
Introduction to MySQL today()
In MySQL, the Today() function is a built-in MySQL Date function that provides today’s date value, where we will be using MySQL stored procedures and functions. With this MySQL Today() function, we will learn to create a special type of MySQL stored program by implementing the CREATE FUNCTION query statement.
In MySQL Today() function, we will build a Date function using some of the MySQL Date functions to access the single Date value, thus called a built-in date utility code. In general, developers use stored functions in MySQL to summarize mutual formulas or implement specific rules that can be reused across multiple SQL statements or stored programs.
Syntax
To get MySQL Today() function to result in today’s date, we will use the built-in functions of the date data type. We must create your own MySQL Today() function as a stored program. As we know CURDATE() function or CURRENT_DATE() function in MySQL provides the current date, and we also use it most of the time to retrieve the current date or time in MySQL queries.
Now, we can replace this MySQL CURDATE() function or CURRENT_DATE() function with MySQL Today() function to make the query statements more comprehensible. This is possible by the succeeding SQL command code structure firstly:
DELIMITER $$ // creating stored function program
CREATE FUNCTION FunctionName(
Parameter1,
Parameter2,….
)
RETURNS Data_Type // Declare the datatype
[NOT] DETERMINISTIC
BEGIN
RETURN Replaceable_Stored_FunctionName; // statements
END$$
DELIMITER ; // end of the procedureExplaining the terms of the above syntax below:
- FunctionName specifies the name we give to the stored function when using the CREATE FUNCTION keyword to name and create it.
- The stored function name followed us; we need to list all the parameters we wanted to mention within the parentheses. All these parameters are the MySQL IN parameters by default, so we cannot state OUT, INOUT, or IN modifiers to those parameters.
- With the RETURNS statement, we will specify the valid MySQL Data type for which we are creating the stored program function.
- Then, we must state the DETERMINISTIC keyword to make the function either deterministic or not. In a deterministic function, it also returns the identical result for similar parameters as inputs, whereas, in a non-deterministic one, it outputs different values for similar parameters as inputs. But MySQL uses the NOT DETERMINISTICkeyword option by default if we do not set anyone.
- Between the BEGIN and END keyword blocks, we can write the code in this body for the stored function. In the body block section, at least a single RETURN query statement should be mentioned, which returns the result value to the calling function. On execution, the stored function terminates instantly if the RETURN query is visited.
After executing the properly stored program syntax above, using valid names for functions, parameters, and data types, the stored function will be created in the MySQL database. We can call the newly built stored program with the following MySQL query and execute the output as desired:
SELECT FunctionName();The term “FunctionName” is mentioned in the above syntax of the stored program function.
How does MySQL Today() Function work?
Let us consider accessing today’s date by implementing the built-in date functions to provide the current date in the MySQL database.
Sometimes, from the database table rows, we want to fetch data having a date column with the Date data type as today, and then the query will be written as:
SELECT ColumnName FROM TableName WHERE ExpiredDate = Today;To acquire today’s date, we can use either the CURRENT_DATE() or CURDATE() function with the query as follows:
SELECT CURRENT_DATE() Today;Output:
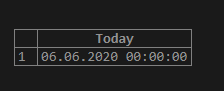
Also, you can use the NOW() function or SYSDATE() function to select the date part from the present date-time resulting by the function as shown follows:
SELECT DATE(SYSDATE()) Today;Output:
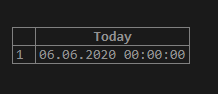
Now, we can alter the query with the following one:
SELECT ColumnName FROM TableName WHERE ExpiredDate = CURRENT_DATE();But suppose the column ExpiredDate includes both date and time types; then you can apply DATE() in MySQL to get them just the date value and equate it with the current value of date:
SELECT ColumnName FROM TableName WHERE DATE(ExpiredDate) = CURRENT_DATE();Examples to Implement Today() function in MySQL
To understand MySQL Today(), we can replace the CURRENT_DATE() function when we use this function many times in the queries.
For this, let us create a stored function named Today() in MySQL with the syntax stated below:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION Today()
RETURNS DATE
BEGIN
RETURN CURRENT_DATE();
END$$
DELIMITER ;Execute the above command in the MySQL database, and you will see that the Today() function is created as a stored program. Now, you can call and utilize it in your query statements.
To implement the created program, we will run the following query with the Today() function along with the MySQL SELECT keyword to fetch the current value of the date:
SELECT Today()Today_Date;Output:
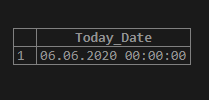
Now, with this MySQL Today() function, a built-in date function with the stored program to output the current date, we can use it to fetch the date of the next day, i.e., tomorrow or more upcoming days. The query can be written as simply as the code below to get tomorrow’s date or the day after tomorrow’s date:
SELECT Today() + interval 2 day Day_after_tomorrow_date;Output:
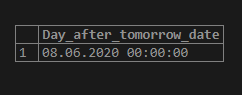
Here, the interval keyword determines the interval value and unit.
Again, let us consider fetching the data which is of either the previous day or, say, yesterday, using the MySQL Today() function as follows:
SELECT Today() -interval 2 day Day_before_yesterday_date;Output:

Conclusion
Likewise, we can also learn and develop the desired function of date or other valid data types in MySQL by applying the stored program and execute it and use it in our MySQL queries. Thus, The MySQL Today() function is a unique stored program we create and query to obtain the current date values. We can use it in MySQL statements to provide the desired output.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL today()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

