query statement is as shown below – Even though the records of employee id with 101 and 103 have the same employee_id in both the tables and the same f_name column value. Still, only one of the occurrences of it persisted in the output of the union operator. |
One of the examples where we have implemented a union operator is as shown below –
The output of the above query statement is as shown below – The records of employee id with 101 and 103 have the same employee_id in both the tables and the same f_name column value; that’s why both occurrences of it persist in the output of the union of all operators. |
Conclusion
The union operator and union operator both do the same job of combining the result set. The only significant difference in their working is that the union operator eliminates the duplicate entries from the final result set. In contrast, the union of all operators persists the duplicate entries as well.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Union vs Union All” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.