Updated May 16, 2023
Introduction to MySQL REINDEX
MySQL REINDEX is also a data structure in a database table. It is a significant part of having a good database maintenance method where it is responsible for reorganizing and managing the indexes and restoring speedy retrieval. Since MySQL INDEX is also defined as a data structure that helps to optimize the database and progresses the speed of the MYSQL operations in a table. We use REINDEX in MySQL to rebuild indexes using one or multiple columns in a table database to have quick data access and improve performance. MySQL REINDEX denotes the re-indexing process to rebuild the indexes on a database if the database is corrupted or needs repair to optimize the tables and fetch the rows using indexes properly using phpMyAdmin.
Syntax
Generally, We can apply MySQL REINDEX or create indexes easily using phpMyAdmin on local servers like WAMP, XAMPP, or on a live server with cPanel. Most MySQL indexes procedures, such as PRIMARY KEY, UNIQUE, INDEX, FULLTEXT& REINDEX, are warehoused in B-trees.
B-tree can be defined as a self-balancing data structure tree that stores data in a sorted manner and allows sequential access, searches, insertions, and deletions based on logarithmic time. It is beneficial for file systems and databases that are engaged to read and write huge blocks of information.
Except some like:
- For spatial data, types indexes are stored in R-trees
- MEMORY tables use hash indexes
- InnoDB supports reversed lists for FULLTEXT types of indexes.
We use the following simple syntax to add MySQL INDEX in a table:
CREATE INDEX [Index_Name] ON [TableName] ([ColumnName of the TableName]);Now, for any reason, you encounter the corruption of an index on the table. You need to re-build that index or all of the indexes on the table or columns using the below basic syntax of REINDEX INDEX or REINDEX TABLE and REINDEX DATABASE to repair particular database indexes.
REINDEX INDEX [Index_Name];
REINDEX TABLE [TableName]; or,
REINDEX TABLE [TableName]([ColumnName of the TableName]);
REINDEX DATABASE [DatabaseName];The given arguments are explained below:
- Index_Name is said to be the name of the index.
- TableName is the name of a particular table.
- ColumnName defines the column where the indexing will be done in the abovementioned table.
- DatabaseName denotes the database name where we need to apply REINDEX in MySQL.
REINDEX recreates the specified indexes for a single table and database index.
How does MySQL REINDEX work?
In MySQL, REINDEX does the following works:
- It can help relocate the indexing information quickly within a database or table.
- Reindexing or simply indexing in MySQL will create an inner catalog stored by the MySQL service.
- It uses the catalog of table rows as it can indicate within a decimal of time using the least effort.
- A REINDEX TABLE redefines a database structure that rearranges the values in a specific manner of one or a group of columns.
- It works first by sorting the data and then works to allot identification for every row in a table.
- The indexes are put together on the top of the tables and perform executions such as SELECT, DELETE, and UPDATE SQL statements quicker to deploy when the data size is huge. The REINDEX or INDEX in MySQL can also be termed a table comprising the records arrangement technique.
- Indexes help search for rows corresponding to a WHERE clause with particular column values very quickly, so if the index is not working correctly, we must use the REINDEX command to operate and rebuild the indexes of table columns to continue data access.
- Eliminates rows from concern if there is the choice between more than one index by selective method indexing, thus supporting the re-indexing.
- Indexing and re-indexing also allow fetching rows from other tables when performing JOINS properly.
