Updated May 25, 2023
Introduction to MySQL SHOW Triggers
MySQL SHOW Triggers is a MySQL statement that performs to display all the triggers present in the server tables. When we create different Triggers, which are stored programs to be invoked during an event execution or when specific queries run in the server, thus, keep log records of SQL commands performed for the linked tables for which the triggers are created. To create, drop, or show trigger statements, we must require the MySQL Triggers super privileges to execute the triggers by creating or dropping respective log records in the associated trigger tables. SHOW Triggers helps to view the existing triggers in the MySQL table with the command codes and type of triggers created for the related tables.
Syntax:
We have a subsequent basic syntax structure for MySQL SHOW Triggers statement query:
SHOW TRIGGERS [(IN | FROM) DatabaseName] [LIKE 'Specified_Pattern' | WHERE Expr_Cond];Here, in this above syntax, the last two MySQL clauses define the database from which we want to show the associated triggers. If not specified, executing the query “SHOW Triggers” will retrieve all available triggers in each database currently on the server.
SHOW TRIGGERS;If we want to view all the triggers in a different database, then we require providing the name of the MySQL database after either the FROM or IN keyword:
SHOW TRIGGERS FROM DatabaseName;OR,
SHOW TRIGGERS IN DatabaseName;Suppose we search for a trigger having a specific pattern that will match the one specified in the SHOW TRIGGER query, then we will implement the MySQL LIKE clause as follows:
SHOW TRIGGERS LIKE 'Specified_Pattern';Even we can use the following query statement with the SHOW TRIGGERS command in the server:
SHOW TRIGGERS FROM DatabaseName LIKE 'Specified_Pattern';Here, the significance of the LIKE clause is identical to that used in the MySQL SELECT statement. Again, we will use the MySQL WHERE clause to list the triggers using a particular expressional condition to search specific ones. For this, we will have the following query statement:
SHOW TRIGGERS WHERE Expr_Cond;Also, we will use this one:
SHOW TRIGGERS FROM DatabaseName WHERE Expr_Cond;How Does SHOW Triggers Statement Work in MySQL?
The MySQL Trigger working is related to creating or dropping any trigger element in a database. When we execute the SHOW TRIGGERS in MySQL, we will view the lists of available triggers defined for the database tables. If the database is not mentioned, the default database will be used unless we have included the database using the FROM clause.
We can also use the LIKE clause in association with SHOW TRIGGERS to indicate the names of tables that match and thus causes the server to output the triggers related to those tables. We can use an option for adding conditional statements, i.e., WHERE clause with SHOW TRIGGERS, to implement the query and output trigger rows.
In MySQL, the result set containing the succeeding columns will be returned as output after the SHOW TRIGGERS statement:
- Trigger: Provides the name of the trigger.
- Event: The event used to invoke the specified trigger. It can be INSERT, DELETE, or UPDATE queries execution.
- Table: It denotes the database table attached to the trigger created.
- Statement: It defines the trigger body with code.
- Timing: It mentions the time for activation of the trigger. It can just AFTER or BEFORE an event.
- Created: It gives the created timing of the trigger.
- Sql_mode: Displays the SQL_MODE when the trigger is invoked.
- Definer: It defines the account of the user that has implemented the trigger.
- Character_set_client: It determines the character set through which the client provides the statements. The trigger sets the session value when creating the trigger for the character_set_client system variable type.
- Collation_connection: This is important for evaluating literal strings, but columns have their own provided collation with higher precedence.
- Database Collation: Defines groups of rules to compare and order the character strings in MySQL. It denotes the database collation in the server with which the trigger is related.
It is to be noted that for the execution of the SHOW TRIGGER query, we need to have the SUPER privilege in MySQL.
Examples to Implement MySQL SHOW Triggers
Let us explain the MySQL SHOW TRIGGERS with the help of the following examples to understand better:
Suppose we have a database named ’empdb’, which consists of some triggers used in the existing tables. Let us create a trigger for the table Emp_data in the empdb database having fields Emp_ID, Emp_Name & Emp_Salary with some records inserted as follows:
1. Creating table Emp_data.
Query:
CREATE TABLE Emp_data (
Emp_ID INT NOT NULL,
Emp_Name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
Emp_Salary VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (Emp_ID)
);2. Insert values into table Emp_data.
