Updated May 16, 2023

Introduction to MySQL Temporary Table
MySQL Temporary Table is a provisional table created in a database to fetch and store the result rows for the short term. That allows us to use it again many times within a session. The Temporary table is known to be very manageable when it is difficult or costly to fetch data with the SQL query having only a SELECT keyword statement along with the JOIN MySQL clauses. Therefore, in such a condition, we can design a Temporary table to keep the instant data result set and then apply another SQL query to execute it.
Syntax
The basic syntax is similar to that of the table Create a statement. Simply put, a Temporary table is generated using the CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE query with a new keyword TEMPORARY added.
The MySQL statement syntax for the Temporary table is:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE TableA(Col1_Definition, Col2_Definition, …… , TableConstaints);But to create a table with an identical structure as per the existing table, we cannot apply this CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE… LIKE query statement. For this, let us introduce a different syntax for the temporary table:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE Temporary_TableName
SELECT * FROM Original_TableLIMIT 0;How Temporary Table Works in MySQL?
MySQL Temporary Table is characterized by the special features below:
We can issue a Temporary table name similar to a standard table, but the existing main table will be inaccessible after it is generated. If you perform any query for the table, it will now apply to the temporary table. But when you delete the temporary table then, the permanent table now becomes available to access and manage things. Generally, it is not recommended to use the same name for both the temporary and permanent tables because it may produce any misunderstanding and possibly may lead to any data loss from the database table unknowingly or suddenly.
Further, for example, during the session time, in case your connection to the MySQL server fails, suppose you again get connected to the server after a while. Now, you cannot distinguish between the temporary and actual tables in this session condition. Then, you may need to query a DROP table statement to delete the table, which will remove the original table instead of the temporary one, making an exceptional case. But you can avoid this crucial situation by using the DROP TEMPORARY Table query statement to remove the provisional table.
How to create MySQL Temporary Table?
We will learn some steps to create the MySQL Temporary Table. Also, firstly let us create a permanent table, Customer, which will work as a sample database table for the examples below using the following SQL statement:
CREATE TABLE Customer(CustomerID INT NOT NULL , CustomerName VARCHAR(255), Credit_Limit DEC(10,2), City VARCHAR (255), PRIMARY KEY (CustomerID));And inserting a few values for data into the Customer table by the below query:
Code:
INSERT INTO Customer(CustomerID, CustomerName, Credit_Limit, City) VALUES ('101','Nikhil','2800','Delhi'),
('102','Chetan','3000','Mumbai'),
('103','Akash','1700','Jaipur'),
('104','Divya','2000','Delhi'),
('105','Ravi','2700','Bareilly');Output:
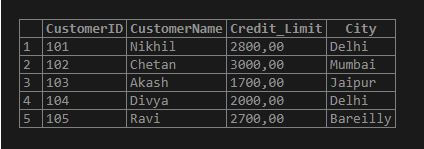
Example #1 – To create a simple Temporary table
Let us first create a new temporary table with the name customer having credits using the following SQL statement:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE Credit(CustomerIDINT PRIMARY KEY, Credit_Limit DEC(10,2));We will insert a few records from the original Customer table into the temporary Credit table. The SQL statement goes like this:
Code:
INSERT INTO Credit(CustomerID, Credit_Limit)
SELECT CustomerID, Credit_Limit FROM Customer WHERE Credit_Limit >0;Output:
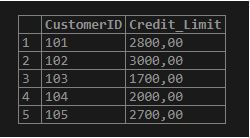
Example #2 – To create a temporary table based on a query example
We will here produce a temporary table that holds data of the top 3 customers by income. But firstly, let us create another table Payment with the following MySQL statement:
CREATE TABLE Payment(CustomerID INT NOT NULL, CustomerName VARCHAR (255),PAmount INT, PRIMARY KEY(CustomerID));Inserting some records into the above table made for the other process with the query below:
Code:
INSERT INTO Payment(CustomerID, CustomerName, PAmount) VALUES
('101', 'Nikhil', '56700'),
('102', 'Rakesh', '80000'),
('103', 'Anita', '67000'),
('104', 'Rahul', '29900'),
('105', 'Vinit', '89000');Output:
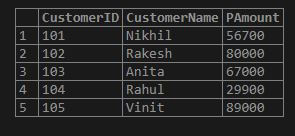
Example #3 – Structure of the temporary table, which is derived from a SELECT SQL statement
Code:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE TopCustomer
SELECT i.CustomerID, n.CustomerName, ROUND (SUM(i.PAmount),2)Sales
FROM Payments17 i INNER JOIN Customers17 n ON
n.CustomerID = i.CustomerID GROUP BY i.CustomerID ORDER BY Sales DESC LIMIT 3;Now to view the data from the top customer temporary table, we can fetch it with the same query we use for the permanent one. This is the SQL query:
SELECT CustomerID, CustomerName, Sales FROM TopCustomer ORDER BY Sales;Output:
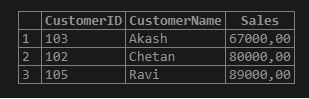
How to insert data in MySQL Temporary Table?
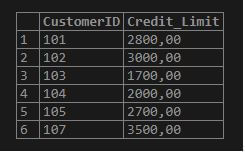
Per the above queries, we have created a temporary table named Credit with fields (CustomerID, Credit_Limit). Here, let us input some rows in the same table to show the records and insertion process. We will use the below query statement in MySQL for entering the values:
Code:
INSERT INTO Credit(CustomerID,Credit_Limit) VALUES ('107', '3500');This structure is similar to what we usually perform to insert rows into the permanent table in MySQL. Here is the result:
Output:
How to delete MySQL Temporary Table?
We need to use the next DROP TABLE SQL statement to delete a Temporary table, not a permanent one, from the database:
DROP TEMPORARY TABLE TableName;Hence, adding a Temporary keyword while creating a short-term table is a good practice. This method will help to avoid the risk of making any changes to the original one, like processing the queries or dropping them by mistake when we give the same names to both tables.
For example, if we apply this query to the above create a temporary table, then, we get the result:
Code:
DROP TEMPORARY TABLE TopCustomer;Explanation: If you suppose you want to delete the original table using the SQL drop temporary statement, you will receive an error or warning saying that the table is unknown to be removed.
Conclusion
MySQL is responsible for automatically removing the MYSQL Temporary table as the session ends or if there is any connection issue that terminates. The user that creates a Temporary table has a privileged view and accesses the table during a session. Two different users can use their own created temporary table with the same name in two separate sessions without causing any effect on each other’s session. But we cannot create two temporary tables with identical names within the same session.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Temporary Table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