Examples to Implement MySQL REINDEX
For using MySQL REINDEX, let us first create some indexes on tables and explain them to know brief the topic:
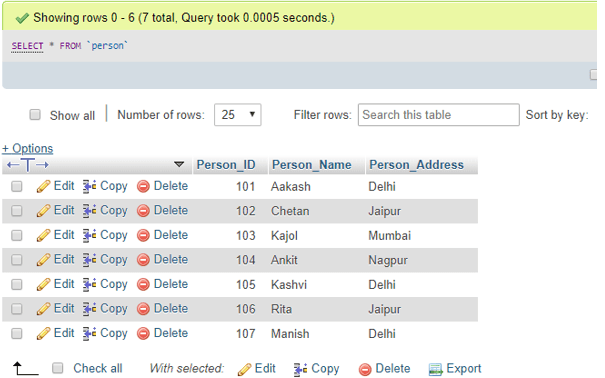
Initially, we have taken a table named Person in the database with fields Person_ID, Person_Name &Person_Address. It contains a few records as follows:
Code:
SELECT * FROM PersonOutput:
Examples #1
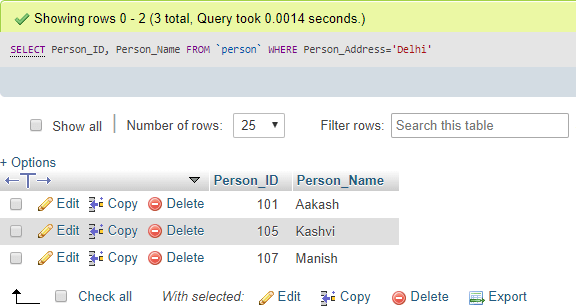
Now, the following query will find the Person whose location is Delhi in the address column using WHERE:
Code #1
SELECT Person_ID, Person_Name FROM Person WHERE Person_Address= 'Delhi';Output:
Code #2
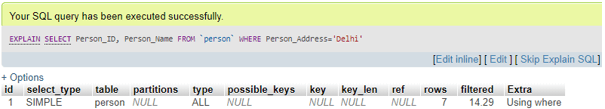
If you want to view how MySQL performed this query internally, use EXPLAIN at the start of the previous query as follows:
EXPLAIN SELECT Person_ID, Person_Name FROM Person WHERE Person_Address = 'Delhi';Output:
The server must test the table containing seven rows to execute the query.
Example #2
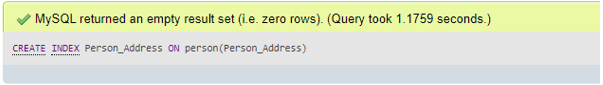
Let us now add an index for the address column by the below statement:
Code #1
CREATE INDEX Person_Address ON Person(Person_Address);Output:
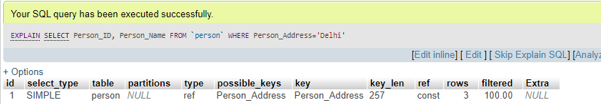
After running the query, again, use EXPLAIN to view the result now.
Code #2
EXPLAIN SELECT Person_ID, Person_Name FROM Person WHERE Person_Address = ‘Delhi’;Output:
The result is clear; now, the index created allows scanning only three rows instead of the entire table, as indicated by the value in the key column.
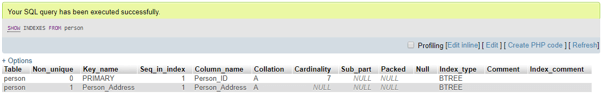
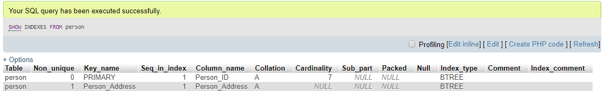
If you want to see the index, use the SHOW query as follows:
Code #3
SHOW INDEXES FROM Person;Output:
Suppose we have any corrupted index or if you no longer get valid data for practical reasons. Still, it may not be possible in theory, like software viruses or failures of hardware. Mysql REINDEX will be responsible for a recovery process to repair the tables or database and rebuild the indexes to maintain the performance, optimization, and quick operations within the databases.
Example #3
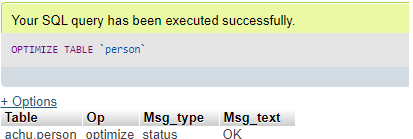
We can use REORGANISE, REPAIR, and OPTIMIZE TABLE statements to rebuild the corrupted table and associated indexes to reduce the memory space and increase the I/O efficiency.
Code #1
REINDEX TABLE 'Person';OR,
OPTIMIZE TABLE 'Person';Output:
After MySQL REINDEX, the indexes will be re-built, and we can view that as output here:
Code #2
SHOW INDEXES FROM Person;Output:
Conclusion
MYSQL REINDEX statement can drop all indexes on a group or recreates them from scratch, which might be costly for groups that contain large data or several indexes. REINDEX is useful when recovering from index corruption in the database or when modifying the description of an ordering structure. Therefore, REINDEX supports regaining the performance and utility to faster access and smooth going operations in a MySQL database table.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL REINDEX” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.