Query:
INSERT INTO Emp_data (Emp_ID, Emp_Name, Emp_Salary)
VALUES(10, 'Rita','5000'),
(11, 'Sahil','7500'),
(12, 'Rekha','4800'),
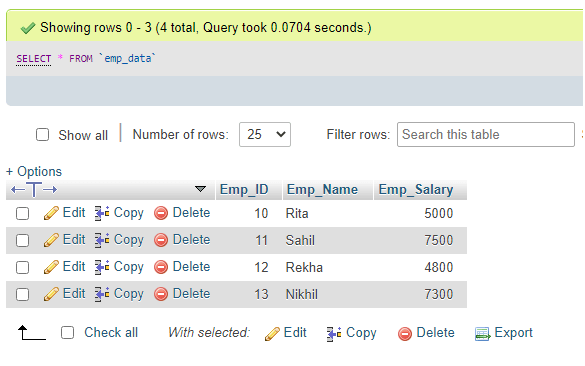
(13, 'Nikhil','7300');3. Select table Emp_data.
Query:
SELECT * FROM Emp_data;Output:
4. We will also create another table to save the logs when triggers are called for query events.
Query:
CREATE TABLE Emp_logs ( User_ID VARCHAR(255), Info_Update VARCHAR(255));Again, let us create a trigger first to show the trigger procedure using the following query:
Query:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE TRIGGER emp_updates
AFTER UPDATE ON Emp_data FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
INSERT into Emp_logs(User_ID,Info_Update) VALUES (user(), CONCAT('Updated Emp_Salary Info (',OLD.Emp_ID,' ',OLD.Emp_Name,' ',OLD.Emp_Salary,') to (',NEW.Emp_ID,' ',NEW.Emp_Name,' ',NEW.Emp_Salary,')'));
END$$
DELIMITER ;Once the emp_updates trigger is created, it will be frequently triggered whenever an update event is executed on each row in the emp_data table.
When updating a value in the Emp_Salary column, the system will insert a new row into the emp_logs table to record the completed changes.
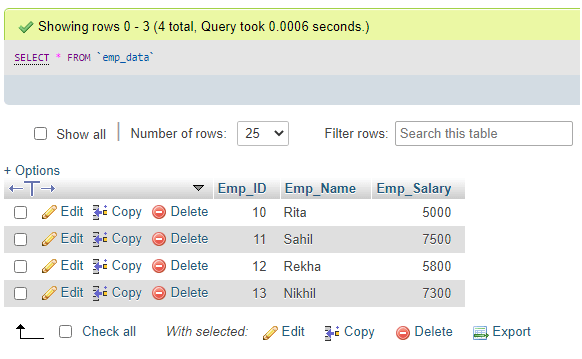
Query:
UPDATE Emp_data SET Emp_Salary = Emp_Salary + 1000 WHERE Emp_Salary<5000;Query:
select * from Emp_data;Output:
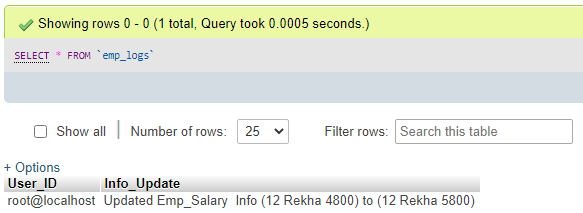
5. Yet again, outlook to your Emp_logs table and check the transformation effect of the AFTER UPDATE trigger using the following query.
Query:
SELECT * FROM Emp_logs;Output:
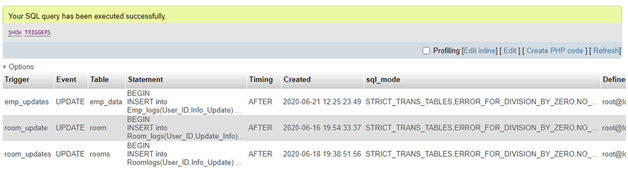
Finally, it’s time to view all the triggers on the empdb database, including the one just created above on the table named Emp_data:
Query:
SHOW TRIGGERS;Output:
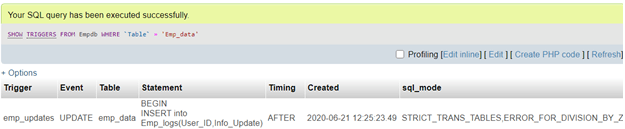
OR, using database and table in WHERE clause:
Query:
SHOW TRIGGERS FROM Empdb WHERE 'Table' = 'Emp_data'Output:
Conclusion
We have learned about the MySQL SHOW Trigger command, which displays the trigger events in a particular database. We can also view the event timings and find out to work for those if needed or search for any specific table linked to a trigger for any information gathering.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL SHOW Triggers” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.